Windows Exchange Server Database Restoration: Expert Tips
In this article, we’ll guide you through the process of recovering a Windows Exchange Server database, ensuring that you can retrieve critical data in the event of an unexpected failure or corruption.

- Backup your data with Windows Server Backup
- Recovering Windows Exchange Server
- Questions and answers
- Comments
A local Exchange Server is an effective email server solution with all security features provided by Microsoft. Still, its databases may get corrupted by incorrect management, physical or logical errors. This is not too bad if you have a server backup – then a damaged Exchange database can be recovered easily. Although a competent administrator can reduce database damage to a minimum, the chances of such misfortune can never be completely excluded. That is why it is always a good habit to have a fresh backup at hand, so that you will never lose important data if something goes wrong.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | A software server for email and calendar, developed by Microsoft. |
| Main Purpose | Provides email, contact management, calendars, tasks, and shared folders in corporate environments. |
| Protocols | Supports various email protocols, including IMAP, POP3, and SMTP. |
| Collaboration Features | Offers the ability to share calendars, contacts, and documents among users within the organization. |
| Security | Includes encryption, authentication, and protection against viruses and spam. |
| Mobile Device Support | Compatible with mobile devices via ActiveSync protocol for syncing email, contacts, and calendars. |
| Web Access | Access to email via a web interface using Outlook Web Access (OWA). |
| Architecture | Can operate locally on a server or in the cloud via Microsoft 365. |
| Management | Provides centralized management of email and related services through an admin console. |
| Integration | Closely integrates with other Microsoft products such as Outlook, SharePoint, and Teams. |

How to Recover a Windows Exchange Server Database
Backup your data with Windows Server Backup
There are many specialized programs to back up Exchange Server 2019, but Windows Server does have its own integrated feature for this purpose – and it’s the component called Windows Server Backup.
Windows Server backup options let administrators choose to back up the entire server, selected volumes or specific folders.
Windows Server Backup is an integrated backup module of the Windows Server operating system.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Backup Type | Supports full backup, incremental backup, and selected file/folder backup. |
| Scheduling | Allows setting up automatic backups on a schedule. |
| Disk Compatibility | Supports hard drives, USB drives, and optical media (DVD/Blu-ray). |
| System Recovery | Enables system recovery to a previous state, including OS and data. |
| File and Folder Recovery | Allows recovering individual files and folders from backups. |
| Flexibility of Settings | Allows backing up both local and remote resources. |
| Encryption | Supports backup encryption to protect data. |
| Logs and Reports | Generates reports and logs on backup success or any errors encountered. |
| Interface | Graphical interface with command-line option for advanced users. |

🗄️ How to Configure Data Backup, Create a Backup Copy and Restore Windows Server 🗄️
How to add Windows Server Backup role to the server
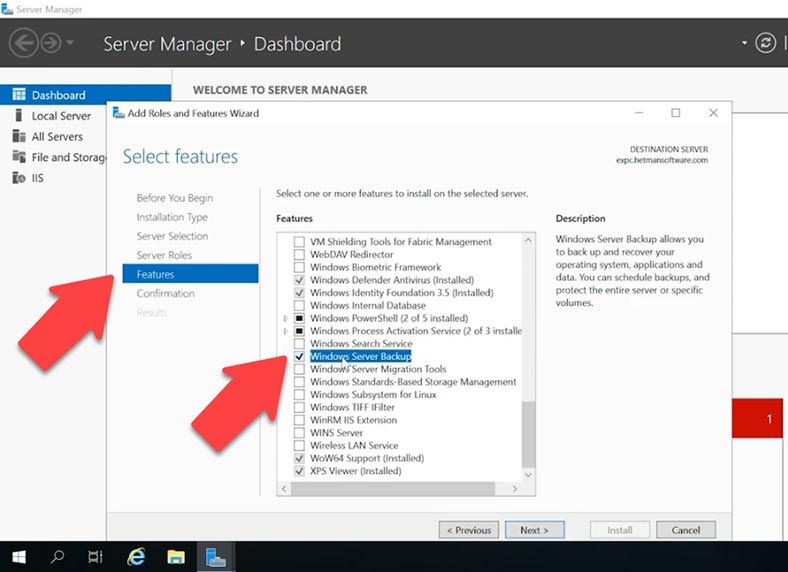
Since the backup feature is not installed by default, you’ll have to do that. Open Server Manager, click on the menu button – Manage – Add Roles and Features.
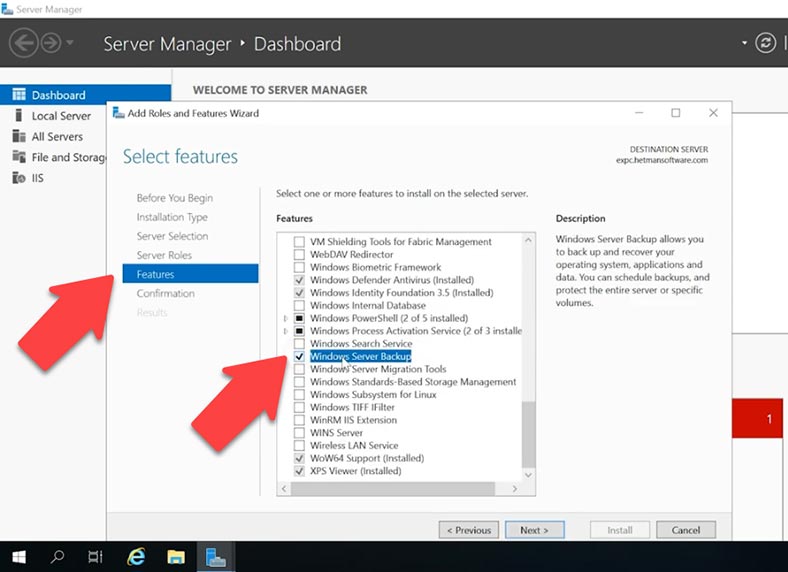
In the window that opens, go to Features and check the box next to Windows Server Backup, then click Next and Install.
How to create a backup with Windows Server Backup
After the utility is installed, open Tools and run Windows Server backup.
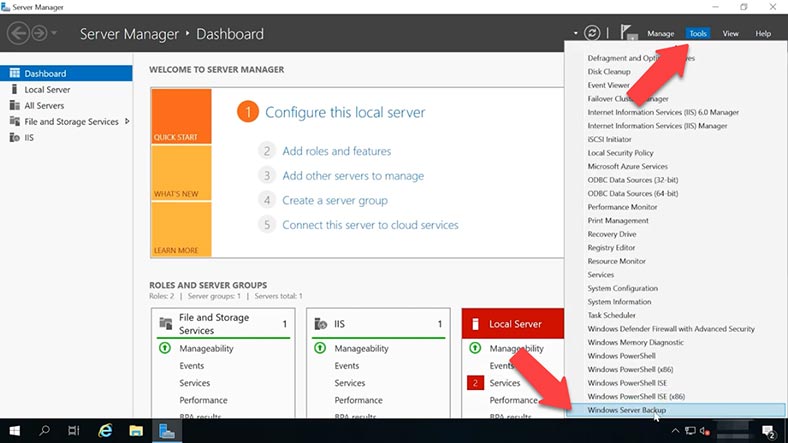
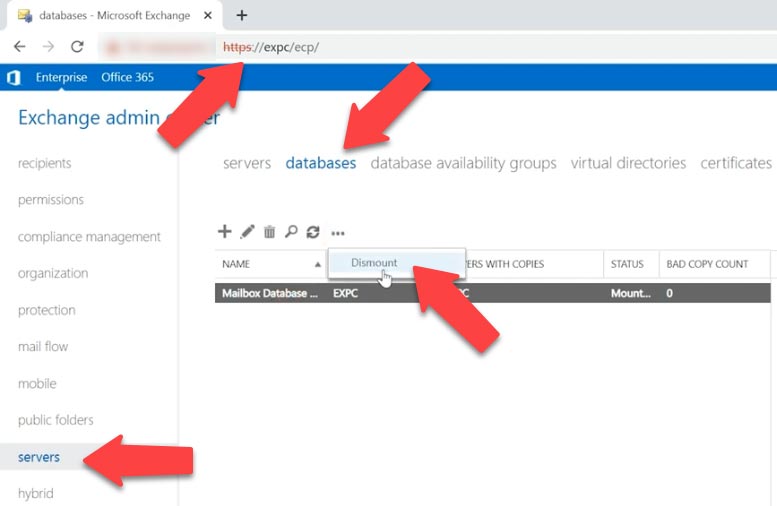
Microsoft claims that with data backup system, you’ll be able to create copies of Exchange databases and recover them. Before creating a backup, it’s recommended to dismount the database. To do it, open Exchange Admin Panel, go to Servers and open the Databases tab, select a database, click on the three dots’ button and click Dismount.
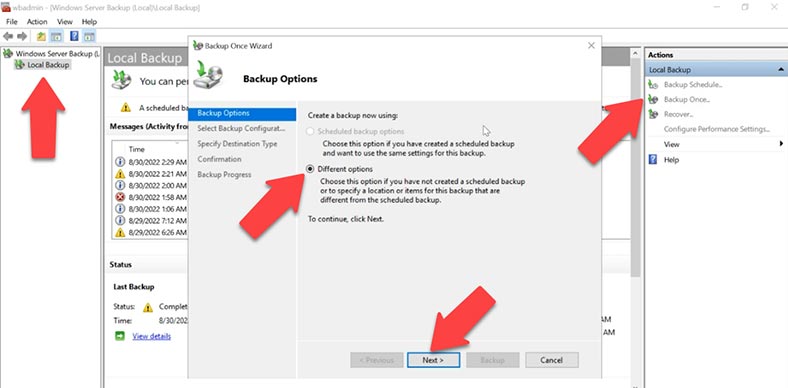
In the Windows Server Backup window that opens, choose Local Backup and then look to the right, in the Actions menu, to select Backup Once. In the Backup Options, select Different options and click Next.
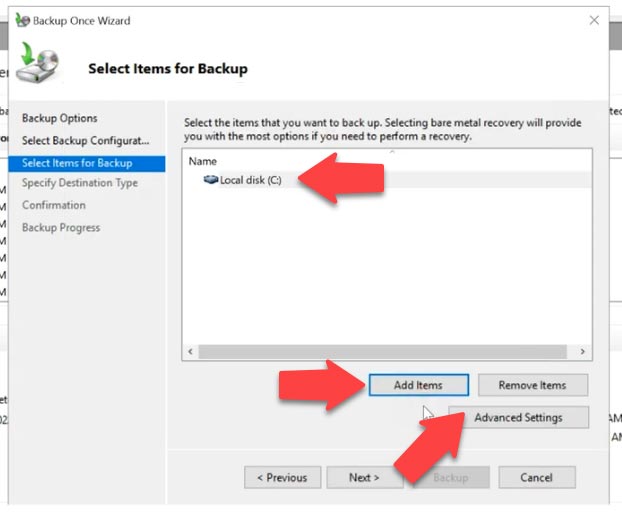
In the Backup Configuration, select Custom and click Next. In the item selection page click Add items, select the disk where your Exchange database is stored, and click ОК. After that, click Advance Settings.
This is where you can add exclusions from the disk, and then such files won’t be copied. Then jump to the VSS Settings tab and check the box next to VSS full backup, click OK and Next.
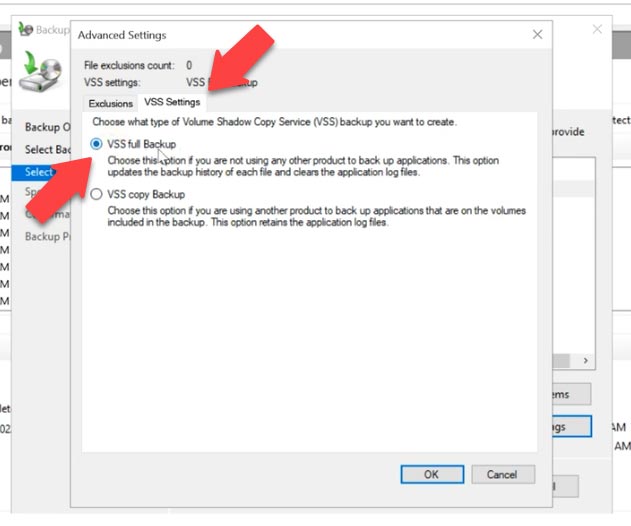
At the next stage, choose the directory where to save the backup – a local drive or a remote shared folder. Then check all the settings and click Backup to start the process. Congratulations: now you have an Exchange mailbox database backup.
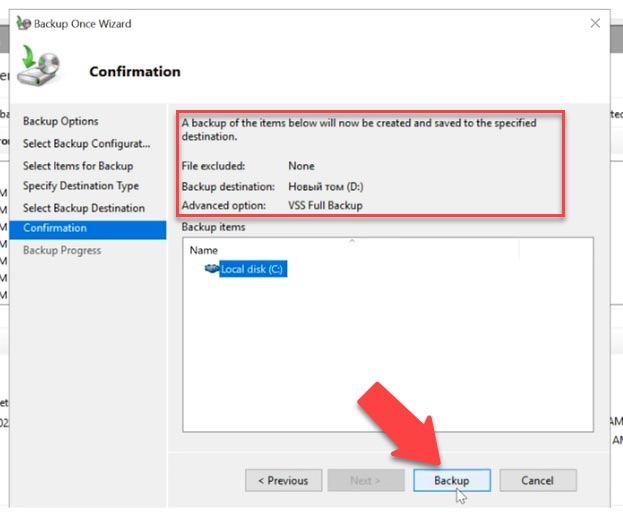
After that, go to the mailbox and check your mail, delete all emails, and you can even delete them from the Deleted Items folder. Now let’s check if they can be recovered from the backup copy.
Recovering Windows Exchange Server
Method 1. How to restore an Exchange Server database from a Server Backup file
It is time to recover a database from the latest file created by Windows Server Backup. To do it, open Server Manager, Tools, Windows Server backup. In the program’s window, select Local Backup, and then choose Recover in the action window.
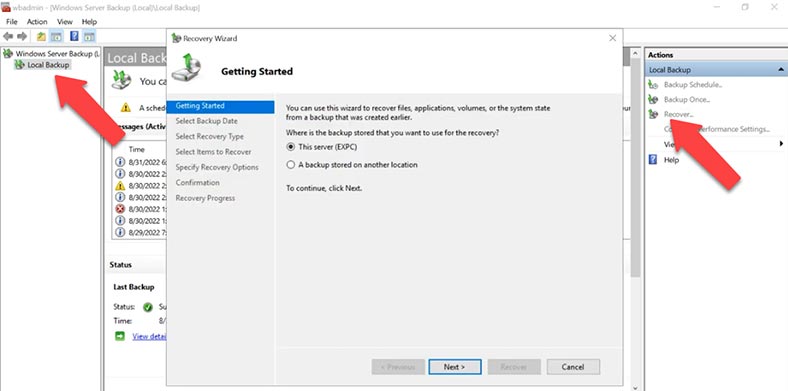
Specify where your backup is stored – on this server or in another location – click Next, give the exact location of the backup – Next. After that, select the server and the date of the backup from which should be used for recovery.
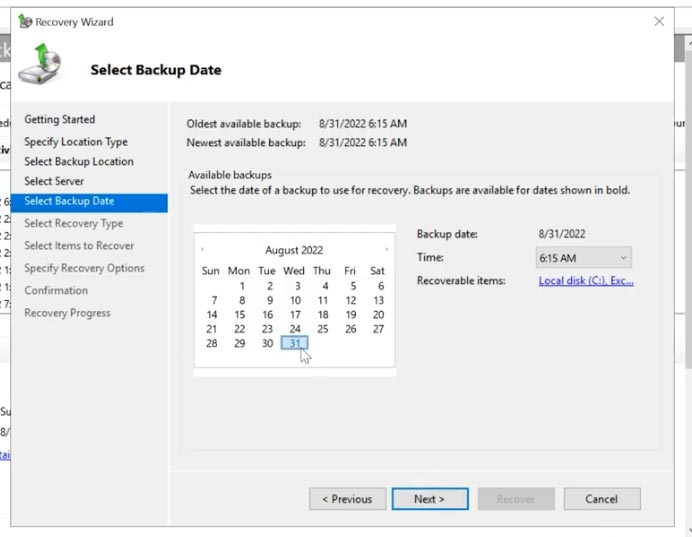
In the Recovery Type page, choose Applications and click Next. In the next window, make sure that you selected the Exchange application and click Next.
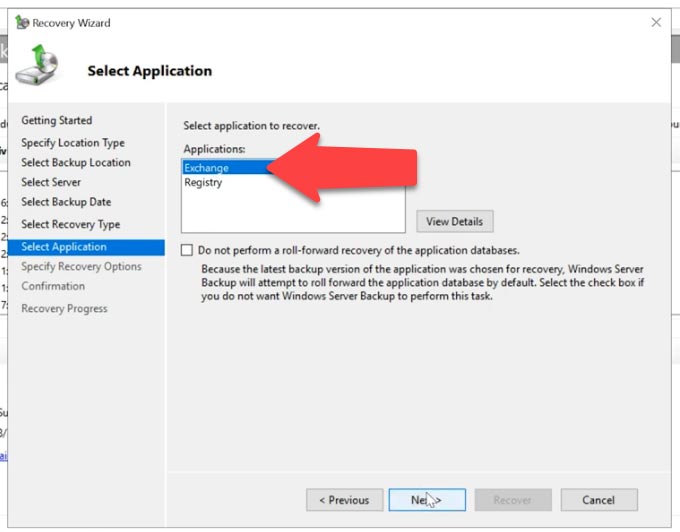
After that, choose Recover to original location if you need to recover Exchange data to its original directory, or Recover to another location if you want to recover specific databases. To start the process, hit Recovery. When it’s over, click on the Close button.
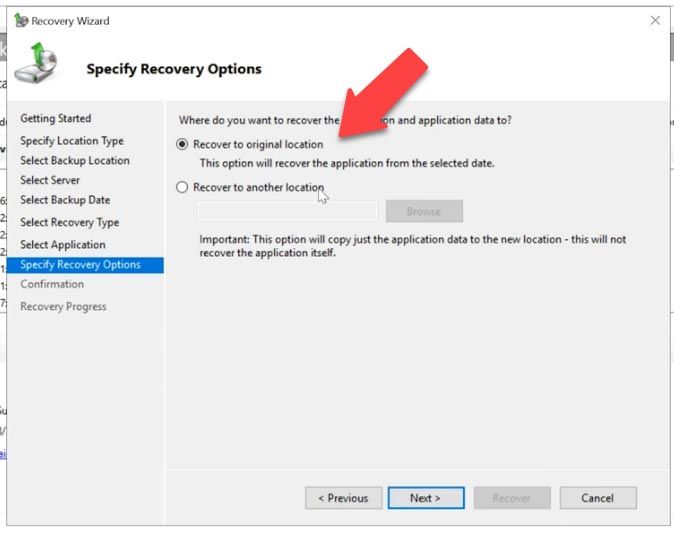
Now all changes and deleted emails will be restored to their condition as of the backup date. Let’s check the mail: as you can see, all emails that were in this mailbox at the time when you backed it up are there again.
This is how you can recover an important email that was permanently deleted from the mailbox, but it can also erase any emails that were received after you created the backup.
However, you won’t be able to recover any emails this way, if the mailbox itself was deleted irreversibly. To have your emails back, you’ll have to create a new mailbox and recover the emails from the recovery database.
Method 2. How to restore a mailbox from the recovery database
One more way to recover mailboxes is to use the recovery database. If you need to recover emails to a new server, or if the first method didn’t help you to recover lost emails, try doing it with the recovery database.
Before recovering a database to a new Exchange server, it should be installed and configured. I will only show you the process of mailbox recovery, since I suppose that you already have a freshly installed and running Exchange Server with Active Directory.
All right, so we have a backup created with the help of Windows Server Backup, and I’ll show you how to use it to recover a database and the folder containing the logs to another disk, and then import all that stuff to a server with a clean installation of Exchange Server.
For starters, you need to recover an Exchange database from backup. This could be a backup created with Windows Server Backup or with another similar tool. From this backup, we need to retrieve the folder containing the database and transaction logs. Let’s explore this process with the example of a backup file created with Windows Server Backup:
- Open Server Manager, look up and to the right, click on the Tools button, and choose Windows Server Backup when you find it at the bottom of the drop-down list.
- In the utility window that opens, choose Local Backup and click Recover.
- Select the location of your backup – This server or Another location, and click Next.
- Select a disk or shared folder, choose a volume, select your server, and click Next.
- After that, choose the latest backup date, and click Next again.
- At the next stage, choose Application and click Next.
- Now select Exchange – Next – and specify where Exchange Server data should be recovered.
- Click Browse, choose a disk or folder, then click Next and Recover.
- Wait for the process to be over, and then close the utility window by clicking Close.
As a result, you get a copy of mailbox database and a folder containing log files. I will copy the database files and take them to another folder – into the root directory of the system drive, so it will be easier to type its path. Also, you can change the names of the folder and the database file, if necessary.
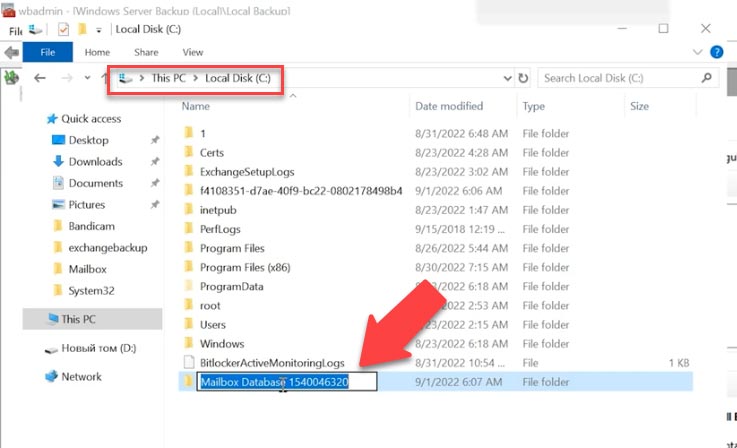
To recover your mailbox, you need to create a recovery database, to which files will be imported from the database and logs recovered from the backup, and then all emails will be transferred to the existing database.
For this purpose, we’ll be using Exchange Management Shell (EMS) and a cmdlet – New-MailboxDatabase.
Go to the folder containing the database:
Cd C:\test
Type the command:
New-MailboxDatabase -Recovery -Name DBR -Server expc -EdbFilePath "C:\test\Mailbox Database 1540046320.edb" -LogFolderPath C:\test
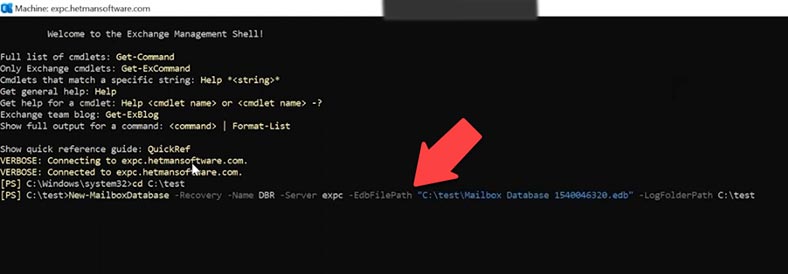
Where,
- DBR is the name of the new recovery database,
- Mailbox Database 1540046320.edb – the name of database file,
- and in the end, there is the path to the folder containing transaction log files.
New-MailboxDatabase -Recovery -Name (the name of the new database) -Server (the server name) -EdbFilepath “the path to the database file” -LogfolderPath “the path to the folder containing transaction logs”
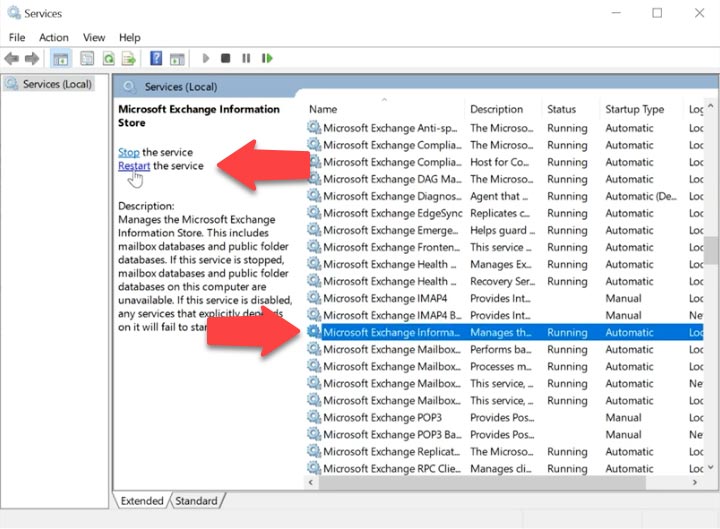
After this command is performed, the Exchange information service should be restarted.
To do it, open the service window, find Microsoft Exchange Information Store on the list, select it and click Restart.
Now let’s check the status of the database that we have recovered; run the eseutil command with the MH key:
Eseutil /MH "Mailbox Database 1540046320.edb"
If you are in a different folder, you should add the path to the file to this command; in my case I just gave the file name as I am in the same folder where the database file is located.
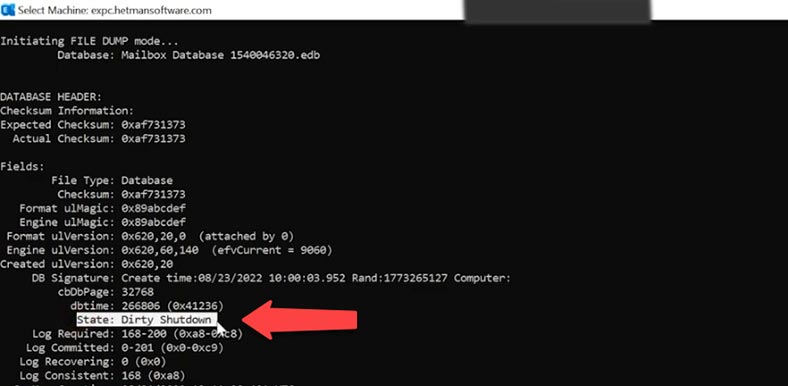
If you get such database state as “Dirty Shutdown,” you’ll have to recover it first, by using another command.
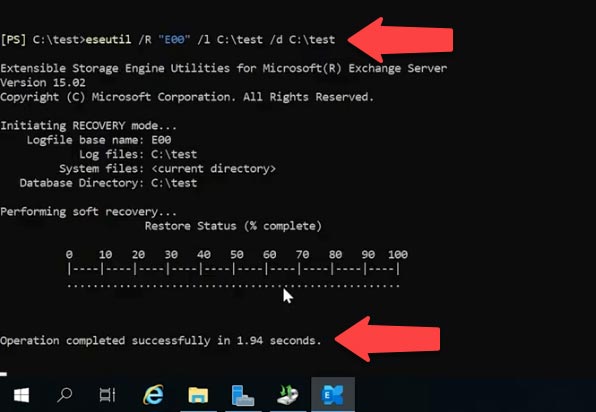
Run eseutil command with the R key.
Eseutil /R "E00"
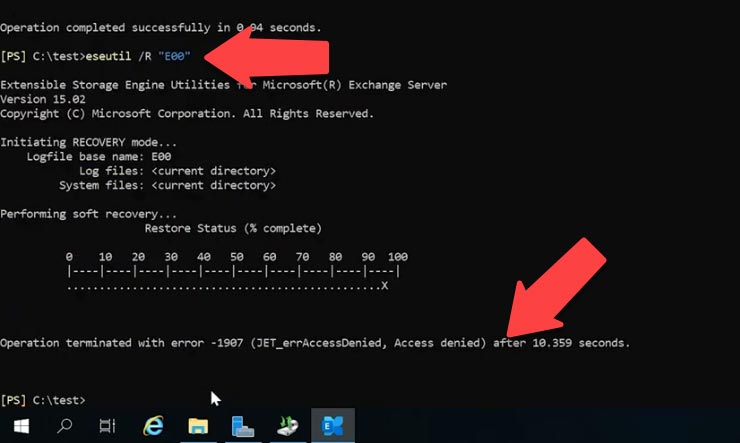
A transaction log prefix has to be added; in my case, it’s E00. Go to the folder containing the logs and view the prefix used for filenames.
If this command doesn’t help you, try another one.
esetuil /r E00 /l C:\test /d c:\test
Here, you’ll need to specify the prefix for transaction logs, and then give the path to the folders containing the logs and the database.
When the database is recovered, you can go on to mount it.
Do it with another command:
Mount-Database DBR
To see if the backup contains any data, you can run this command – Get-mailboxStatistics
Get-MailboxStatistics -Database DBR | Format-Table DisplayName,MailboxGUID -AutoSize
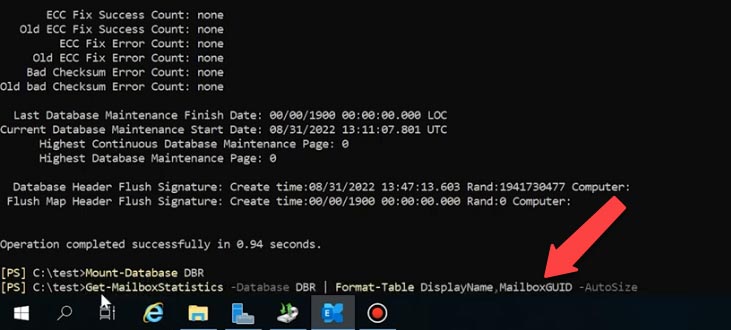
As a result, you’ll get the list of mailboxes stored in the recovery database and their ID, which you will need later to transfer emails to the new mailbox.
Here is the command to use:
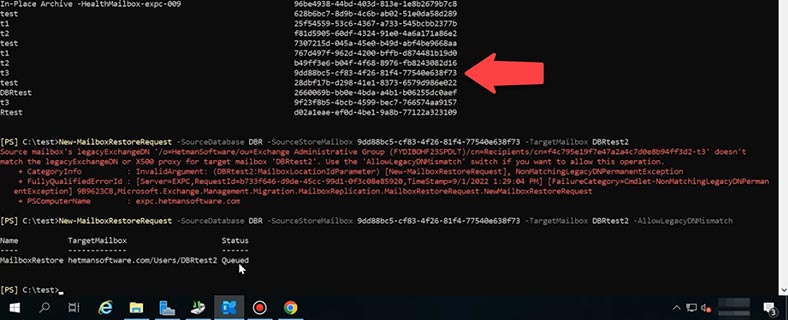
New-MailboxRestoreRequest -SourceDatabase DBR -SourceStoreMailbox 9dd88bc5-cf83-4f26-81f4-77540e638f73 -TargetMailbox DBRtest
In it, you should give the name of the source database (the recovery database), the ID of the source mailbox, and at the end of the command - the name of the target mailbox.
If this error appears when the command is performed:
Source mailbox legacuexchangedn doesn’t match
Then add the following value at the end of the command:
New-MailboxRestoreRequest -SourceDatabase DBR -SourceStoreMailbox 9dd88bc5-cf83-4f26-81f4-77540e638f73 -TargetMailbox DBRtest -AllowLegacyDNMismatch
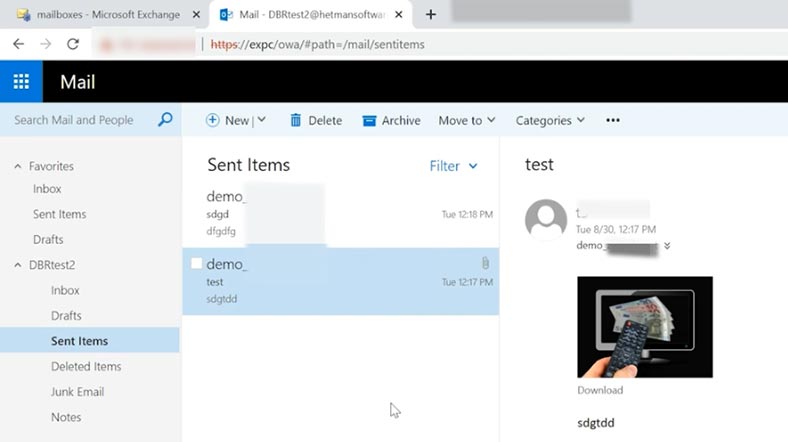
Now test the new mailbox. As you can see, all the emails that were stored in the lost mailbox, have been transferred to the new one. We managed to extract the data from backup and import it to the new server. Now you can perform the same procedure for the remaining mailboxes.
Method 3. Recovering a database
If the database is damaged or the logs are missing, it may need to be recovered. For this purpose, we’ll use the eseutil command with the p key.
eseutil /p "Mailbox Database 1540046320.edb"
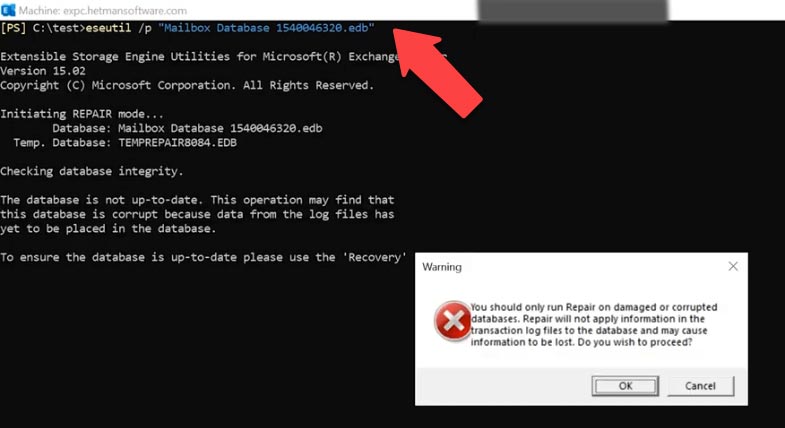
As a result, you’ll see a warning that this process is irreversible, and some data is going to be lost anyway.
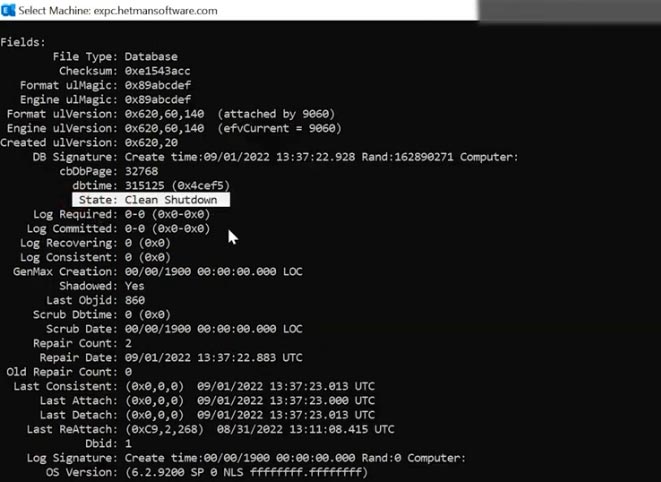
Now let’s check that the database is in good condition:
eseutil /mh Mailbox Database 1540046320.edb
Its status should change to “Clean Shutdown”
After that, you’ll need to defragment the data.
eseutil /d "Mailbox Database 1540046320.edb"
During defragmentation, a new database is created, and all healthy data will be moved there.
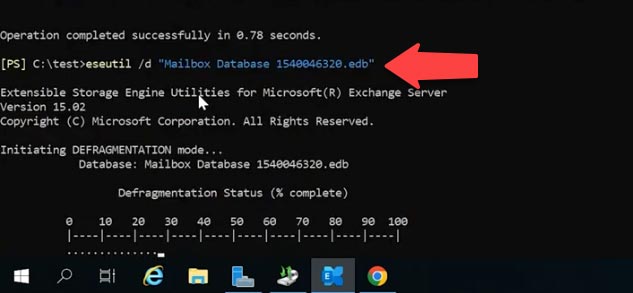
When the defragmentation process is over, the original database file will be removed.
Now you need to mount it and run a checkup command.
Here is the command to use:
Mount-Database "Mailbox Database 1540046320.edb"
And this command starts the checkup:
Get-MailboxRepairRequest -Database "Mailbox Database 1540046320.edb"
Now the Exchange Server database recovery process is over.
Method 4. Recovering a mailbox database from a non-working Exchange Server

How to Install and Configure Exchange Server 2019. Active Directory Domain Services
If your server is out of order, its mailbox database or transaction log folder is damaged or deleted, a specialized data recovery tool - Hetman Partition Recovery - will help you. You can use it to scan the hard disk, find the deleted files, recover them, and bring them back to the Exchange server.
Hetman Partition Recovery supports the majority of popular file systems, but if your database was stored on a RAID array, try another product - RAID Recovery. It will automatically rebuild the damaged RAID system with the available disks, and you’ll be able to retrieve your Exchange database files.
Let’s explore how it works - with Hetman Partition Recovery and default location of the database.
Download, install and run the program. It will scan your computer automatically and display the connected hard disks.
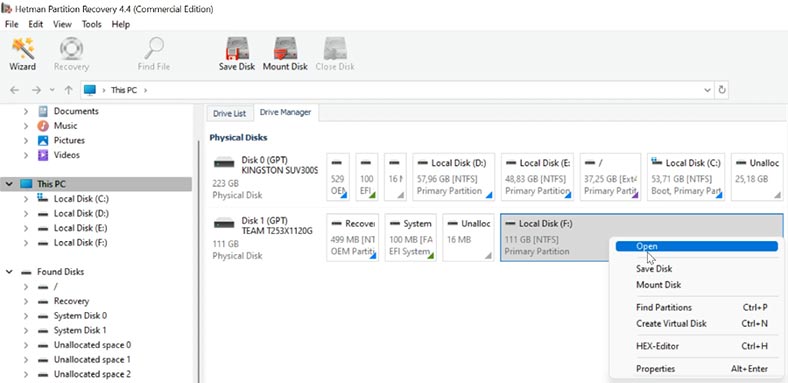
Right-click on the disk where the database was stored and choose Open, then select the analysis type - Fast scan or Full analysis. Run a fast scan first - it will take less time.
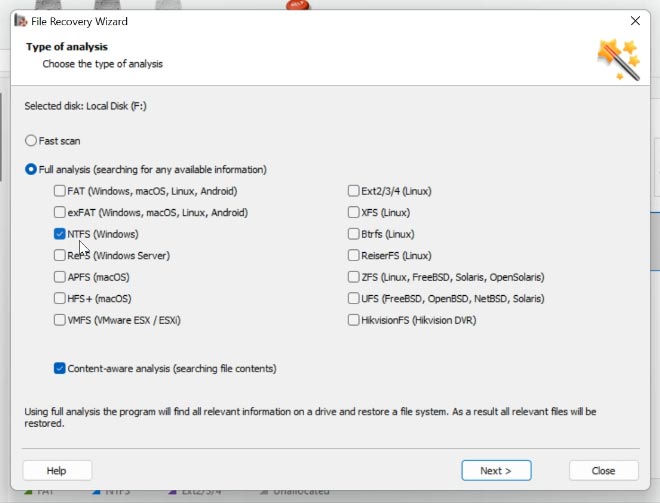
If the program can’t find the missing files, then go for Full analysis. Right-click on the disk - Analyze again - Full analysis - specify the file system for this disk - then click Next.
Go to the folder where the Exchange Server database was stored, select the directory and click Recovery. After that, specify the disk and folder where to save the database, and hit Recovery again. When the recovery process is over, the folder containing the files will be placed into the directory you have chosen.
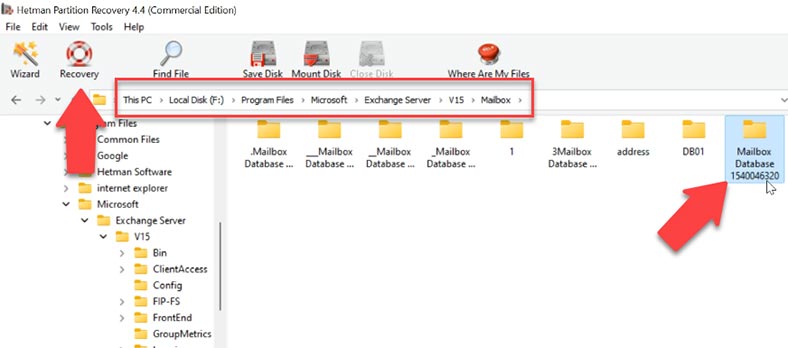
By default, the database is stored in this directory.
C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\Mailbox
For your convenience, the program features file search by name, which helps to reduce the time required to find the desired files. Also, you can save a disk image and then use this image to perform all scans.
Now that the database is recovered, you can use it to create a recovery database, and then transfer the necessary emails to a new server - and we’ve already discussed how to do that.
Before recovering a database to a new Exchange server, the Exchange Server with Active Directory should be installed and configured.

How to Add DNS Records - SPF, DKIM, DMARC - and Configure POP3 and IMAP4 Mail Protocols