Data Recovery Software For Corrupted RAID 0, 5, 6 Arrays
Has your RAID storage system crashed and it doesn’t work anymore? Have you lost data because of a RAID controller error or motherboard issues? Have multiple member disks within your array failed and you can’t restore RAID automatically? Is a RAID rebuilding process frozen and your RAID crashed?

This program recovers data from non-operational RAID systems or from disks within such systems. It reads all the information about the controller, the motherboard or the software used to create a disk array. Our product can rebuild the crashed RAID and it lets you copy all critical information from there.
The integrated constructor wizard helps you recover a failing RAID in a step-by-step mode. You can use one of the presets or chose the required data in the damaged array, and RAID Recovery™ will collect the disks together to provide you with access to the data.
Watch the video tutorial below to learn about the product’s features and see for yourself how easy it makes to recover information. You can download the demo free of charge, scan the disk, preview recoverable files – and then upgrade to the full version instantly without the need to re-scan your disk.
Recover software or hardware RAID of any type: JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 10, RAID 5, RAID 50, RAID 6, RAID 60, etc.

Both hard disk types, HDD and SSD, have a limited operational life. Certainly, server-type NAS or SCSI disks can last longer than their SATA counterparts intended for home use only, but there is no such thing as a hard disk that works endlessly. For most RAID arrays, the day when one or two disks fail means loss of all information, from all disks within this array. Reliability of the entire array decreases with every disk which is added to it.

Mistakes when replacing one of the disks within the storage system, accidental “rebuilding” of the array instead of “restoring” it, disconnecting and reconnecting the disks in a wrong order, incorrect RAID initialization or rebuild – any of these things will certainly result in the loss of information. After such errors, RAID can’t restore itself automatically.

A controller is the element containing information of critical importance which is vital for building a disk array and gaining access to all of the files stored on the disks. A controller failure may both result in losing service data and cause several disks to fail. The most expensive controllers use an additional battery and non-volatile memory. Such elements improve the whole system’s reliability and are supposed to help save data even if a power interruption occurs.

Creating a RAID based on specific motherboard features is a cheaper (though less reliable) solution in comparison with buying an expensive controller. Motherboard failures, botched BIOS updates, low CMOS battery, power surges, disconnecting or reconnecting disks – all these things may cause your RAID to crash. As the entire system is very sensitive to all kinds of power issues, problems with your power supply unit may cause crashes as well.

Software RAID systems based on the functionality offered by an operating system – Windows, macOS, Linux, FreeBSD, Ubuntu – depend largely on the health of that operating system. Upgrading your hardware, or updating other software may cause errors that prevent the computer from booting and make the data inside such array inaccessible.
Unlike hardware RAID systems, the software-based arrays are made of logical partitions rather than physical disks. Operations that involve formatting or removing partitions can easily destroy such array.

Both software and hardware solutions store information about the RAID structure on every disk within the array. A virus attack may not only damage system files and prevent the operating system from booting, but also modify the disk partition table or overwrite the disk area which stores data vitally important for the RAID to work properly. Any of these nasty things will make the array inoperable.

Usually, when there is an attempt to write information to a faulty sector, RAID will enter the data on such sector into a special table so that it doesn’t get used any longer, and will use a free sector for writing. However, everything changes when one of the disks within the array breaks down. To continue work, you need to replace the disk and rebuild the array. The process of automatic recovery reads all the data from the remaining disks to recreate the data from the missing disk. Such recovery process can’t be accomplished when there is at least one bad sector.

Unfortunately, not all manufacturers give you the opportunity to move to new hardware without having to rebuild your RAID. To prevent loss of data, you have to copy all of that from the old array, then create an array with the new hardware, and finally transfer the data to this new RAID. This procedure applies to situations when you are upgrading controllers, motherboards, hard disks – and even operating systems, if you prefer using a software-based RAID.

When one of the disks within the array is connected to another piece of equipment or computer, it may cause its service information to be overwritten. When such disk is reconnected to your RAID again, the system doesn’t start and it just fails.
Disks should be connected and disconnected only with the storage system powered off. If you attempt to start a computer with some of its disks missing, RAID will switch into an emergency mode, and reconnecting the disks to the array will not help to restore the situation back to normal.
RAID Recovery™ is a versatile solution to restore RAID systems to working condition and recover data lost after RAID crashes. You don’t have to be an advanced user, a software engineer, or a recovery expert to use this program effectively.
In fact, a lot of service information is written to the disks included into a RAID system: what disks make up the array, in what order they are connected to the controller, the RAID type, block size and the procedure of writing blocks, number of disk groups, and the data on the array size.
Having collected all the available information from the system and connected disks, the utility displays the automatically built arrays immediately, as soon as the program starts. In most cases, the program manages to restore RAID on the fly and suggests you to analyze the identified partitions and save any available data.
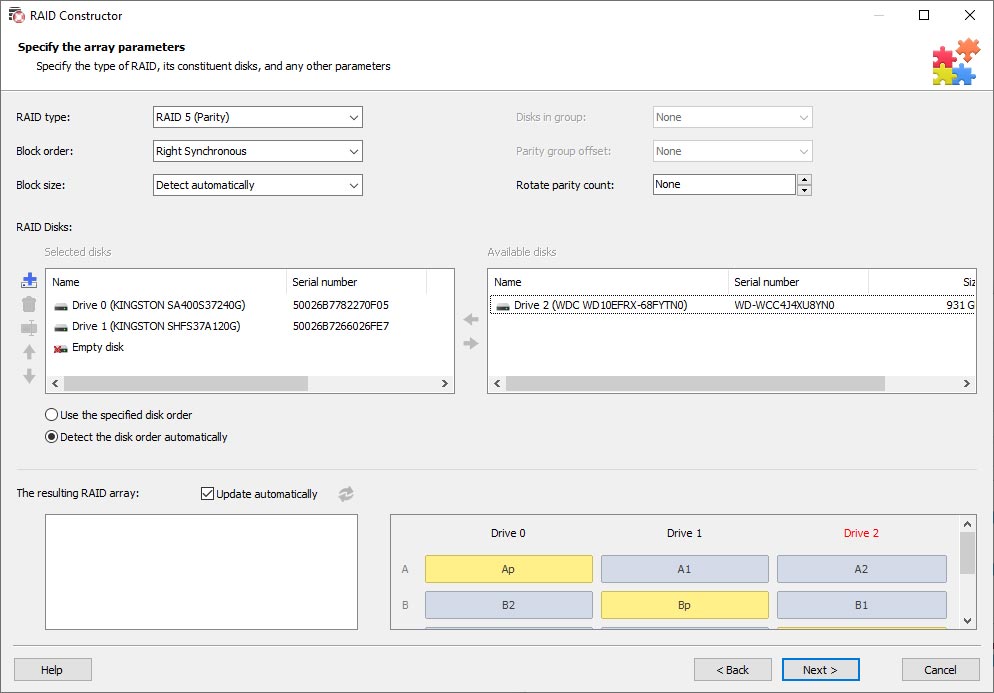
In this mode, the program asks you to give the number of disks within the array and specify the disks. After that, it searches through all possible combinations of these disks that can be used to build a RAID system.
For every valid combination, the program tries to find the file system structure – logical partitions, a directory tree and files. If typical file system elements are found, the utility suggests saving such configuration and using it to search and recover files.
This approach lets you restore a RAID even if you don’t know the block size, RAID type and rules of writing blocks to disks. However, processing all possible combinations for 6 and more disks may take a very long time.
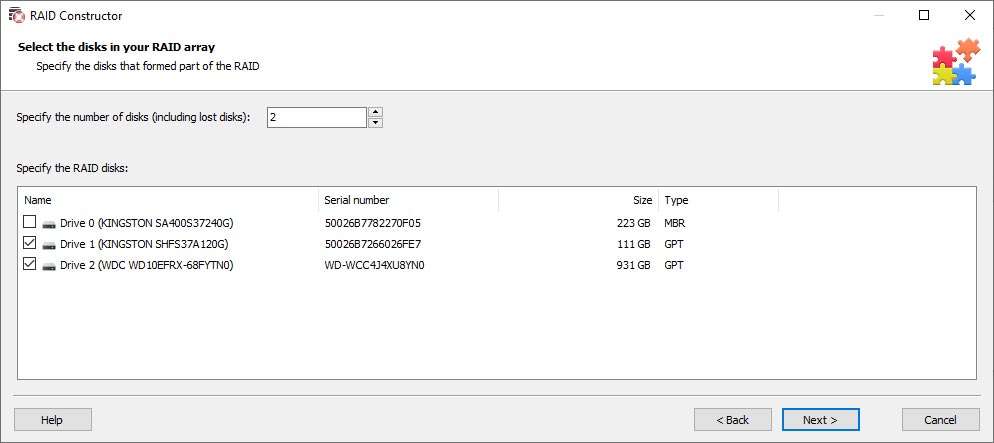
The program contains possible array combinations used by popular controller manufacturers, as well as patterns applied by software-based or combined RAID systems. Using the data on the hardware manufacturer, our utility can reduce both the number of combinations it needs to explore and the time required to find the right configuration.
With manual mode, you can create a storage system of any configuration. The program will ask you for RAID type, the disks it used to consist of, and their order, as well as for additional information such as parity group offset, parity delay, and block size. This mode is designed for professionals and lets you specify data about the crashed RAID in a fastest and most accurate way. Optional settings will be selected automatically by the system.
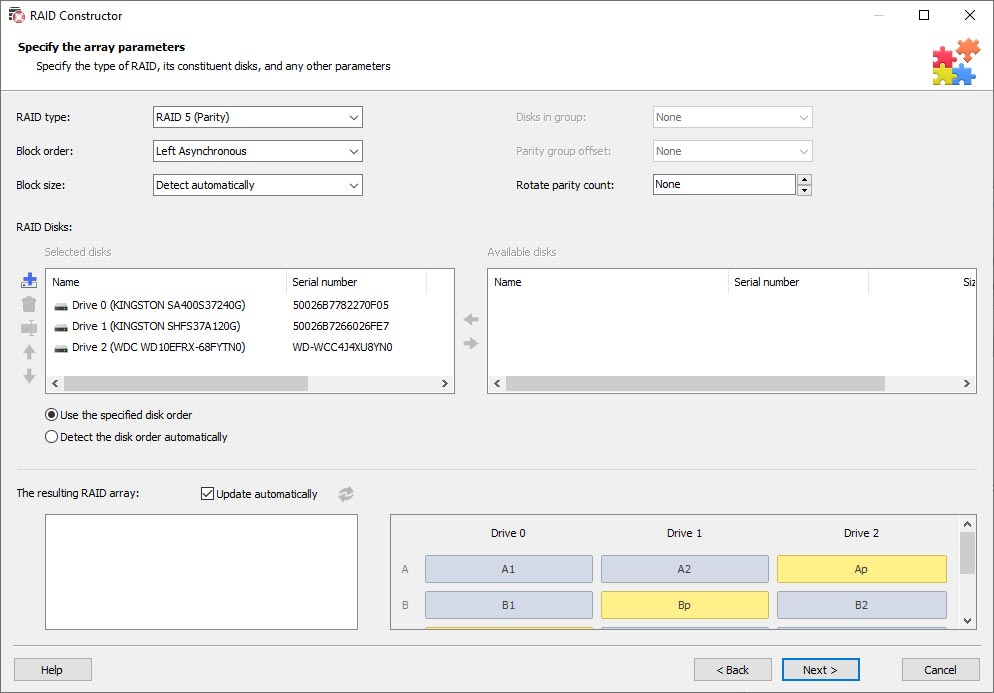
Our program supports disk arrays created both with the help of the features offered by the specific operating system or motherboard, and with specialized controllers / external storage solutions provided by various manufacturers.
Disk array types:
- JBOD – combining several disks sequentially into one larger logical one. When one disk is full, data will be written to another one. This array type is used to increase available space. It requires at least 2 (two) disks.
- RAID 0 – striping the data written to blocks across two disks or more. This array type is used to increase available space and gain faster access time. At least 2 (two) disks are required.
- RAID 1 – mirroring (copying) data to all disks within the array. This array type is designed to protect data from loss caused by disk failures. At least 2 (two) disks are required.
- RAID 10 (1 + 0). At least 4 (four) disks are required.
- RAID 1E (1 + 0 combined, striped mirroring). At least 3 (three) disks are required.
- RAID 5 – data striping with saving checksums (parity). It can restore itself automatically even if 2 (two) disks fail. The idea is to gain a disk performance boost, more disk space, and protect data against loss. At least 3 (three) disks are required.
- SHR, SHR-2 (Synology Hybrid RAID) – is Synology's automated RAID management system.
- RAID-z, RAID-z2, RAID-z3 – the technology of combining data storage devices into a single storage developed by the Sun Company.
- RAID 50 (5 + 0). At least 6 (six) disks are required.
- RAID 5E and 5EE (types similar to RAID 5, but with an extra hot spare drive sitting next to the array waiting for a drive to fail). The difference between 5EE and 5E is that the former array includes a hot spare drive that is actively used in the array operations. At least 4 (four) disks are required.
- RAID 6 – data striping with double parity. Reed - Solomon codes are used. It can restore itself automatically even if 2 (two) disks fail. RID 6 is used to increase disk space, boost read and write speeds, and improve reliability over the level provided by RAID 5. At least 4 (four) disks are required.
- RAID 60 (6 + 0). At least 8 (eight) disks are required.
- RAID 2 combines two groups of disks, one containing data and the other containing error correcting code. It is based on Hamming code and is relevant for systems combining large numbers of disks. At least 3 (three) disks are required.
- RAID 3 is similar to RAID 5, but with one drive allocated to store drive parity information instead of striping parity across all drives. This, however, means more wear and tear for the parity drive. This level uses blocks of 1 (one) byte.
- RAID 4 – the successor of RAID 3, their difference being that now the block size can exceed 1 (one) byte.

Networked storage:
- D-Link;
- Synology;
- Qnap;
- Linksys;
- Promise;
- ZyXel;
- NETGEAR;
- Buffalo;
- LaCie;
- Plextor;
- Intel;
- IOMEGA;
- Western Digital (WD);
- Toshiba;
- Cisco;
- Iomega;
- Acer;
- Thecus;
- Seagate;
- Micronet;
- Terra;
- My-Ditto;
- Oyen Digital.
RAID controller manufacturers:
- Adaptec;
- Areca;
- Dell;
- HP;
- Silicon image;
- Promise;
- LSI;
- Mylex;
- Intel;
- SUN;
- HighPoint;
- EMC;
- Infotrend;
- NEC.
Manufacturers offering motherboards with RAID support:
- ASRock;
- MSI;
- ASUS;
- Gigabyte;
- Biostar;
- Supermicro;
- Colorful;
- ECS;
- PocketBook;
- Remington.
Where software-based RAID is possible:
- Windows;
- MacOS;
- Linux (LVM / MDADM);
- FreeBSD;
- Solaris;
- BtrFS;
- ZFS;
- Ubuntu.
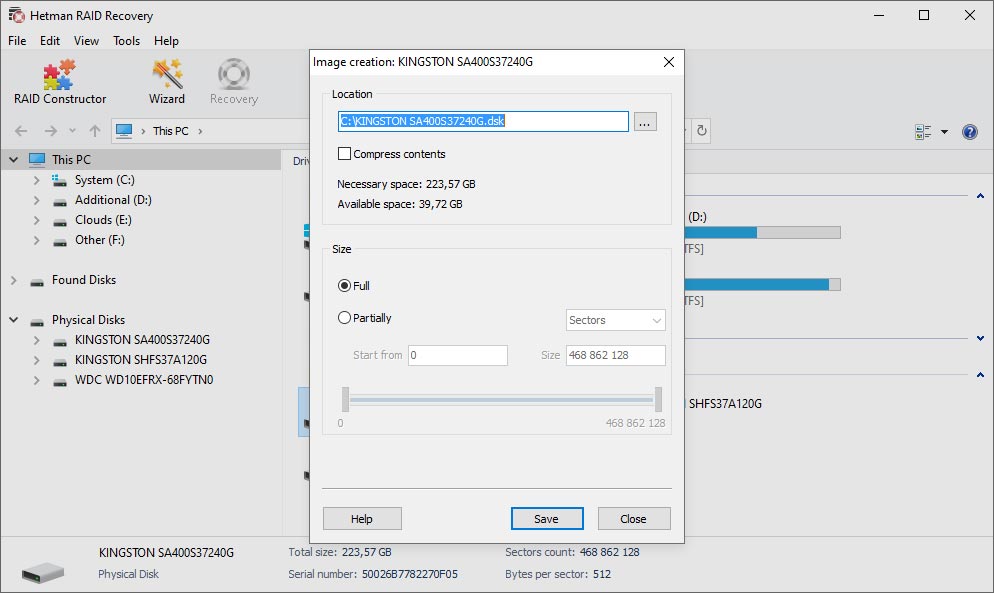
When working with failing disks (which contain bad sectors), there are high chances to lose all data altogether while trying to read information from the disk. For safety reasons, it’s better to create a disk copy, as recovering RAID data is a long process that involves multiple operations to access the disk contents.
Our utility lets you create an image of any storage device / media or a separate logical partition. At any time later, you can open this image in the program and continue the process of rebuilding RAID and recovering its data. RAID Recovery™ supports both creating images in its own format (*.dsk), and handling the following image file types: *.hdd, *.vdi, *.vhd, *.vhdx, *.vmdk.
Our program can recover accidentally deleted files from disk arrays, and any data lost after emptying the Recycle / Trash Bin in Windows, macOS, Linux, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, and Solaris systems. Scan a logical partition or the entire RAID, and it will show you the files it can find and recover.
You can view the file contents and make sure they can be recovered, and register the program only after you know what to expect. Finding the necessary files is much easier with the integrated filtering, sorting and search features.
Our program can find deleted files even when the file system structure is shattered to pieces. Scanning the disk entirely, RAID Recovery™ finds the boot sector (and all of its copies), partition table, root directory, logs and information on the files deleted from, or existing on the disk.
Using all this data, the utility rebuilds the file and folder structure and then displays it as if it were a commonplace file manager. If all service information is erased, file contents can be recovered by running a signature search across the disk.
Usually, RAID systems are designed with the ability to restore themselves if one of the disks fails. Of all the variety, only RAID 6/60 can be rebuilt after two disks get out of order. Yet we often need to restore the missing information after two or more disks are lost, partially or completely.
Such a scenario means that most part of the file system data is gone, as well as a part of the data that makes up the contents of large files. Our utility will unite the data which remained intact on the disks within the array, and do it by calculating the missing parts with the use of special formulas from the parity blocks. The blocks with missing information will be replaced with empty ones, and this will let the program rebuild the array and restore the data.
When a RAID is restored, the file system structure needs to be read to enable data recovery. Our utility supports the following file systems:
- FAT/ExFAT. The file system commonly found in USB pen drives and memory cards on Windows / Apple / Linux / Android.
- NTFS. The frequently used file system for both system disks and common disks in Windows.
- ReFS. The file system found in Windows servers.
- APFS. The file system used by Apple devices with macOS High Sierra 10.13 and newer.
- HFS+. An outdated file system you can see on iMac, MacBook, MacMini, etc.
- Ext / ReiserFS / XFS. This one is used in Linux operating systems.
- UFS / ZFS. This is the main file system for FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, and Solaris.
This utility is designed for Windows, MacOS and Linux.
Windows
- Windows XP;
- Windows Media Center Edition;
- Windows Vista;
- Windows 7;
- Windows 8;
- Windows 8.1;
- Windows 10;
- Windows 11;
Windows Server
- Windows Server 2003;
- Windows Server 2008;
- Windows Server 2012;
- Windows Server 2016;
- Windows Server 2019;
- Windows Server 2022;
macOS
- macOS 10.12 Sierra;
- macOS 10.13 High Sierra;
- macOS 10.14 Mojave;
- macOS 10.15 Catalina;
- macOS 11 Big Sur;
- macOS 12 Monterey;
- macOS 13 Ventura;
- macOS 14 Sonoma;
- macOS 15 Sequoia;
OS X
- OS X 10.7 Lion;
- OS X 10.8 Mountain Lion;
- OS X 10.9 Mavericks;
- OS X 10.10 Yosemite;
- OS X 10.11 El Capitan;
Linux
Ubuntu:
- 10.04 Lucid Lynx;
- 12.04 Precise Pangolin;
- 14.04 Trusty Tahr;
- 16.04 Xenial Xerus;
- 18.04 Bionic Beaver;
- 20.04 Focal Fossa;
- 22.04 Jammy Jellyfish;
- 24.04 Noble Numbat;
Debian:
- Debian 6.0 Squeeze;
- Debian 7.0 Wheezy;
- Debian 8.0 Jessie;
- Debian 9.0 Stretch;
- Debian 10.0 Buster;
- Debian 11.0 Bullseye;
- Debian 12.0 Bookworm;
Fedora:
- Fedora 13 Goddard;
- Fedora 20 Heisenbug;
- Fedora 25 / 30 / 33 / 36 / 40;
Linux Mint:
- Linux Mint 9 Isadora;
- Linux Mint 13 Maya;
- Linux Mint 17 Qiana;
- Linux Mint 18 Sarah;
- Linux Mint 19 Tara;
- Linux Mint 20 Ulyana;
- Linux Mint 21 Vanessa;
- Linux Mint 21.3 Virginia;
openSUSE:
- openSUSE 11.3;
- openSUSE 12.1;
- openSUSE Leap 42.1;
- openSUSE Leap 15.0;
- openSUSE Leap 15.5;
- openSUSE Leap 15.6;
Arch Linux
-
What is the difference between a hardware and software RAID?
A hardware RAID makes use of a dedicated physical controller that stores information about hard disks and manages both how the data is written and how the volume is accessed. Therefore, hard disks are connected to a RAID controller card which is inserted into the PCI-Express (PCI-e) slot on the motherboard. This is implemented similarly both in large servers and desktop computers. However, in external devices RAID controllers are built-in.
A software RAID includes a commonplace disk controller, while all drives within the array are managed by special software. This could be a much cheaper way to build a RAID data storage system, but it can also be considerably slower since it adds more workload on the CPU and RAM.
-
Is it possible to recover data from JBOD if one of the disks fails?
JBOD is a combination of several physical disks into one logical volume, without division into partitions. In such configuration, disks can be filled with data in a sequence, from the first to the last, which means that failure of one disk does not necessarily cause loss of data from all other disks.
However, in real life the file system may use any blocks available across the whole volume, so files can get fragmented and scattered all over different disks.
The possibility of data recovery in such case depends on the algorithms used by the file system as well as the intensity of write operations, since these two factors determine the sequence in which the data is allocated.
Another important factor is the ability to read file system metadata which is usually found on the first disk within the JBOD.
Generally speaking, if one of the disks in such system fails, complete data recovery will be impossible without repairing such disk.
-
Is it possible to recover data if several disks fail within a RAID array?
Chances of data recovery after simultaneous failure of several disks within RAID depend on the RAID type and the number of disks that failed. Here are several main scenarios:
- RAID 0. In this RAID type, data is spread across several disks without redundancy. Even if one disk fails, it becomes nearly impossible to recover the data.
- RAID 1 duplicates data to several disks. If more than one disk fails, the chances of successful data recovery are still high. If at least one full set of data is preserved, the information can be recovered.
- RAID 5 uses parity to ensure data recovery if one disk fails. If two or more disks are out of order, data recovery becomes very complicated.
- RAID 6 can survive the failure of two disks due to its additional parity. If more than two disks fail, the data is almost impossible to recover.
- RAID 10. Recovery opportunities depend on which disks have failed. If one disk fails in each pair of mirrored disks, recovery is possible. But if two disks fail in one mirrored pair, data recovery is out of the question.
-
Which RAID type is best for data recovery?
The choice of RAID type for probable data recovery depends on your specific circumstances.
RAID 1 and RAID 10 ensure easier and quicker recovery due to mirroring, but the disk capacity is used less efficiently.
RAID 5 and RAID 6 offer a better capacity to reliability ratio, but data recovery may take more time and resources. RAID 6 is more suited for environments where high reliability is required.
-
Are there any hardware tools for data recovery from RAID?
Yes, there are there certain hardware tools for data recovery from RAID that professionals use in their activities.
The following products are worth mentioning:
- PC-3000 Express RAID System by ACE Laboratory.
- DeepSpar Disk Imager 4 (DDI4) with RAID module.
- RapidSpar.
- Atola Insight Forensic.
Post a testimonial
Read user reviews of Hetman Software programs or share your experiences. Your review will be published after being moderated. We value your opinion! Total reviews: 39. Average ratings: 5.






-
Internet Spy™ 4.0
- The program for analyzing and restoring the history of web browsers.
-
- OS Support:
- Release date:
-
Uneraser™ 7.1
- A cheap program to recover accidentally deleted files from any device.
-
- OS Support:
- Release date:
-
File Repair™ 1.1
- The program to fix errors in damaged files. List of supported files in the program description.
-
- OS Support:
- Release date:

