HFS+ Drive Recovery: Exploring the Best Tools to Recover Your Lost Data
Unlock the Power of Data Recovery from HFS+ Drives! Lost important data from your HFS+ drive? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered! In this article, we’ll explore the top data recovery tools that can help you recover your lost files with ease. Whether you accidentally deleted files or experienced a drive failure, these tools are designed to rescue your data. From scanning your drive to recovering lost files, we’ll walk you through the entire data recovery process. Say goodbye to data loss worries and get back your valuable files today!

- HFS+ file system (Mac OS Extented)
- Test 1. Top data recovery tools
- Test 2. Volume Header removed
- Test 3. Alternate Volume Header removed
- Test 4. B-tree nodes removed
- Test 5. Index Node removed
- Conclusion
- Questions and answers
- Comments
HFS+ file system (Mac OS Extented)
HFS+ or Mac OS Extended is the update for the previous file system format by Mac OS known as HFS, or Hierarchical File System.
HFS+ introduced journaling, which increased reliability of data storage.
Journaled operating system keeps a log file (journal) of changes which helps to recover the hard disk quicker after failures, and accelerates the work of Time Machine.
Just as its predecessor, HFS+ uses the so-called B-tree to store a major part of metadata.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | HFS+ (Hierarchical File System Plus) |
| Developer | Apple Inc. |
| Purpose | File system for Mac OS, supports Mac, iPod, Time Capsule, and others. |
| File System Type | Journaled (journaling), providing data recovery after crashes. |
| Maximum Volume Size | 8 Exabytes (8 × 10¹⁸ bytes), typically up to 2 TB on standard disks. |
| Maximum File Size | 8 Exabytes (8 × 10¹⁸ bytes), although practical limits may be smaller depending on the driver. |
| Maximum File Count per Volume | Theoretically 2⁶³ files, but practically it depends on volume size and file structure. |
| File Name Types | Supports Unicode (UTF-16), allowing characters from various languages. |
| Case Sensitivity in File Names | Depends on settings — usually case-sensitive on Mac OS, but it can be configured for case-insensitivity. |
| Journaling | Yes, supports journaling to protect data from corruption during failures. |
| Fragmentation Algorithm | Uses methods to minimize fragmentation, but does not support automatic defragmentation. |
| Encryption | Supports encryption via FileVault and additional encryption at the volume level. |
| Metadata Support | Yes, including file tags, types, sizes, and modification data. |
| Formatted Block Size | 512 bytes or 4 KB, depending on formatting settings. |
| Network Protocols | Supports AFP, SMB, NFS for volume access. |
| Large File Support | Yes, maximum file size — 8 EB. |
| Minimum macOS Version | macOS 8.1 and higher. |
To manage the process of data allocation on the disk, HFS+ stores special service information known as metadata. The following elements are most important for the proper operation of the file system and are of special interest when searching for missing data:
- HFS boot blocks located in sectors 0 and 1.
- Volume header which is located in the second sector.
- Allocation file.
- Catalog file. The Catalog File is a B-tree that contains records for all the files and directories stored in the volume.
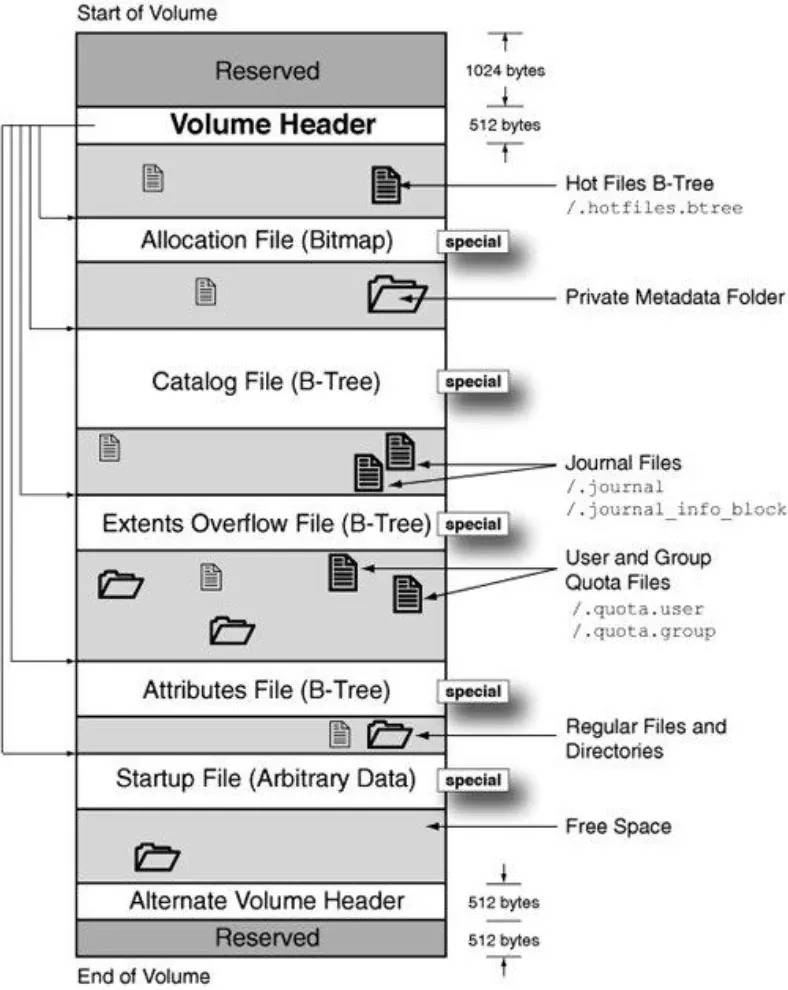
Recovering data from HFS+ file system is more difficult than from other file systems. One of the aspects causing difficulties is that HFS+ uses B-trees to store most volume metadata on allocation of files. After a file is removed, the B-tree is updated immediately, so the information on where the removed file was located is lost at once.
For full-scale and successful data recovery, you need to select the right software tool.
Test 1. Top data recovery tools

🔝 Top Tools to Recover Data from HFS+ Drives. How to Recover a MacOS Extended Drive 🍏
We have selected the best popular data recovery tools supporting HFS+ and ran some benchmark tests after erasing data on the disk. Below, we will present the test results.
For the benchmark, we have chosen the following tools: Hetman Partition Recovery, R-Studio, EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard, Disk Drill, UFS Explorer and Recuva.
As we examined the tools more closely, we had to exclude Recuva from the list as it doesn’t support HFS+ file system. So in the end, we will compare efficiency of the five specialized utilities.
We have created a test disk on the computer with Mac OS Catalina, copied some files there (photos, videos, and documents), and then removed some of the data.
We connected this disk to another computer with Windows 10, with all recovery tools already installed, and started testing them.
Testing Hetman Partition Recovery
The first tool on the list is Hetman Partition Recovery.
It recognized the test disk, the type of its file system – HFS+, and displays its name.
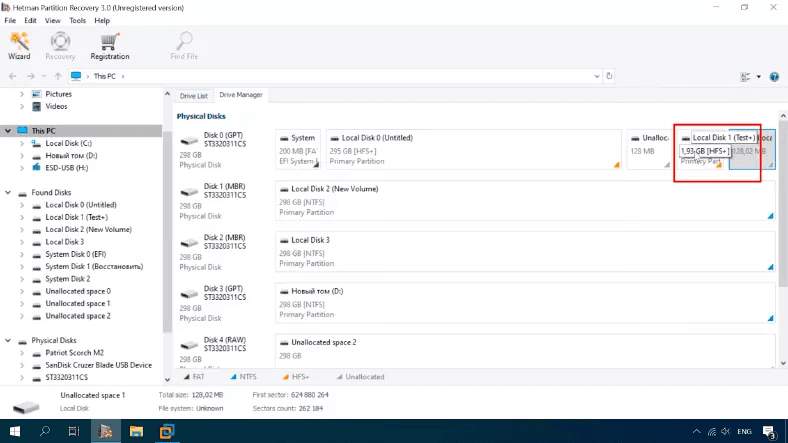
In this case of a simple deletion, a fast scan will suffice.
Here is the scan result: all files and folders are still on the disk, and the ones that have been removed are marked with a red cross. The disk structure and file names are retained. All the files are displayed in the preview window and available for recovery.
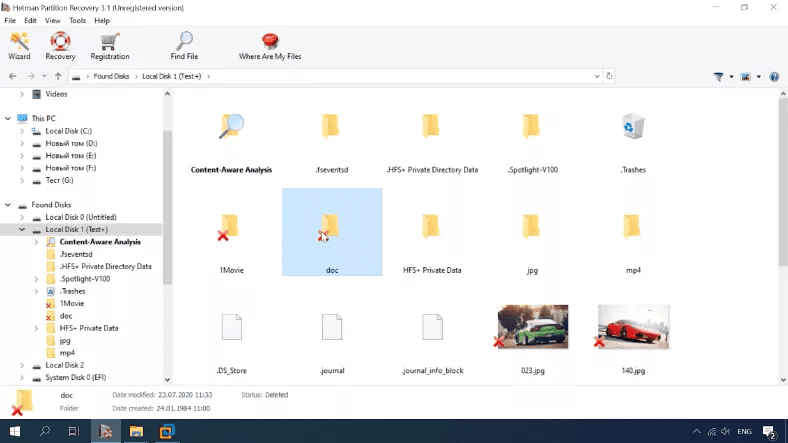
The program has completed this test successfully and met the challenge just as it should.
Testing RStudio
RStudio also displays the test disk, its name and file system type.
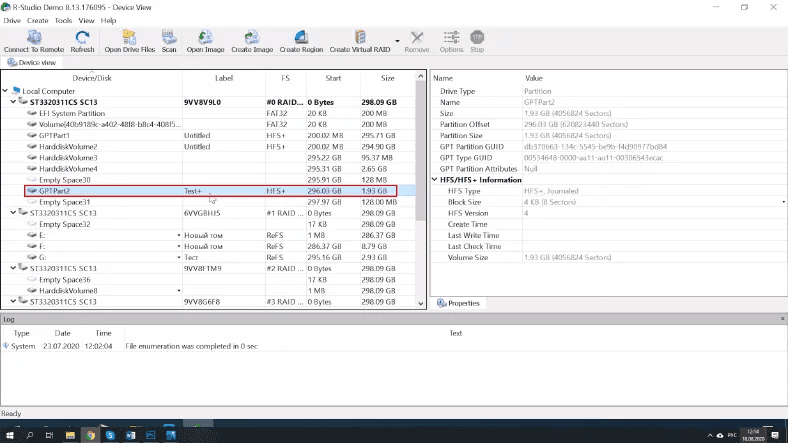
For some reason, it doesn’t display the folder 1Movie after a quick scan: most likely because the program couldn’t find it; also, some folders are shown twice and marked as deleted, though they are not. Other files are available for preview and recovery.
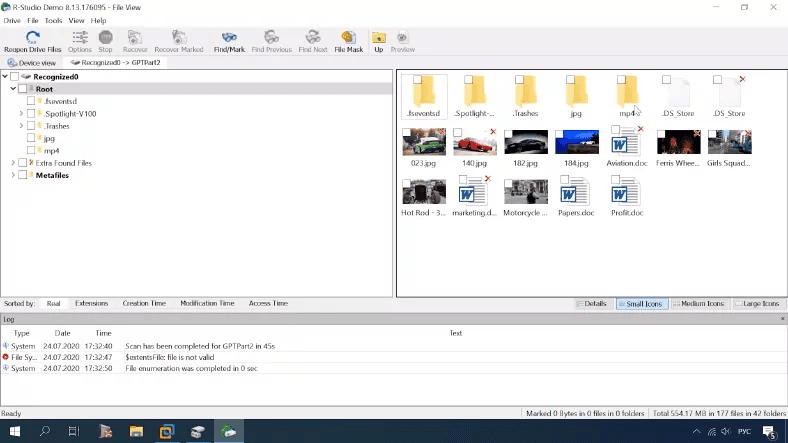
This tool completed the task partially as it couldn’t find one folder with a file. Generally, the final result is a little worse in comparison with Hetman Partition Recovery.
Testing EaseUS
Testing EaseUS, we can see it also displays the test disk, its name and file system type.
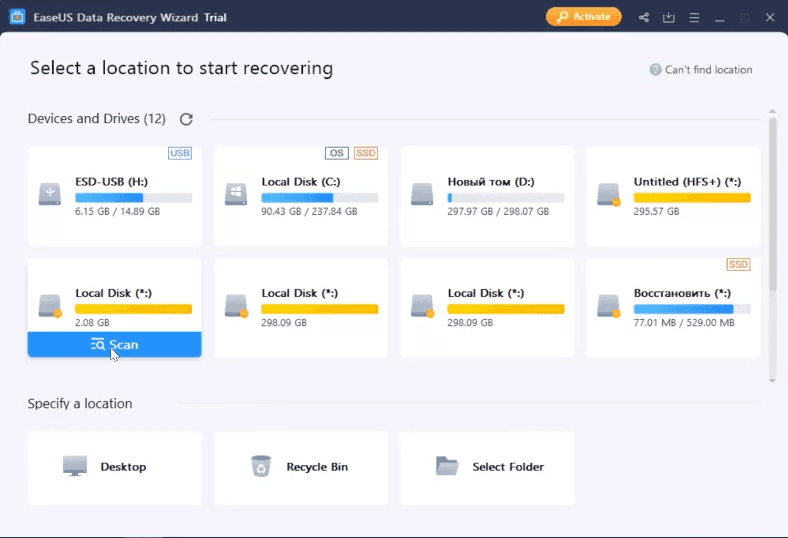
There is no option for a quick scan in EaseUS: as soon as you try to open the disk, it triggers an advanced scan. It may count as the first disadvantage of this product.
After the advanced scan, the result is 259 files.
The program displays all files and folders, all files can be viewed, but it is difficult to understand which elements were removed, and which are still on the disk. Also, some files are duplicated and you can’t view them.
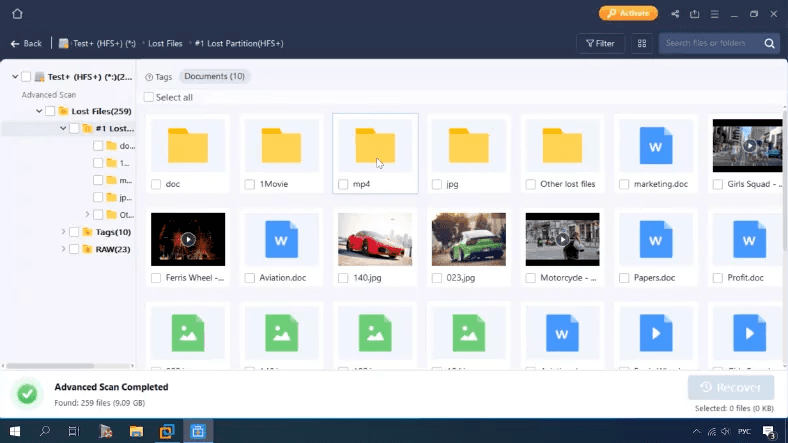
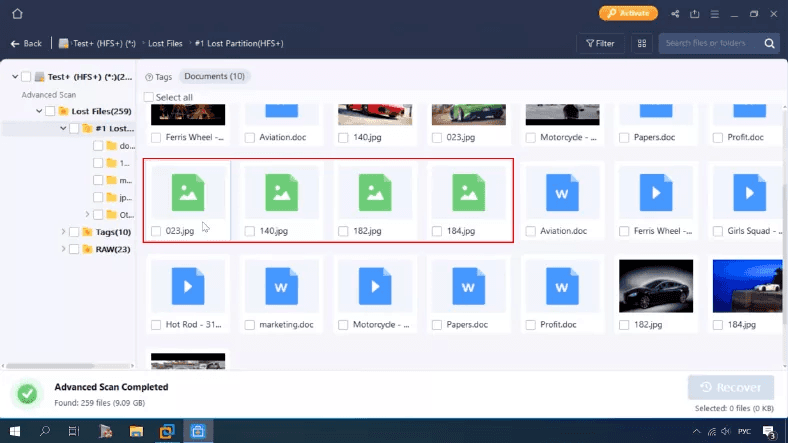
In the end, this product managed to find all the files, both deleted and those still on the disk, but it would be more convenient to have a sort of marking to distinguish between the two types. Some files got duplicated. The program has completed this test successfully.
Testing DiskDrill
DiskDrill displays the disk size, its file system type is indicated as HFS, the disk name is missing.
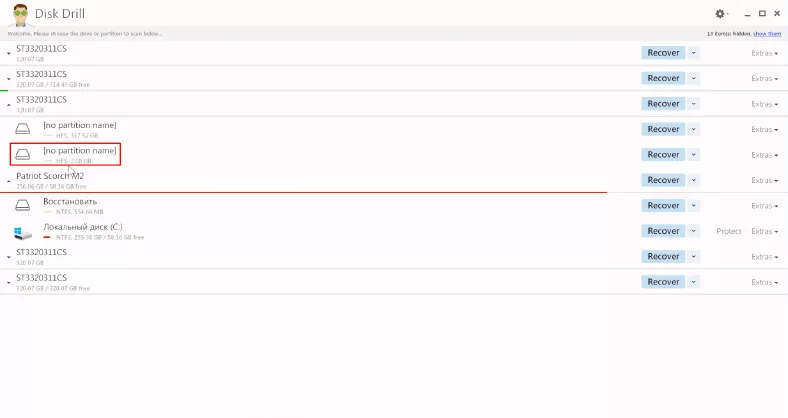
With quick scan, the program failed to find the deleted data, and only displayed the information which is still on the disk.
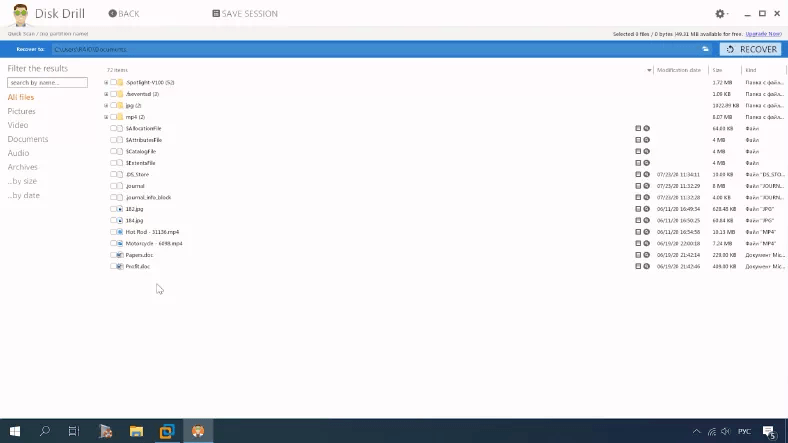
Only a deep scan is available.
Here is what the deep scan says: the disk structure is lost as well as file names, and there are some duplicates as well. They are arranged by type into various folders, and it’s hard to tell which of them were removed. Also, it’s hard to tell if the program was able to recover all data.
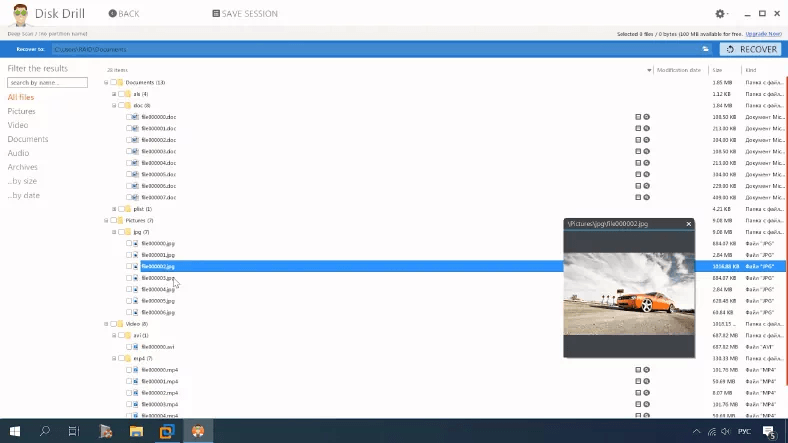
Videos and documents are unavailable for preview, so I can’t say for sure if they can be recovered.
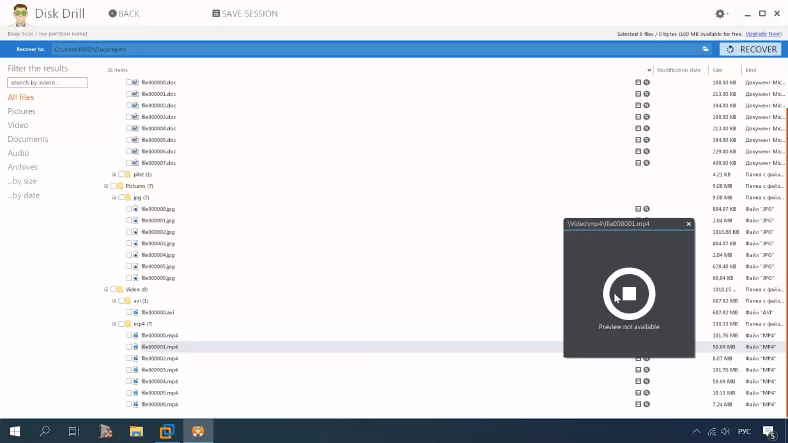
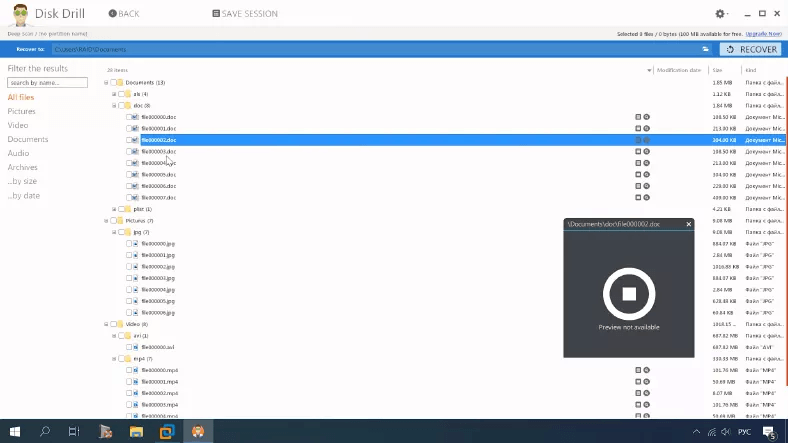
This tool has coped with the task partially, and so far, we give it the last position in our rating, because some files are unavailable for preview, and the deep scan takes quite a long time.
Testing UFSExplorer
UFSExplorer is the next product to be tested.
UFSExplorer can recognize the test disk, its file system type, but fails to display the disk name.
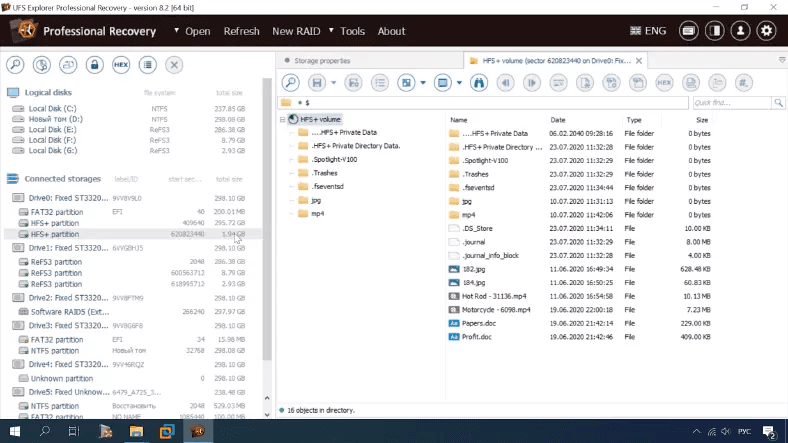
There is no quick scan option either.
Here is what full scan shows us: deleted data is found, the disk structure and file names are retained, removed elements are marked with a different color.
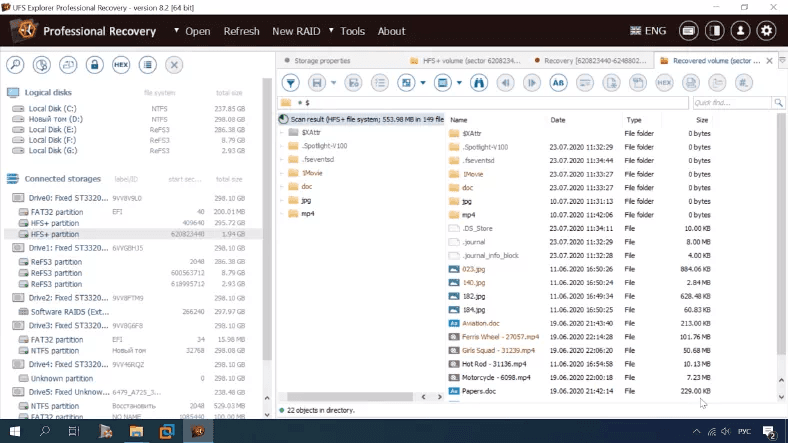
Photos and videos can be previewed. All folders can be located easily. The only disadvantage is that you can’t view documents. Photos and videos have no preview issues.
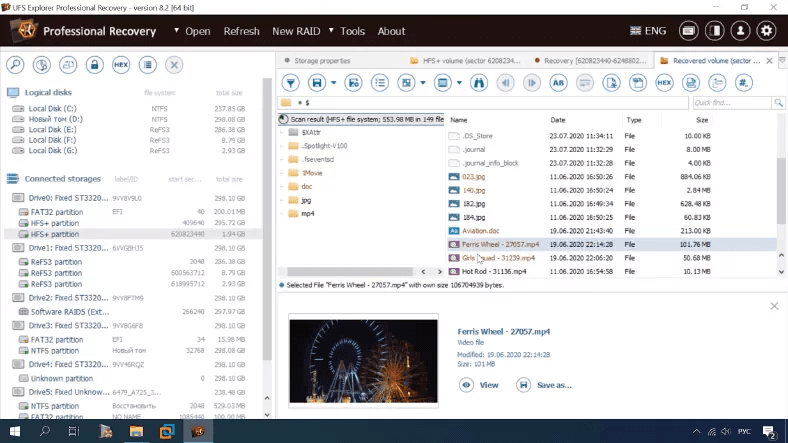
Talking of document recovery, there is much to be desired.
Summing up, we can say that the tool has coped with the task partially, as it encountered difficulties in displaying documents.
After the first round of testing, the two best tools are Hetman Partition Recovery and EaseUS as they both didn’t have any issues when analysing the test disk. The only downside in EaseUS is that it lacks the quick scan option. Other utilities have minor drawbacks. RStudio failed to detect one folder with a file, while DiskDrill and UFSExplorer couldn’t preview certain files.
In the following tests, we have erased file system elements, one by one: Volume Header, Alternate Volume Header, Header Node and Index node of the second level.
Test 2. Volume Header removed
In HFS+, the Volume Header is located in the second sector (from the beginning) and in the second-to-last sector (from the end of the volume), so that’s why we have erased the main header in the second sector at the beginning of the disk, then run the analysis to compare performance of the tools selected for the benchmark.
Testing Hetman Partition Recovery
The program displays the test disk, its name and file system type.

Fast scan gives the same result as in the previous test: all elements can be located, disk structure and file names are retained, everything can be previewed and available for recovery.

The program has completed the second test successfully.
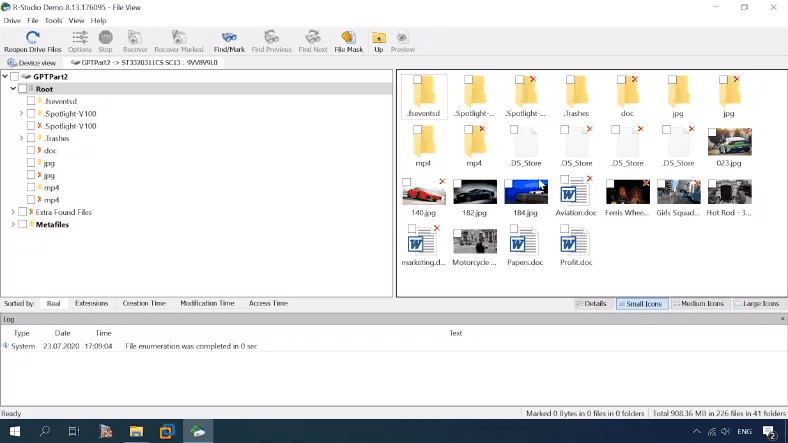
Testing RStudio
It also displays the test disk, its name and file system type.

Quick scan in RStudio lets us see the same result as before: the program is unable to find one folder with a video file and some folders are duplicated.
Testing EaseUS
The program can recognize the disk, but without its name and file system type.
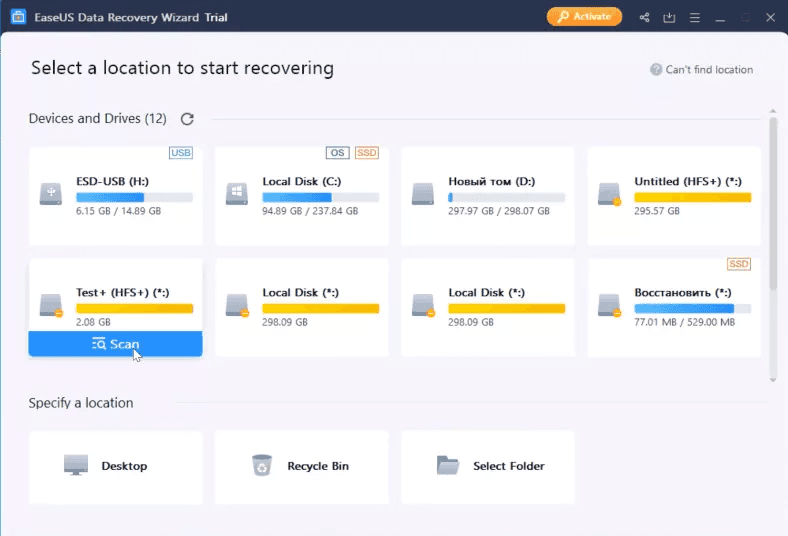
The result is the same as in the previous test – some files got duplicated.

Testing DiskDrill
The same result as before: files are sorted into folders, disk structure is lost, no preview for documents and videos.

It was the last test involving this product. Its results are unimpressive at all and there seems to be no use testing it anymore – we already know what to expect, and this tool ranks the last in our benchmark.
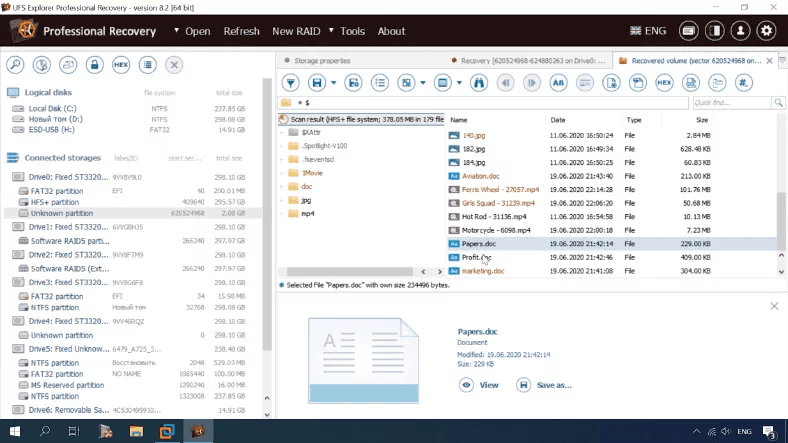
Testing UFS Explorer
The program can detect the disk, identify its file system type and size, but fails to display its name.
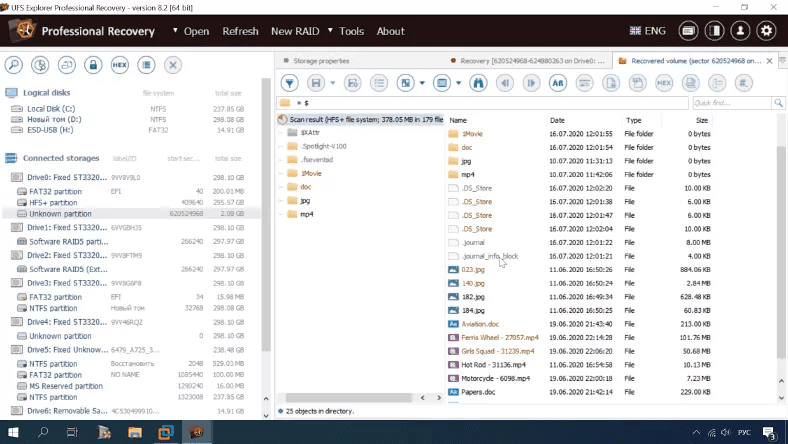
The program shows the same result as before, and documents can’t be previewed. All other things are OK.
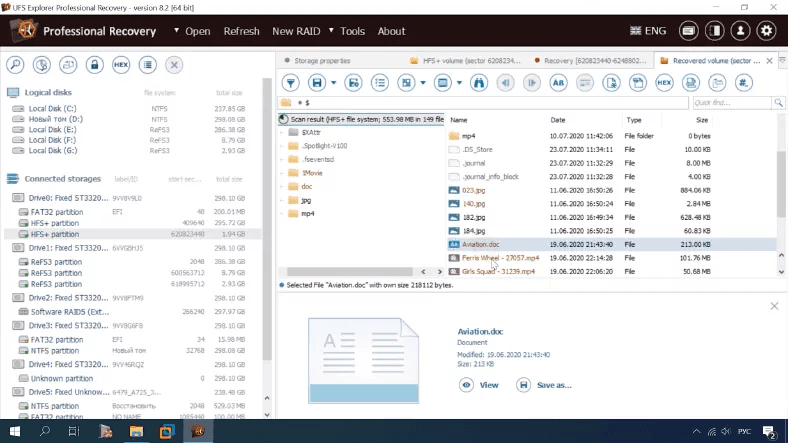
Test 3. Alternate Volume Header removed
For the next test, we have removed Alternate Volume Header which is located in the second-to-last sector from the end of the volume.
Testing Hetman Partition Recovery
The program displays the disk but without showing its name or file system type. All we know is the capacity.
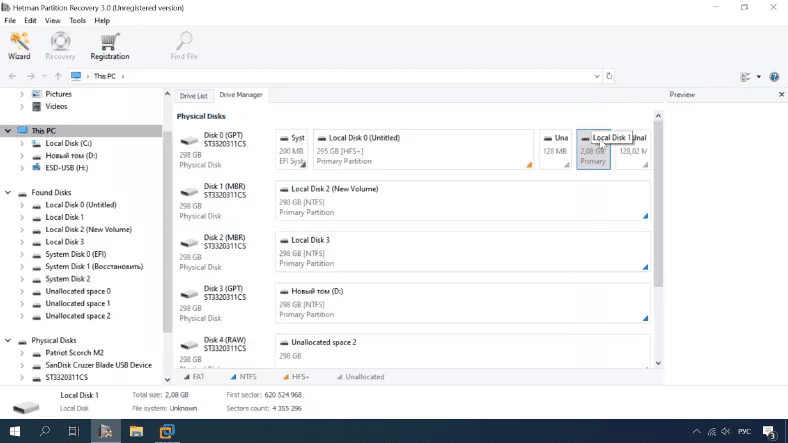
In this case, fast scan is no longer available.
After full analysis, the tool managed to find the test disk, identify its name and file system type.
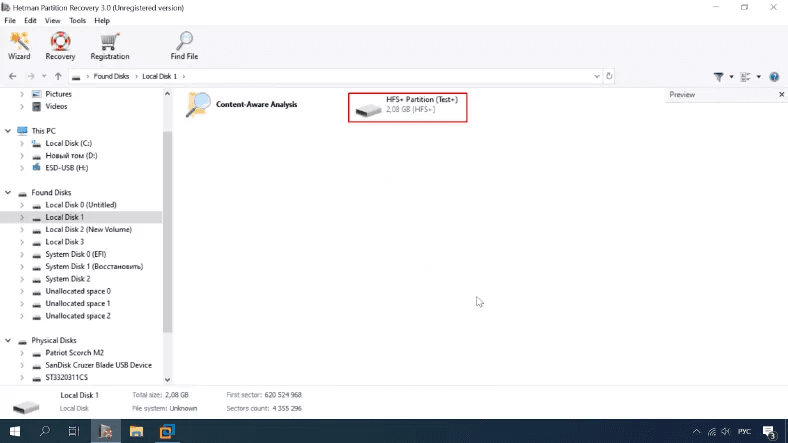
The disk structure and file names are retained. Everything is available for preview.
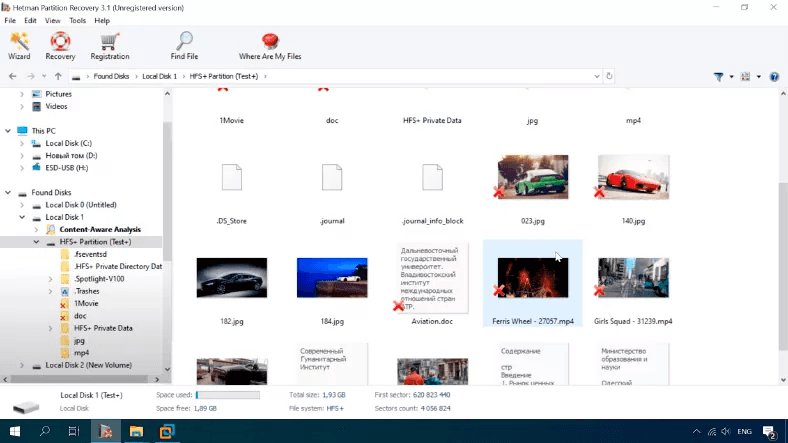
The test has been completed successfully.
Testing RStudio
The program detects the disk but without showing its name or file system type. Quick scan is not available too.
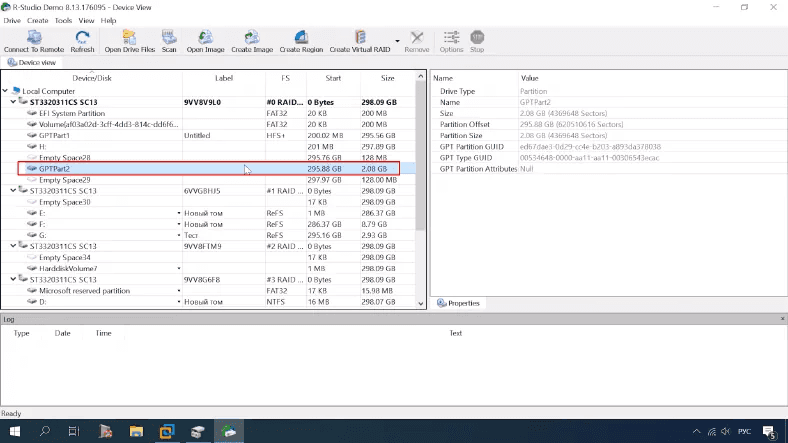
After full scan, the program managed to identify the disk name and file system type.
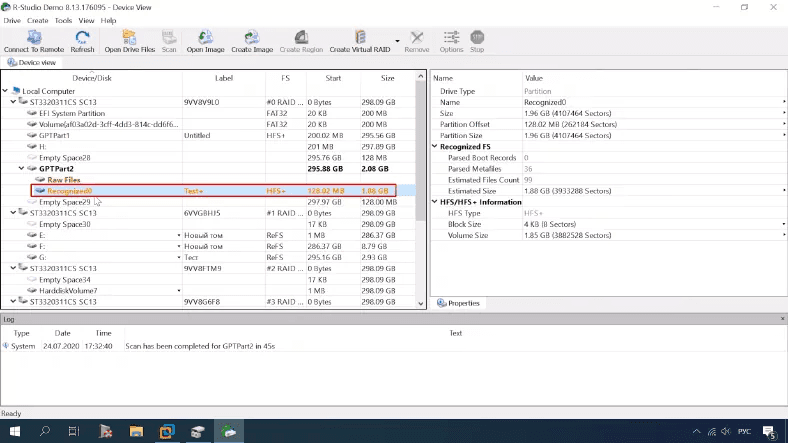
It was unable to find certain folders, particularly the folder “1movie” containing a video file, and the folder “doc” containing a document. Other data was located successfully.

Testing EaseUS
No real disk name or file system type.

We can see the same result as before, with some files duplicated. However, all data is available for recovery.
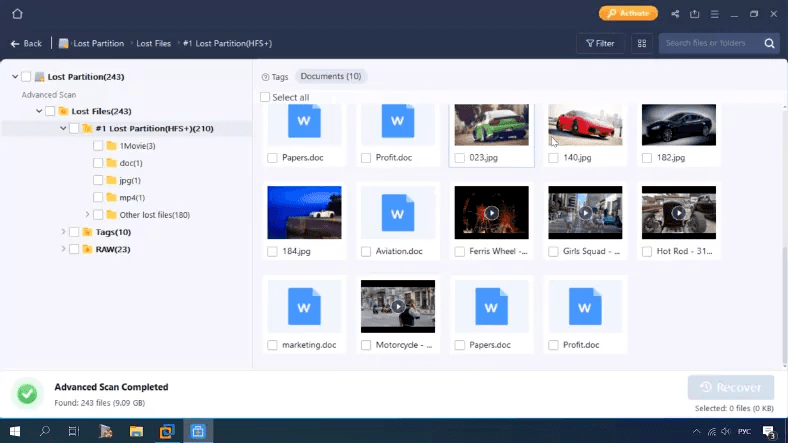
Testing UFS Explorer
The disk is shown as an unknown partition, without any name or file system type.
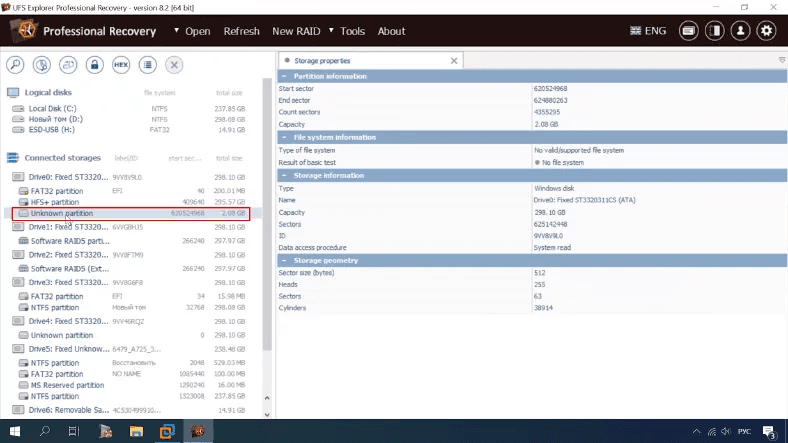
This time, result is no different: the data is found, but documents cannot be previewed.
Test 4. B-tree nodes removed
For the next test, we have erased B-tree nodes such as Index node, header node leaf, node header.
Testing Hetman Partition Recovery
The program can recognize the disk, but without its name and file system type.

After full analysis, the program managed to find the test disk, identify its real name and file system type.

The disk structure and file names are retained, all data is available for recovery.

The program has coped with the task successfully.
Testing RStudio
It shows the disk without its real name or file system type.

After full scan, the program managed to identify the disk name and file system type.

Similarly to the previous test, it was able to find the folder “1movie” containing a video file, and the folder “doc” containing a document. The rest of the data has been located, the disk structure and file names are retained. Everything is available for preview.

Testing EaseUS
Now it is time to test EaseUS.
It shows a disk without name or file system type.

The result is similar to what we’ve seen before – file duplicates. Everything is available for preview and recovery.

Testing UFS Explorer
It shows the disk as unknown volume.

After the scan, it identified the file system, retained the disk structure, and all files and folders can be located; the only disadvantage is that documents can’t be previewed.


Test 5. Index Node removed
In the final test, we will remove Index Node of the second level from the disk, in addition to all that we’ve erased before. In other words, we have removed all B-trees.
Testing Hetman Partition Recovery
The program shows the disk without its name or file system type.

After full analysis, it identified the file system type and disk name.

All files are available, the disk structure and file names are retained, everything is available for preview. All you have to do is to save the recovered files.

The program has completed all the tests with excellent results.
Testing RStudio
Again, the program shows the disk without a name or file system type.

After analysis, the program managed to find the test disk, identify its name and file system type.

Everything is the same as it was in the previous test. The tool was able to find the folder “1movie” containing a video file, and the folder “doc” containing a document. Not bad, at least it managed to cope with the task partially.

Testing EaseUS
No changes when it comes to testing EaseUS.

The scan result is perfect: all photos, videos and documents are present, available for preview and recovery. Well done.

Testing UFS Explorer
It shows the disk as an unknown device.

Here is the scan result: the disk structure and file locations are retained, photos and videos are available for preview, but documents aren’t.

In the folder “1Movie” you can’t preview one video file.
On the whole, we can say that this tool is a bit worse than RStudio, which failed to find some folders, but was able to preview all files without exception.
Conclusion
Summing up, by results of all tests, there are four tools that have passed them – Hetman Partition Recovery, Easeus Data Recovery Wizard, RStudio and UFS Explorer. Disk Drill failed the tests because lmost half of the files were not displayed in the preview mode. You have seen the exact figures above, so choosing the tool to use is entirely up to you.
There is only one thing I’d like to add – the algorithm used in Hetman Partition Recovery allows to retain the folder structure and file names which makes it easier to search for certain data and saves your time; also, it managed to find all the data that the disk used to contain.
In addition, our program lets you create a disk image and then recover data from there, which is the industry standard for deaing with faulty drives. Another favorite, Easeus, has very good results but doesn’t offer this option.