Cisco NSS3000 NAS Data Recovery Unleashed: In-Depth Guide
Struggling to recover data from your non-operable Cisco NSS3000 NAS? You’re in luck! Our comprehensive guide will walk you through expert strategies and techniques to successfully retrieve your valuable data. Don’t let data loss keep you down – reclaim your files with ease!

- Why NAS devices fail
- How to create a RAID
- How to create a shared folder
- How to enable an FTP server
- Data recovery from Cisco NSS3000
- Conclusion
- Questions and answers
- Comments
A network-attached storage (or NAS for short) is a data storage server connected to a network that allows its users to access the information stored on such server. A NAS could be a good solution if you want to protect your data from loss or damage, as it is based on the RAID technology.
Although RAID provides a reliable way to store and access your files, there are factors unaffected by how reliable your disk array is. Any hard disk within a NAS is a mechanical device, after all, and it may break down one day, causing you to lose your data because you don’t have access to the disk array. Just as any other device, NAS systems have a certain operating life. It means that after a few years in active use all storage devices tend to fail, sooner or later. On average, you may expect them to remain in service for about 5 years.

💿 How to Recover Data from a RAID System Based on a Non-Operable NAS Cisco NSS3000 💿
Why NAS devices fail
It usually happens after a power failure, voltage surges, overheating, accidental formatting, reinstalling an operating system, damaging the file system, or as a result of mechanical issues affecting the hard disks or the RAID controller. Very often, data can be lost from NAS devices when users decide to update their firmware. In the end, you will need a specialized data recovery tool to rebuild the RAID and restore access to your files.
Some manufacturers offer dedicated software tools to help you restore operability of the hard disks. However, the problem is that the main function of such tools is often limited to merely formatting those disks. When you do that, you just lose all the information they contain, and it’s going to be difficult to restore it.
| Reason | Description |
|---|---|
| Hard Drive Wear | Constant use of the NAS leads to gradual wear of the hard drives, which may cause their failure. |
| Overheating | Insufficient ventilation or high ambient temperature can lead to the overheating of device components. |
| Power Issues | Voltage fluctuations or sudden power outages can damage NAS hardware components. |
| Software Errors | Firmware or software failures in the NAS can cause instability and data access loss. |
| RAID Array Failures | Failure of one or more disks in a RAID array can result in data loss or device malfunction. |
| Mechanical Damage | Physical shocks or damage may cause the failure of NAS components like boards or disks. |
| Malware Attacks | Cybercriminals may exploit NAS vulnerabilities for attacks, leading to data loss or device blockage. |
| Insufficient Maintenance | Irregular maintenance, such as dust cleaning and software updates, can shorten the NAS lifespan. |
How to create a RAID
For starters, let’s explore how to create a RAID system with this CISCO network storage device. Open any browser on a computer connected to the network that includes your NAS, and type the IP address of the server: in this model, it is displayed on the special screen. Log in as the administrator. Expand the Storage tab and find the RAID option.
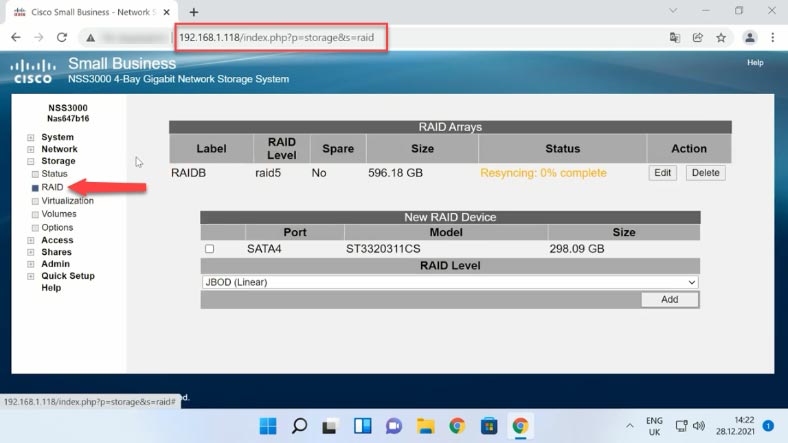
If you need to rebuild the existing array, click “Edit”. You have the option to expand it by adding the fourth disk. Click “Add” to increase the storage size. After that, its status will change to “Spare”.
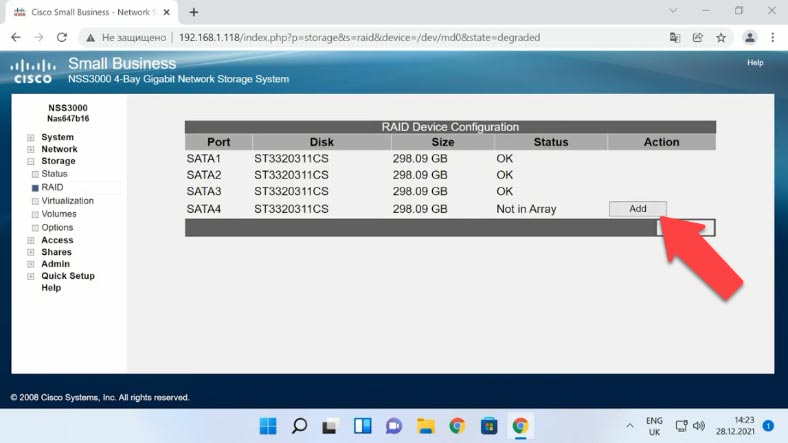
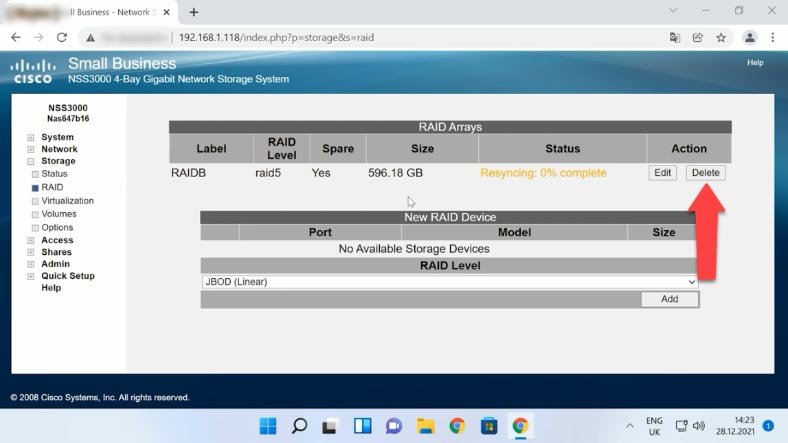
To remove the RAID, click “Delete” next to the array and click OK to confirm the action. As a result, the RAID will be removed and all the information on its hard disks will be erased.
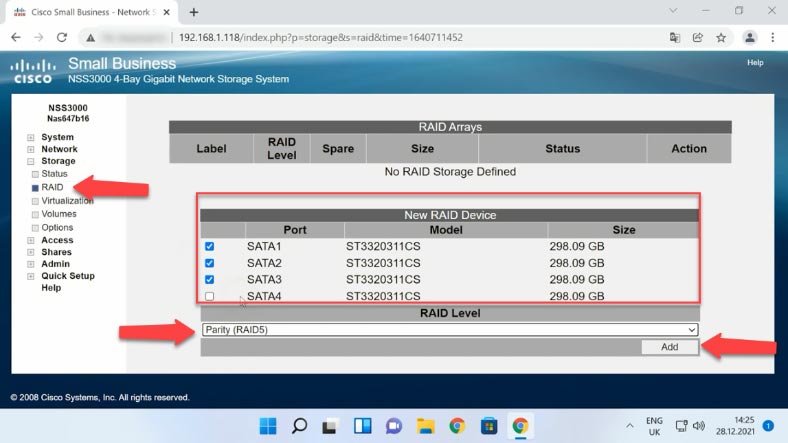
To create a new disk array, use this management menu to select the hard disks that your future RAID should consist of, choose the level from the drop-down list, and then click “Add”. You will see a warning on the screen saying it will erase all the data on the selected disks. Click OK to continue.
After that, the system will start creating and resynching the disk array. It is a very long process, but luckily for us, it can run in the background, so we can proceed with further configuration.
How to create a shared folder
While the resyncing process is running, you can create a new shared folder and configure network access. To do it, find the Volumes tab. Select an array from the drop-down list, assign a name to it, and specify its size. If necessary, you can enable encryption and protect access to the network drive with a password.
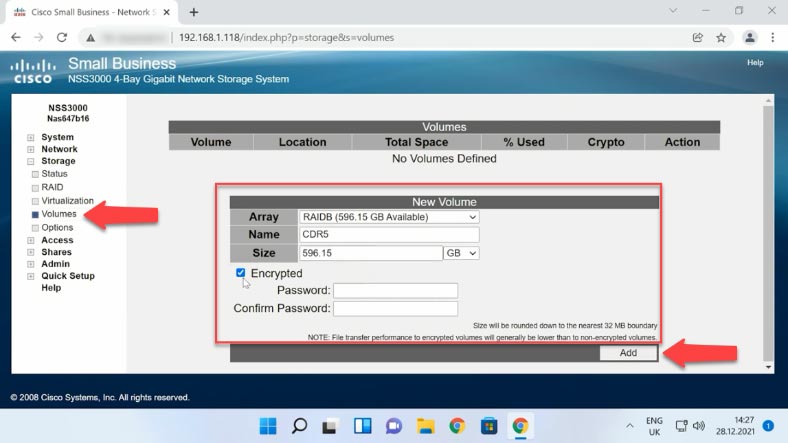
When all the properties are given, click “Add”. Now the new volume is ready, so let’s move on to network connection.
How to enable an FTP server
To configure network access, open the Shares tab, and check the Shares option here. In the window that opens, click “Create Share”. Give the folder name, select location, set access attributes, and choose required network protocols (CIFS, NFS, FTP). Look below to assign privileges to certain users, then click OK.
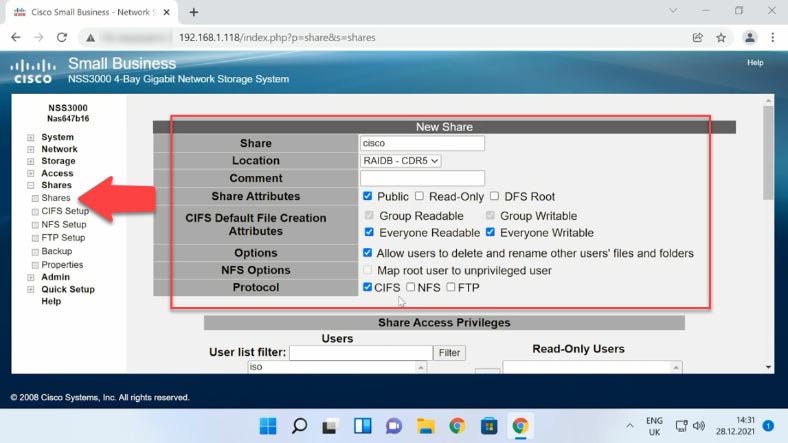
If you did everything right, the folder will appear on this list. If necessary, you can edit the settings or even remove the directory you have just created.
Data recovery from Cisco NSS3000
Method 1. How to recover data from a non-operable NAS
When a network storage system breaks down, it’s going to be very difficult to access the data which still remains on the hard disks inside the storage device. As long as Linux is the natural environment for most NAS servers, and hard disks within a RAID are formatted into file systems supported by Linux, it is possible to try using Linux in order to get access to the files. However, if you know little about this operating system, we don’t recommend trying this method: a single mistake in commands may erase all information on the hard disks for good.
The best solution would be to use a specialized tool for recovering data from network-attached storage systems. It is both quicker and more convenient, and it can save you the trouble of having to type lots of various commands. Hetman RAID Recovery supports most popular file systems, RAID technologies and types, and in most cases it will be able to rebuild the damaged RAID automatically.
Before you start, make sure you have enough data and power cables to connect all your hard disks. It’s better to use a bunch of SATA cables to connect the disks directly to the motherboard of your computer, but if you have only a few free SATA ports, you can use USB-to-SATA adapters when necessary. Also, you will need an additional storage device to copy the retrieved data to; it can be an external hard drive, another network-attached storage, or some other device with sufficient capacity.

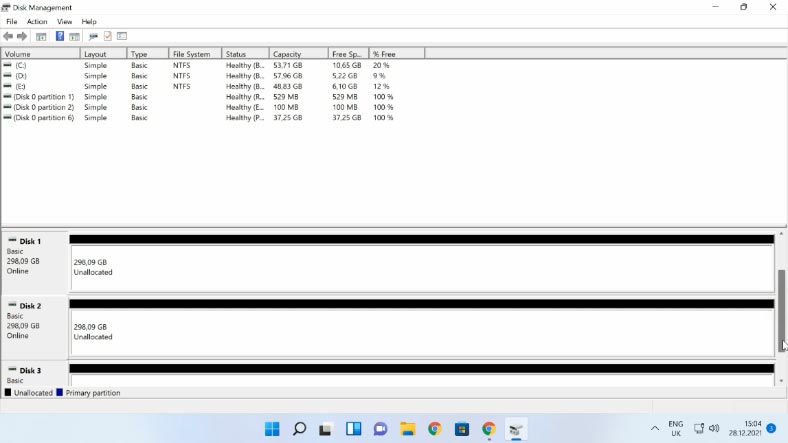
Take the disks out of the NAS device and connect them to a Windows computer. When the operating system has booted, open Disk Management and check if the added disks are recognized. As you open Disk Management, the operating system may suggest you to initialize or format them. Remember to never agree to either operation, because it can erase the remaining information completely.
Download, install and start the data recovery tool. Hetman RAID Recovery will identify the disks automatically, read their service information and rebuild the damaged RAID system. In the program’s interface, the RAID volume is shown at the top of the Drive Manager window. By default, this NAS model creates a disk array with the XFS file system, and you can’t change it into another file system you prefer.
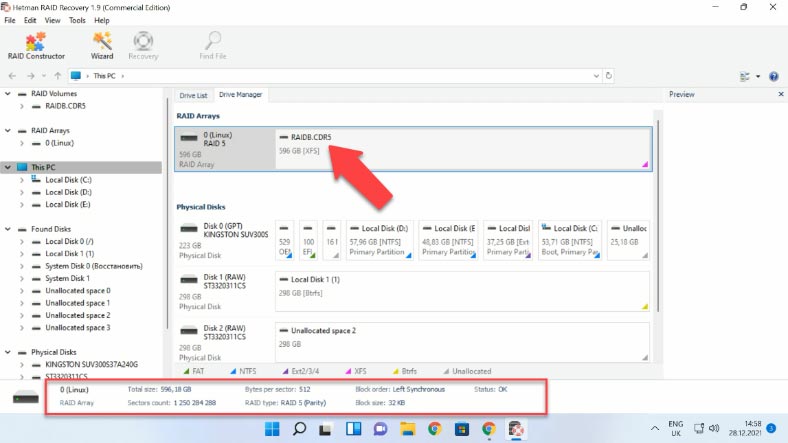
Important: during the format operation, the XFS file system driver divides the disk into groups. Each of these groups contains a superblock that describes general properties of the file system. Also, each group contains a number of other file system structures, the most important of them being the inode table. Inode is a data structure in a Unix-style file system that describes a file-system object such as a file or a directory.
To access the volume contents, you need to scan it first. To do it, right-click on the volume and choose “Open”.
In the next window, you should choose between the two options, “Fast scan” and “Full analysis”. Select “Fast scan”, click “Next” and wait. When this process is over, switch to search results by clicking “Finish”.
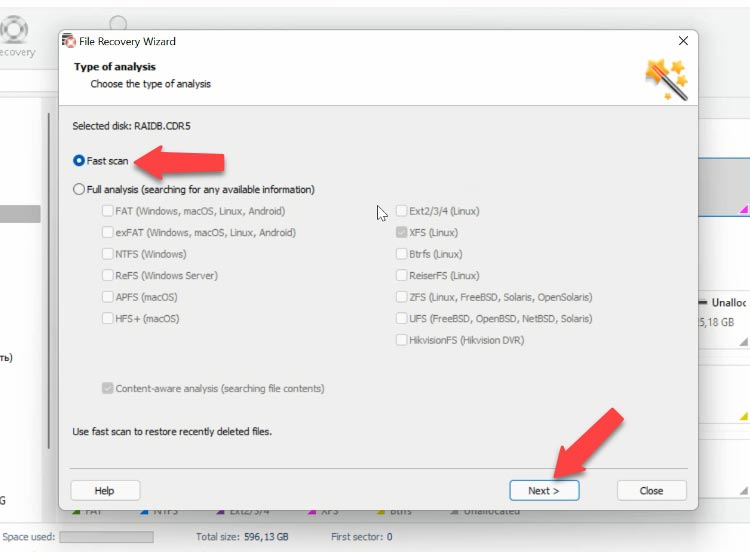
The directory tree has not changed so you won’t have any difficulties in finding the proper folder with the files you are looking for. If you know the file name, you can use the search function. You can check file contents with the preview feature. The principle is simple: if you can see the contents, this file can be recovered.
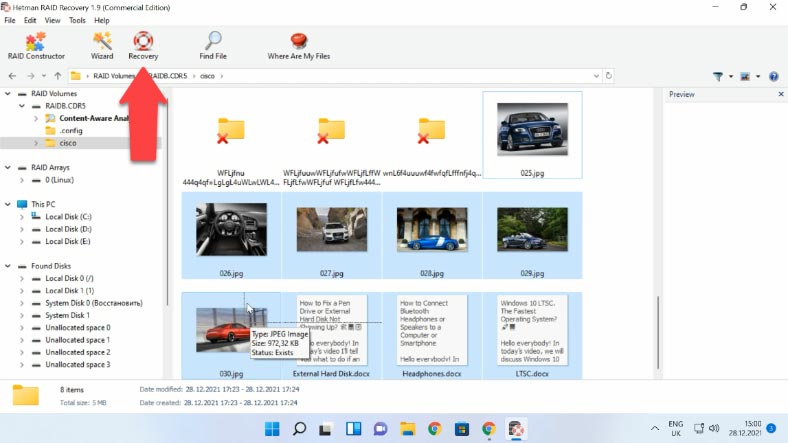
Select all the elements you want to recover and click “Recovery”, choose the disk where to save them and specify the directory, then click “Recovery” and “Finish”. After that, follow the path you have chosen and check if the recovered files are there.
Hetman RAID Recovery offers extra features to improve effectiveness of working with RAID disks that have hardware issues. It lets you create disk images and then analyze these images instead of the actual hard disks in order to reduce disk usage and prevent them from breaking down at the most inappropriate moment.
Method 2. How to build a RAID manually
In some cases, when disks are damaged or their service information is erased, Hetman RAID Recovery may have difficulty in automating the array rebuild process. If the program failed to rebuild the RAID with the available hard disks but you know its properties, you can perform this operation manually, with the help of the RAID Constructor.
To do it, open the Constructor, and select the “Manual mode” option here. In the next window, fill in all the RAID properties you know: the RAID type, block order and size, add the disks it used to include, use the arrows to specify their order, and replace the missing disks with empty drives by clicking the “plus” button. Also, in case of creating a RAID manually, you need to specify the offset that helps to locate the beginning of the disk. Sometimes, the program may have difficulty in identifying it automatically.
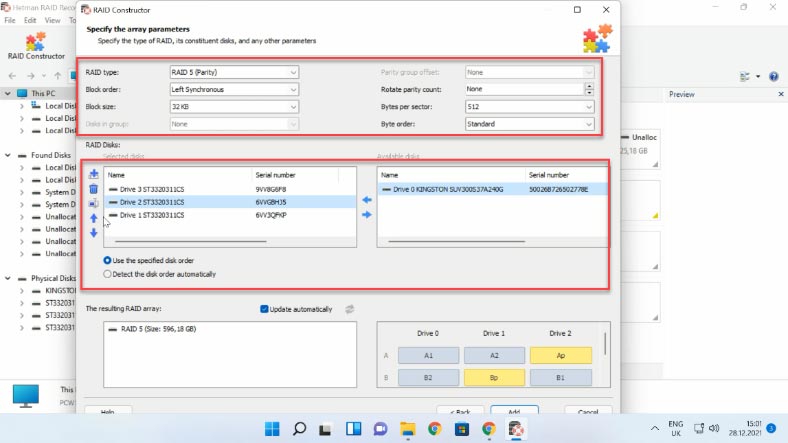
When you specify all the properties you know, click “Add”, and the array you have built manually will appear in the Drive Manager. After that, start the scan, look for the files you want to recover, and hit “Recovery”.
Conclusion
We hope that this article was helpful as we tried to describe all the main stages in building a RAID system, configuring it, and recovering its data.






There are several specific factors that play an important role in data recovery. The manufacturer of the hard drive affects these factors, so our experts should inspect the hard drive to assess its respectability.
Important drive characteristics that affect data recovery
RPM; hard drive capacity; susceptibility of hard drive firmware to damage; quality of electronic components; inner drive material; PC operating system and file system; internal drive resistance to damage and contamination. In the process of media recovery we open the case of the drive in a special lab. Our experts always compare hard drives in order to establish the basis of faults and eliminate them quickly.
It has
The file system (or file system) is the primary mechanism for managing data on a storage medium.
It not only controls how the operating system distributes, stores and processes data, but it also determines how data is handled when a file is deleted or storage is formatted.
Therefore, in the event of any problem or the need to recover deleted information, the chances of success in recovering data depend fundamentally on the behavior of the file system used.