The Ultimate Guide to Oracle Database Data Backup and Restore
Learn how to backup and restore Oracle Database data with ease in this comprehensive guide. Whether you’re a beginner or experienced user, discover step-by-step instructions and essential tips to seamlessly backup and restore your valuable data. Dive deep into the Oracle database backup and restore process and explore insider techniques to maximize your chances of successful data restoration.
- Database structure in Oracle Database
- Creating a backup copy of Oracle Database
- Restoring a lost database in Oracle Database
- Database backup and restore with Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN)
- Questions and answers
- Comments

How to Recover MySQL, MSSql and Oracle Databases ⚕️👨💻🖥️
Database structure in Oracle Database
In the course of its work, Oracle Database uses several groups of files which should be archived (backed up) for further recovery. They are as follows:
-
Data and tablespace files (*.DBF).
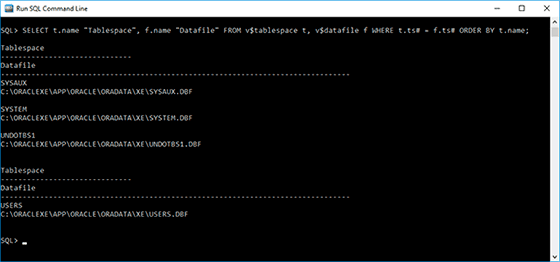
Names of data and tablespace files as well as the paths to them can be viewed with SQL Plus by executing the following query:
SELECT t.name "Tablespace", f.name "Datafile" FROM v$tablespace t, v$datafile f WHERE t.ts# = f.ts# ORDER BY t.nameAs a result of such query, a detailed report will be generated:
-
Database configuration files (*.ora).
Oracle database configuration files have the extension *.ora and can be found in this folder:
C:\oraclexe\app\oracle\product\11.2.0\server\dbs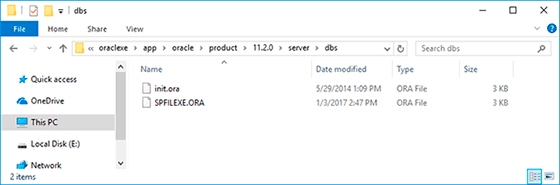
-
Database control files (*.DBF).
The easiest way to determine the path to, and the names of control files is to find in the configuration file *.ORA the line control_files, where the control files used by this database will be listed.
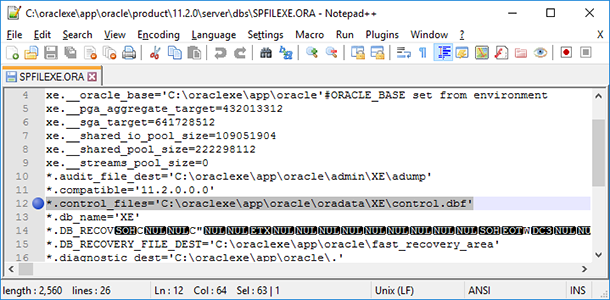
Also, you should execute this query in SQL Plus to determine the names of, and paths to the control files:
SELECT value FROM v$parameter WHERE name = "control_files"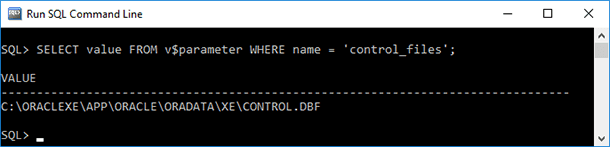
-
Transactions log files (*.LOG).
To learn the names of online transactions logs and paths to them, you should execute this query in SQL Plus:
SELECT member FROM v$logfileAs a result of such query, a detailed report will be generated:
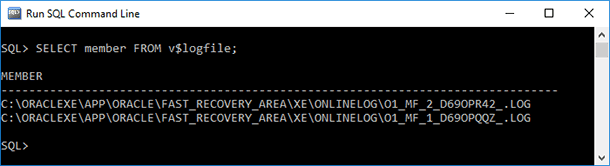
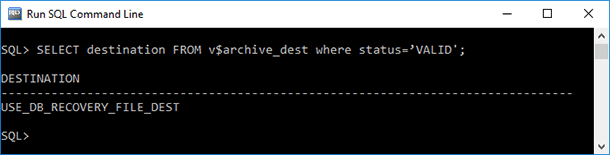
To determine the paths to folders where archive transactions logs are stored, you should execute this query:
SELECT destination FROM v$archive_dest where status="VALID"As a result of such query, a report will be generated:
-
Password files (*.ora).
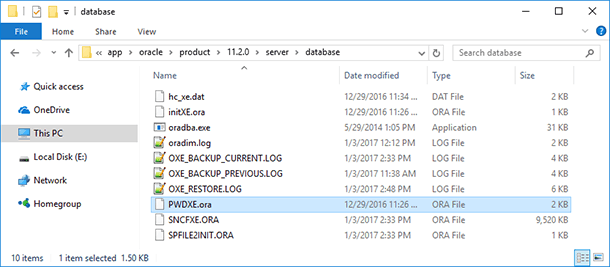
As a rule, these are files with the extension *.ora, their names beginning with PWD symbols.
example: PWDXE.oraPath C:\oraclexe\app\oracle\product\11.2.0\server\database
So, to save, archive or backup an Oracle Database file, copies of the abovementioned groups of files should be created, namely:
-
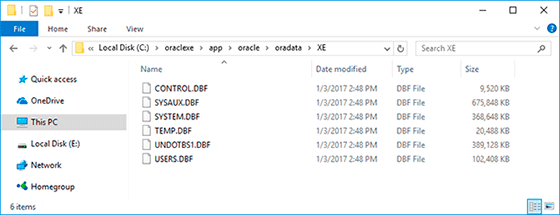
*.DBF - data files, tablespace files and database control files. Their location:
C:\oraclexe\app\oracle\oradata\XE -
*.ora – database configuration files and password files.
Configuration files:
C:\oraclexe\app\oracle\product\11.2.0\server\dbs
Password files (PW…ora):
C:\oraclexe\app\oracle\product\11.2.0\server\database -
*.LOG – transactions log files:
C:\oraclexe\app\oracle\fast_recovery_area\XE\ONLINELOG
where ХЕ is the database name, in our case.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Format | .DBF (dBASE) |
| Data Types | Numbers, text, dates, logical values |
| Maximum Number of Fields | Depends on the format version. For example, in dBASE IV – up to 255 fields |
| Record Size | Usually fixed for each record and determined by the number of fields and their sizes |
| File Size | Depends on the number of records and fields. Typically, files are small, up to a few megabytes |
| File Header | Contains metadata: number of records, table structure (fields), date, and other parameters |
| Field Types |
- **Character**: Text fields (strings) - **Numeric**: Numeric fields - **Date**: Date fields - **Logical**: Logical values (TRUE/FALSE) |
| Compatibility | Supported by many programs, including various DBMS like MySQL, PostgreSQL, LibreOffice Calc, Microsoft Access |
| Software | dBASE, FoxPro, Clipper, Excel, LibreOffice, DBF Viewer, Access |
| Header Structure | The header consists of 32 bytes that contain information about the number of fields, field types, number of records, etc. |
| Encoding | Typically uses ASCII or other encodings that support localization |
| File Extensions | Usually, one file has the `.DBF` extension, but additional files may be associated, such as `.MDX` for indexes |
| Additional Files | Index files (e.g., `.NDX` or `.MDX`) that store indexes for fast access to data |
Creating a backup copy of Oracle Database
A database backup of Oracle Database can be created in two ways:
- With the means of the operating system.
- With the built-in tools of Oracle Application Express – Import / Export.
Method 1. Archiving with the means of the operating system
Archiving with the means of the operating system suggests manual copying of all working database files such as:
- Tablespace files.
- Control files.
- Transactions log files.
- Configuration files.
In this case, the process of archiving consists is mere copying of the control files, tablespace files, configuration files and archived transactions log files into a backup directory or a backup server. Archiving is performed with the stopped database, and users cannot work with it then.
To restore a database damaged because of a failure, it should be stopped, and backup copies of working files and transaction logs should be written to their previous location.
Method 2. Archiving and restoring with the tools Export / Import
In Oracle Database, you can archive (backup) and restore a database with the help of Oracle standard tools - Export and Import. To improve data safety, you should perform a complete export operation regularly, depending on how often you work with the database. If changes to the data are made frequently, you should export the database once a week.
To do it:
-
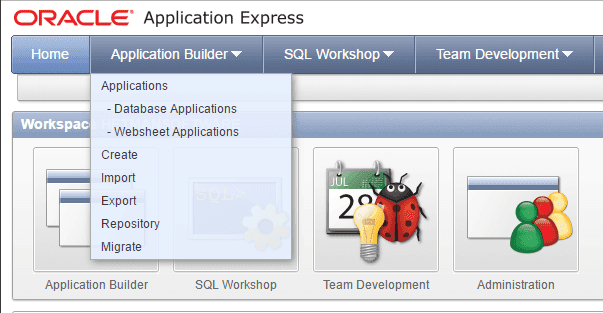
Open Oracle Application Express and select the menu Application Builder / Export
-
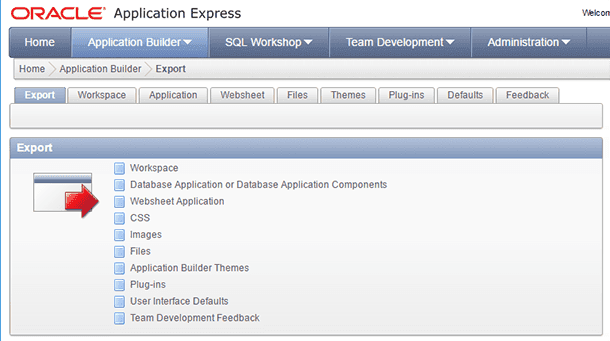
Specify the export type: the entire workspace or one of its components
-
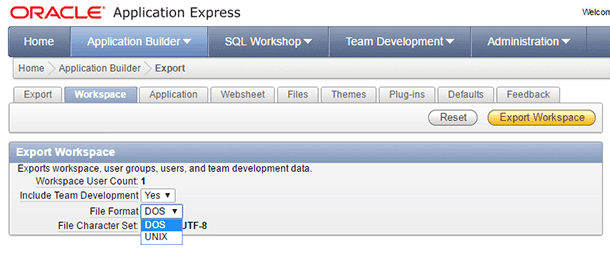
Set the file format to export the data into, and click on Export Workspace (it’s on the right)
-
After you specify the location where the data export file will be saved, it is saved into a SQL file.
Similarly, you can import a file or a previously created archive:
-
Open Oracle Application Express and select the menu Application Builder / Import

-
Select the file to import and specify its type
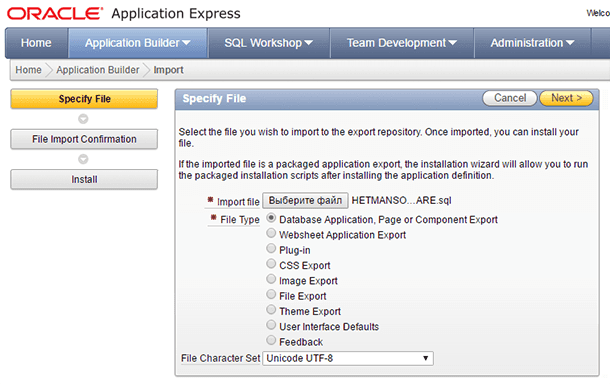
-
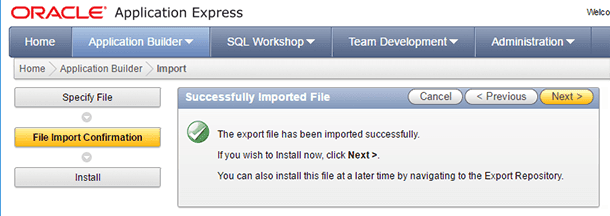
Install the imported database
Restoring a lost database in Oracle Database
If a database from Oracle Database is deleted or lost for any reason, it can be restored by recovering its files with Hetman Partition Recovery and then restore them as described in the part «Archiving with the means of the operating system».
To do it:
-
Run Hetman Partition Recovery and scan the disk where the database was stored
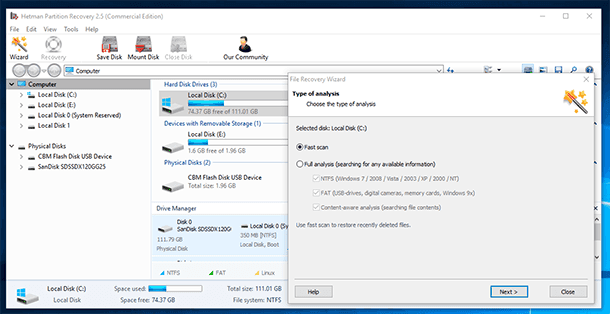
-
Wait until the process is finished and use the program to go to the folder where the necessary Oracle Database files are located.
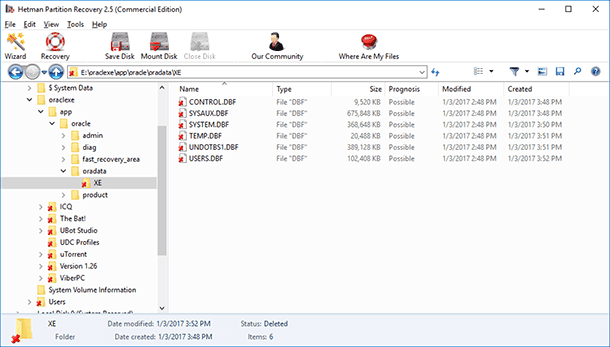
-
Recover them
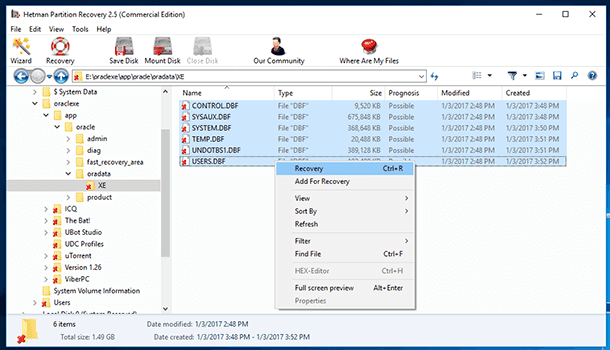
-
Replace the existing Oracle Database files with the recovered ones.
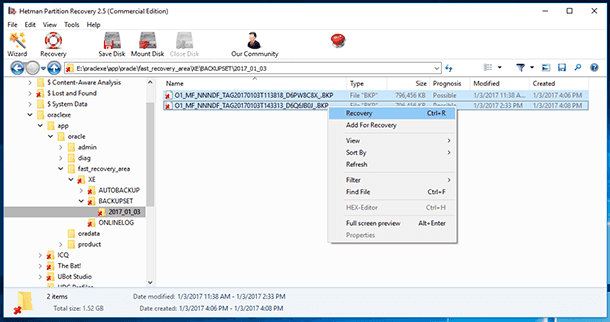
As an example of recovering database files, here is how *.DBF files can be recovered. However, take into account that to recover all data in an operable base you should also recover the corresponding *.ORA and *.LOG files.
Database backup and restore with Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN)
Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) is one more tool for creating a backup database copy in Oracle Database. It differs from other tools by its ability to create an entire copy of the database rather than copy only the data from there. What is more important, Oracle Recovery Manager combines the functions of SQL Command Line while making the user independent from its commands. This tool is installed at the same time as Oracle Database.
To create a database backup copy with Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN):
-
Run the file Backup.bat in the folder
C:\oraclexe\app\oracle\product\11.2.0\server\bin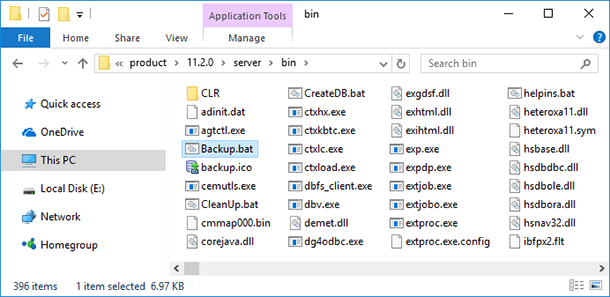
or select Backup Database among other applications in the Start menu
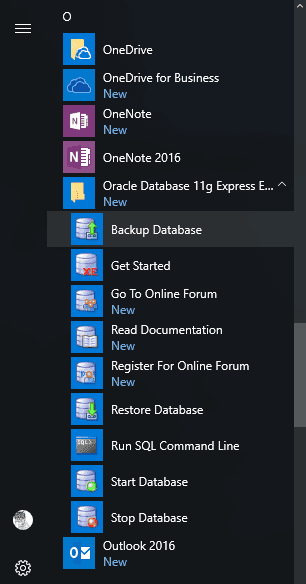
-
Wait until the backup by RMAN tool is complete
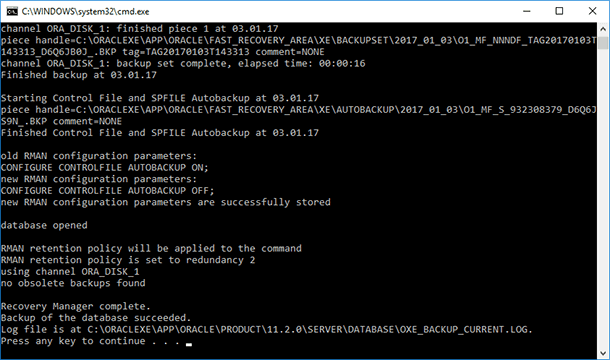
-
As a result, a backup file with the extension *.BKP will be created in the folder with the name which is the date of creating the backup file
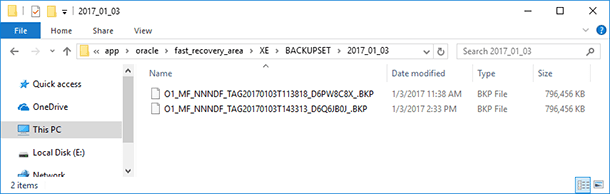
To restore a database from a backup copy with Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN):
-
Run the file Restore.bat in the folder
C:\oraclexe\app\oracle\product\11.2.0\server\bin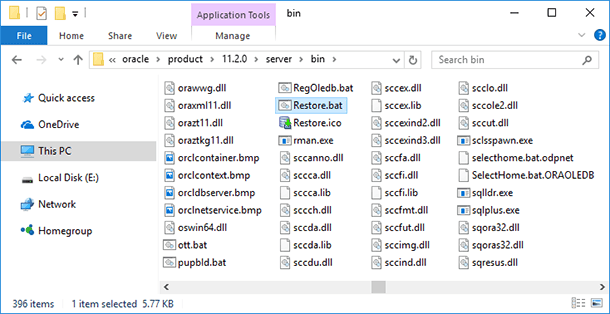
or select Restore Database among other applications in the Start menu
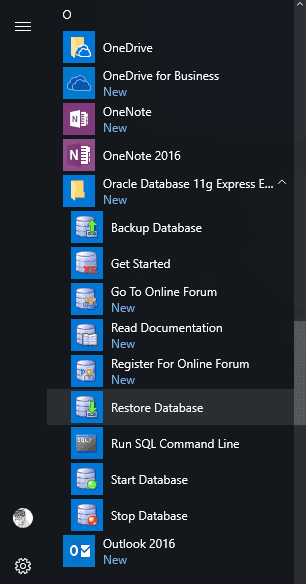
-
Wait until restore operation from a previously created backup by RMAN tool is complete
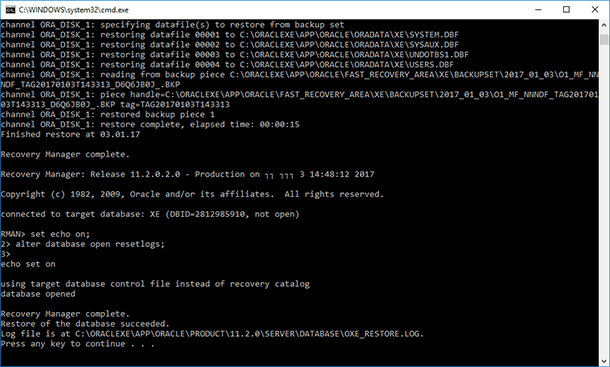
By the way, in case of losing or deleting a backup file of Oracle Database, the *.BKP backup file can also be recovered with Hetman Partition Recovery, and then restored, as we have shown above, with the use of Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN).