Windows Safe Mode: How to Boot Your PC Safely
Protect Your PC: Learn How to Boot Windows in Safe Mode with Ease! Need to troubleshoot Windows issues or remove problematic software? Booting Windows in safe mode is the solution! In this comprehensive tutorial, we’ll show you step-by-step how to boot Windows in safe mode. Whether you’re experiencing startup problems or need to perform maintenance tasks, safe mode provides a stable environment for troubleshooting. From accessing advanced startup options to selecting safe mode options, we’ve got you covered.
Safe Mode in Windows 10
If you already spent some time working in Windows 10, you must have noticed that old ways of booting a computer in Safe Mode don’t work anymore. That is, pressing the keys F8 or Shift + F8 while booting you can no longer send your machine into the Safe Mode.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Safe Mode loads the system with a minimal set of drivers and services to troubleshoot issues that may be caused by third-party software or drivers. |
| Types of Safe Mode | With networking support (for internet access) and without networking support. |
| Mode Activation | Via boot options in the Windows menu or by pressing F8 during system startup (may need to be enabled in Settings). |
| Diagnostics | Helps identify and fix problems with drivers, programs, or viruses that prevent normal booting. |
| Exiting Safe Mode | Rebooting the system returns it to the normal Windows mode. |
| Additional Features | Command Prompt support for running additional diagnostic and repair commands. |

How to Create a Recovery Partition for a Computer or Laptop with Windows 10, 8 or 7 💻🛠️📀
However, it doesn’t mean that Windows 10 no longer has Safe Mode. It’s just the sequence of steps you have to take has changed. Let’s explore each one in detail.
When you enter Safe Mode in Windows 10, the operating system boots a minimalistic interface and only the most necessary services and drivers which are required for Windows to operate.
Method 1. With the System Configuration utility (msconfig.exe)
The easiest way to boot Safe Mode in Windows 10 is with the System Configuration utility. It is well-known by its actual name, msconfig.exe.
To start this utility, launch the Run window with the key combination Windows + R and type in the command msconfig.
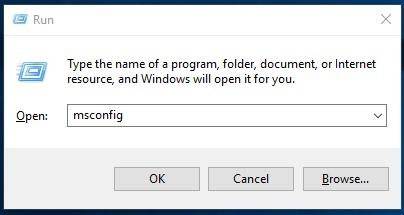
In the System Configuration window that opens jump to the tab Boot, and in the section Boot options select Safe boot.
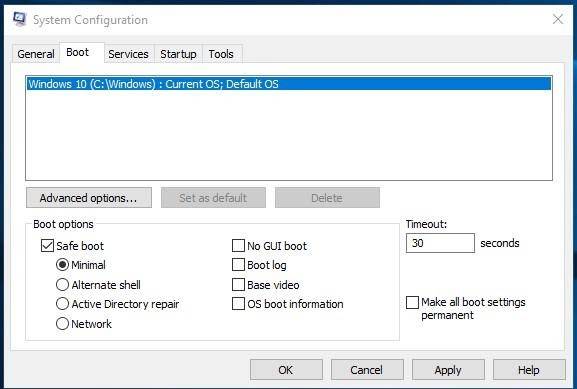
After that, the operating system will suggest restarting the computer for the changes to take effect. You can continue working with the computer without restarting, or restart it, and it will boot in Safe Mode automatically.
Method 2. Restart the computer with pressing the Shift key (Shift + Restart)
One more way to enter Safe Mode in Windows 10 is to restart the computer while holding down the Shift key.

Windows Back Up (OneDrive, File History, System Image, Recovery Disk) 💻⚙️🛡️
To do it, open the Start menu, click the Power button while holding down the Shift key and select Restart.
You can also use this key combination from the lock screen.

After that, Windows 10 will restart and suggest you to choose one of the menu items. Select Troubleshoot / Advanced options.
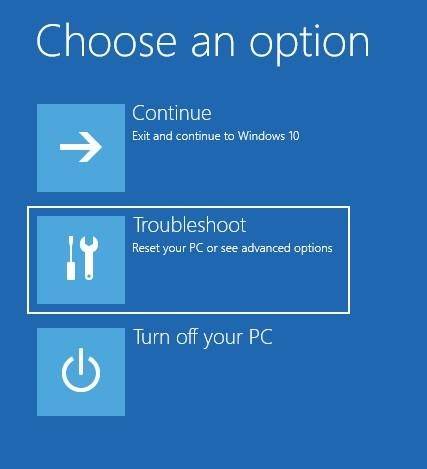
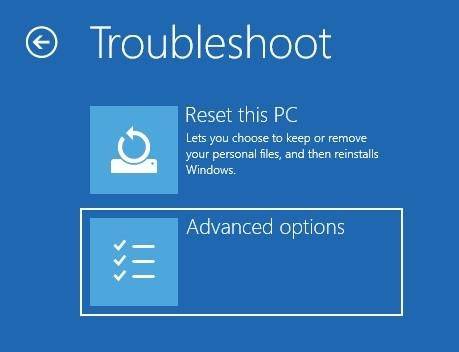
In the Advanced options window, select Startup settings

Windows 10 will notify the user that the operating system can be restarted to enable advanced options, one of which being Safe Mode. Then click on Restart.
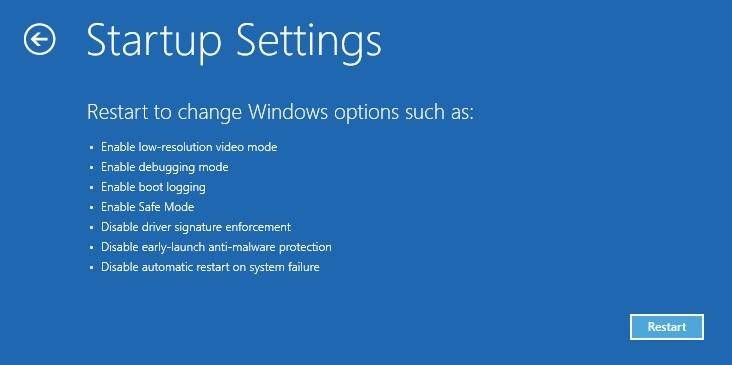
After the computer restarts, choose what settings you need to boot the operating system. To boot the system in Safe Mode there are three options (F4 – F6).

Method 3. Booting with a recovery disk
Windows 10 features a specialized tool to create recovery disks.
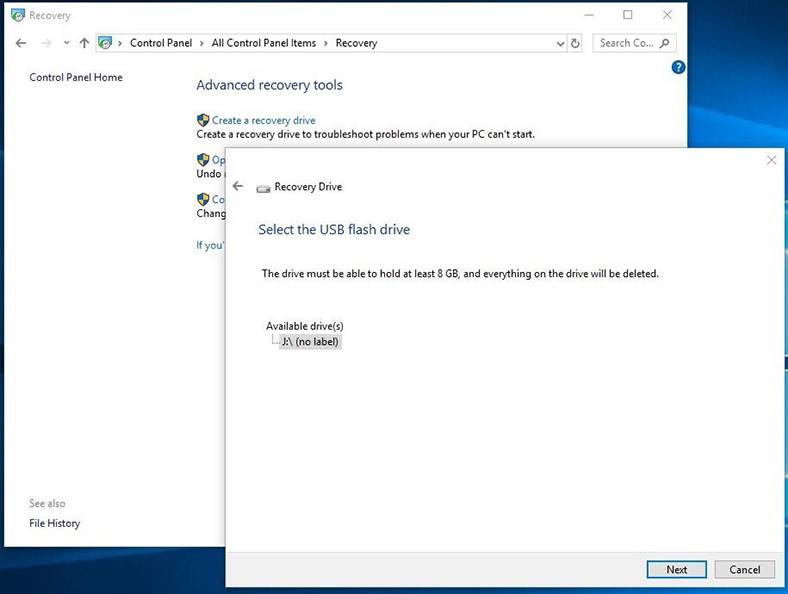
Boot Windows 10 with such a recovery disk. After that, the operating system will suggest you to select the keyboard layout, and then choose Troubleshoot / Advanced options. Further actions are similar to those described in the previous part of the article.

How to Create 💻 a Multiboot USB Drive 💽 for Windows 7, 8, 10 or Ubuntu
Method 4. Advanced Boot options
Although there are a few ways to boot Windows 10 in Safe Mode, this one would be the most correct – provided that the operating system which you need to boot in Safe Mode is fully operational.
Doing it is quite easy:
- Open Settings
- Go to Update and Security / Recovery
- In the Advanced startup section click on Restart now.
- After that, Windows 10 will restart and suggest you to choose one of the menu items. Select Troubleshoot / Advanced options.
- After that, follow the sequence of actions described in Method 2.
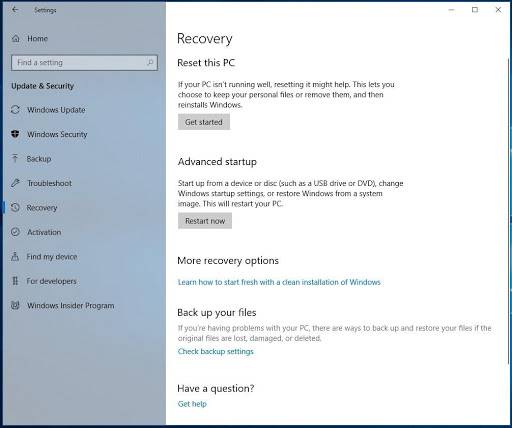
The ways of booting the operating system in Safe Mode as described here can be applied both for Windows 10 and Windows 8.1.
In these versions of Windows, Safe Mode is no longer the feature that only IT professionals use in their work. On the contrary, now it is only one of the OS features available to every user, which can be applied to restore the computer’s operability and regain access to personal data.