How to Recover Files and Folders Deleted with the Terminal (rm, rmdir, mv) in Linux?
Read this article to find out how to recover files and folders lost in Linux after deleting or relocating, or after using such Terminal commands as rm, rmdir, or mv.

- How to delete a file with Linux Terminal
- How to delete a folder with Linux Terminal
- How to recover files and folders deleted with Linux Terminal
- How to recover files and folders relocated with Linux Terminal
- Conclusions
- Questions and answers
- Comments
In Linux, files and folders can be deleted in many ways, and each of them offers a different level of control and flexibility depending on your needs. One of the most common methods is to use the rm command which provides options to delete files, directories, and even recursive removal for entire directory trees.
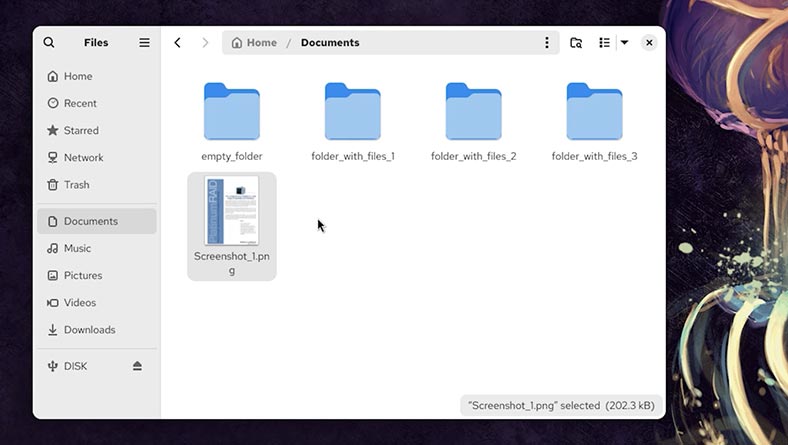
So, here’s what we’ve got:
- Files in the Documents folder (Screenshot_1.png).
- Empty folder (emty_folder).
- Folders with files (folder_with_files).
The Terminal commands and ways to recover data will be illustrated with the example of CentOS. However, they are also relevant for other versions of Linux.

How to install a data recovery tool on Linux_ with a terminal or a file manager
How to delete a file with Linux Terminal
Now I run Terminal from a specific folder and delete a certain file. Let it be an image. For this purpose, I’ll be using the command rm.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -f | Deletes files without confirmation request (force). |
| -i | Requests confirmation before removing every file. |
| -I | Requests confirmation before removing more than three files or in case of recursive deletion. |
| -r or -R | Deletes directories and their contents recursively. |
| -d | Deletes empty directories. |
| -v | Displays information about every deleted file or directory (verbose). |
| –preserve-root | Protects the root directory `/` from accidental deletion (enabled by default). |
| –no-preserve-root | Disables protection for the root directory `/`, allowing to delete it (dangerous!). |
| –help | Displays information about the command `rm`. |
| –version | Displays version of the command `rm`. |
So I type the command – rm, then follow it with the file name and its extension (type):
rm Screenshot_1.png
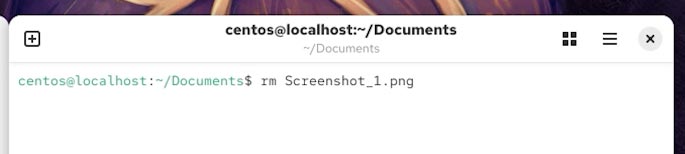
The file is deleted. And it has not landed in the Trash.
How to delete a folder with Linux Terminal
To delete an empty folder, we’ll use the command rmdir.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| --ignore-fail-on-non-empty | Ignores errors for attempts to delete directories, which are not empty. |
| -p or --parents | Deletes a specified directory, and if it becomes empty, its parent directories. |
| -v or --verbose | Displays a notification about each successfully deleted directory. |
| --help | Displays information about using the command `rmdir`. |
| --version | Displays information about the version of the command `rmdir`. |
To do it, I type the command - rmdir, and follow it with the name of the folder:
rmdir empty_folder
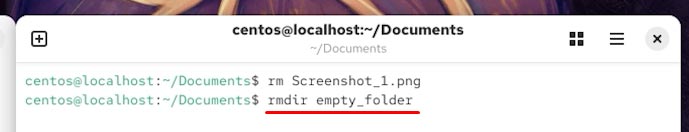
However, this command is not suitable to delete a folder with files. To delete files in a folder, you need to go to that folder and run the Terminal from there. Only then, you can delete a specific file with the help of the rm command, as we did before.
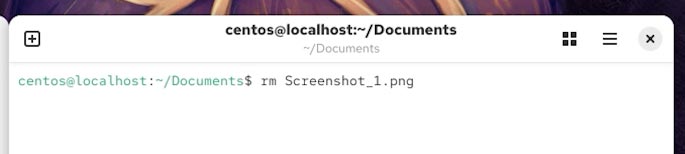
Otherwise, to delete all files from a directory, that is, to clean its contents, type the following:
rm folder_with_files_1/*
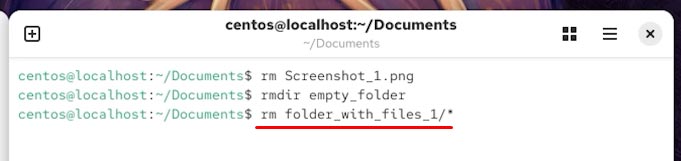
If you want to delete a folder with all of its contents, use the command rm with the option -r (recursively).
rm -r folder_with_files_2
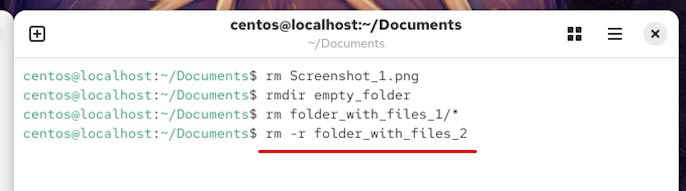
Now we have deleted a file from the Documents folder, cleaned the contents of one folder, and deleted one folder completely, together with its contents. All these files and folders cannot be found in the Trash. So how can we recover them?
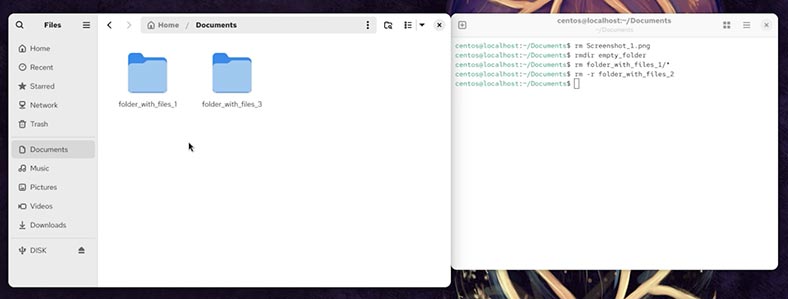
How to recover files and folders deleted with Linux Terminal
Folders deleted with the rmdir command, as well as directories and their contents deleted with the rm command never end up in the Linux Trash folder. That is why it is believed that they can’t be recovered.
Let’s try recovering such files and folders with a good data recovery tool - Hetman Partition Recovery.
-
Run Hetman Partition Recovery;
-
Click on the disk where this data used to be stored;
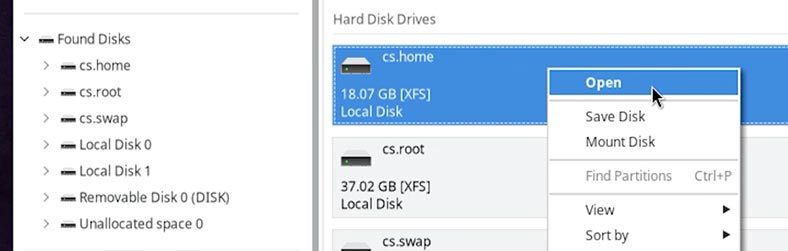
-
Choose the scan type. For starters, a Fast scan will be enough.
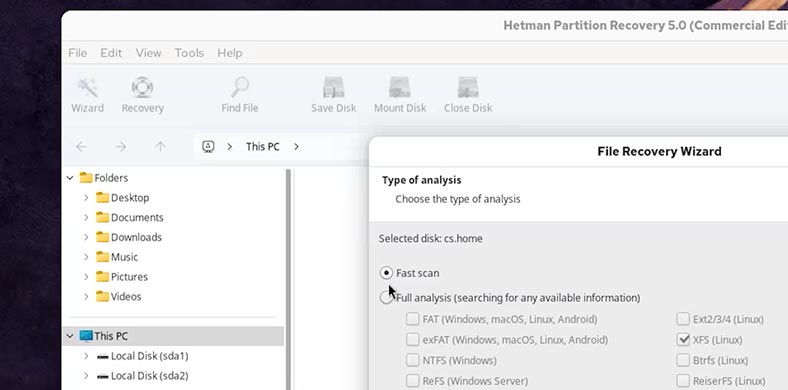
-
When the scan is over, click Finish;
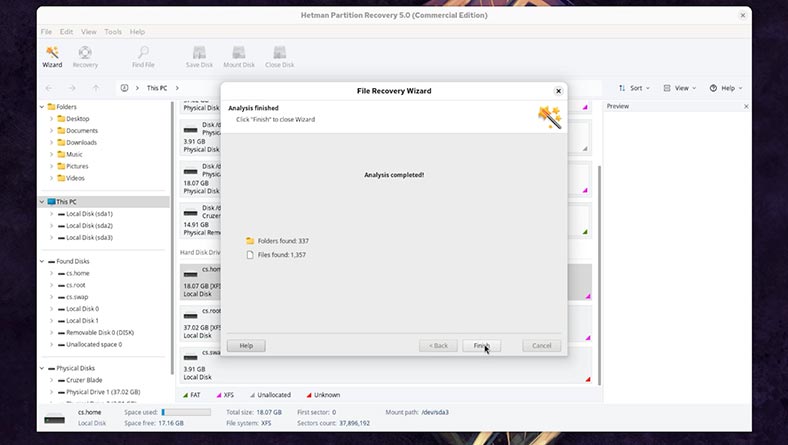
-
The program has found our files:
- The files in the Documents folder
- Empty folder.
- Folders with files.
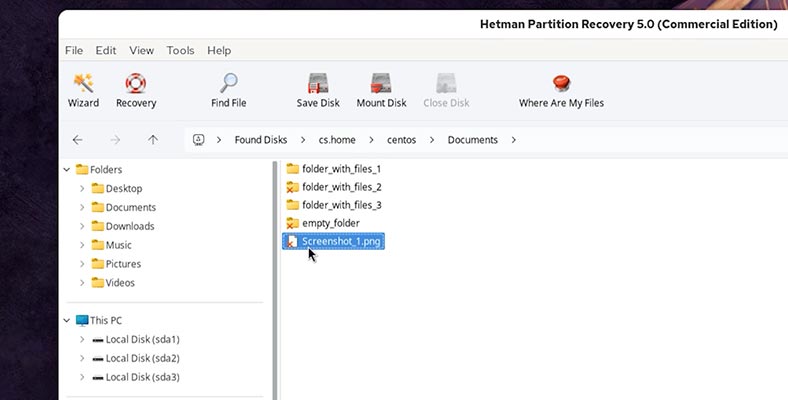
-
We can also view the files in the preview window.
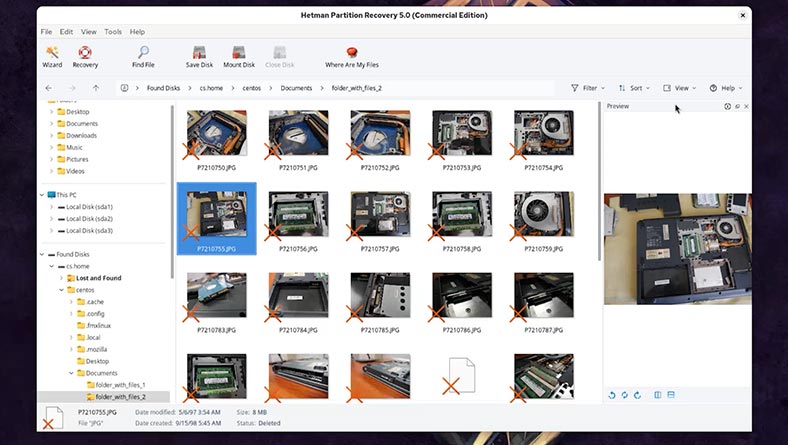
-
To have the files restored, select them and hit the Recovery button;
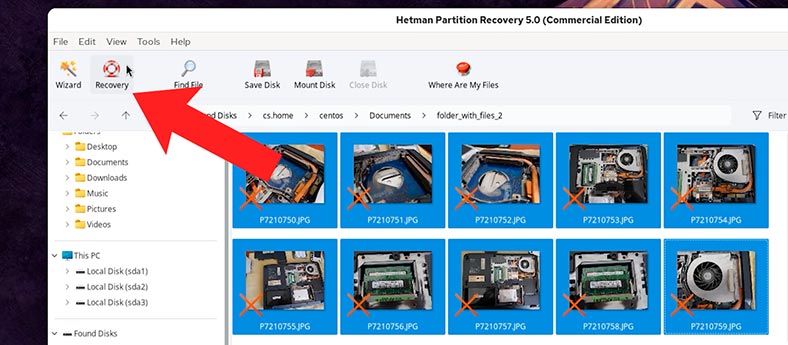
-
Choose the method to save them;
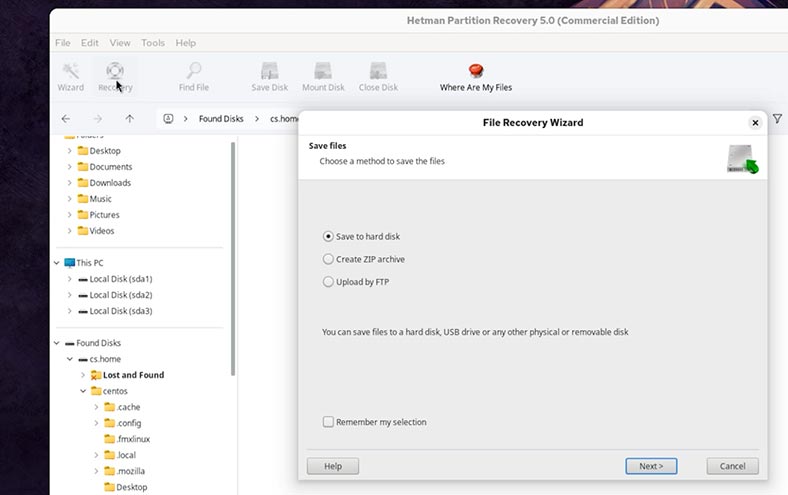
-
Next;
-
Select the folder where to save them;
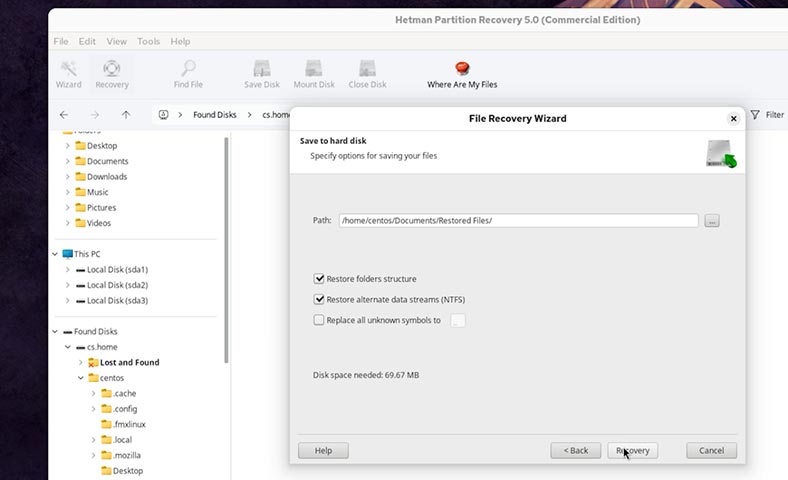
-
Recovery.
-
When the operation is complete, all files will be placed into the folder you have chosen.

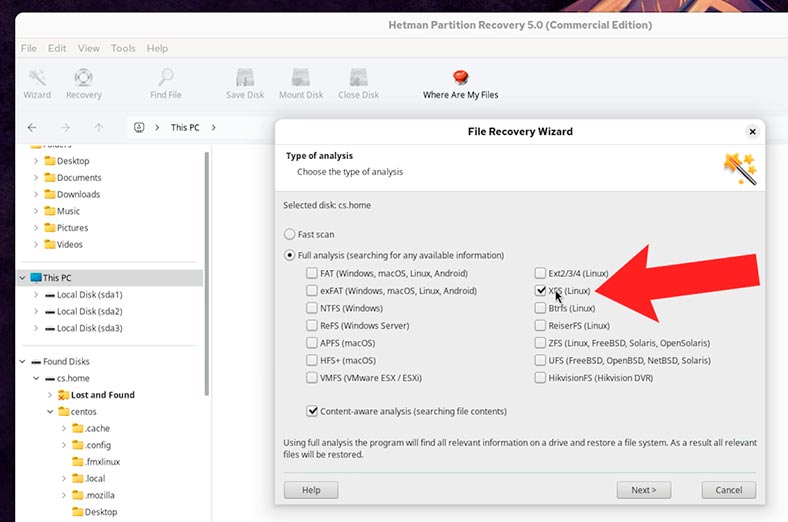
If the files were deleted a long time ago, and it is only now that you realize they are missing, or if the program couldn’t find the necessary data during Fast scan, then scan the disk using Full analysis.
To do it:
- Right-click on the required disk;
- Choose Analyze again.
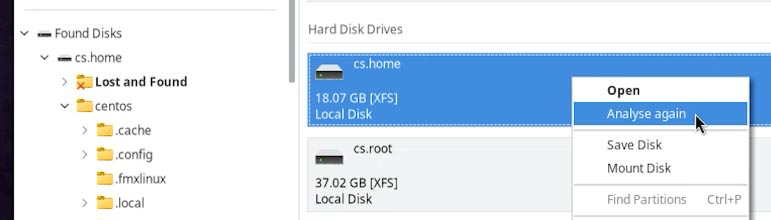
As a rule, the program identifies the file system of the disk automatically. However, if you need to know the file system used for a specific disk, go to the Disks utility to find this information.
How to recover files and folders relocated with Linux Terminal
I’d like to add a few words about the feature to relocate files and folders in Linux.
The mv command in Linux operating systems is used to move - or rename - files and folders.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -b | Backs up a file before relocating or renaming it. |
| -f | Forcibly replaces the existing files without confirmation request. |
| -i | Requests confirmation before overwriting an existing file. |
| -n | Prohibits overwriting for existing files. |
| -u | Relocates a file only if the source file is newer than the target file, or if the target file is missing. |
| -v | Displays information about every step of the process (detailed output mode). |
| --backup | Backs up a file before overwriting it. |
| --suffix=suffix | Determines the suffix for a backup (by default `~`). |
| --strip-trailing-slashes | Removes final slashes (`/`) from file names. |
| --target-directory=directory | Indicates the target directory for file relocation. |
| --no-clobber | The same as `-n`, doesn’t overwrite the existing files. |
| --verbose | The same as `-v`, displays information about actions of the command. |
To relocate a folder, type a special command. For example, let’s put the folder onto a USB stick:
mv folder_with_files_3 /media/ubuntu/USB
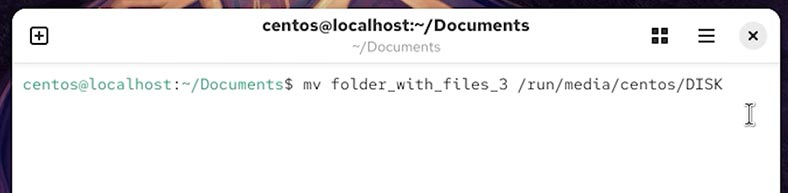
Disconnect the USB stick from the computer. Now the folder with files is lost.
Run Hetman Partition Recovery;
-
Click on the disk where this folder used to be stored;
-
Choose the scan type. For starters, a Fast scan will be enough.
-
When the scan is over, click Finish;
-
The program has found our folder and marked it as deleted.
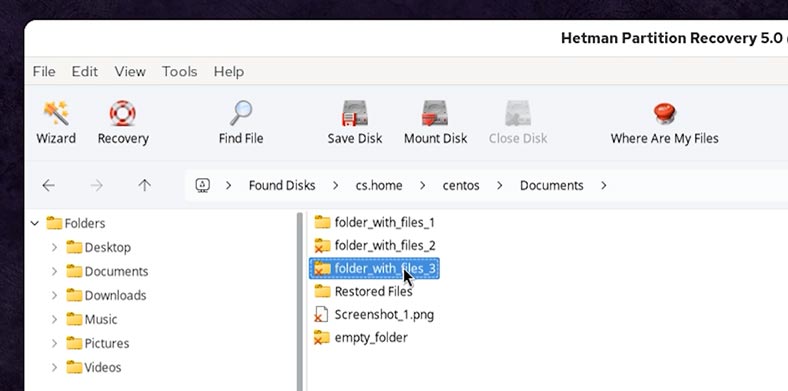
That is, files and folders lost as a result of moving them, can also be recovered.
Conclusions
Deleting files in Linux is a powerful process, and errors can result in data loss. Before using commands, make sure you have given the correct path to a folder, and important files won’t be affected.
Choosing the suitable way of deleting depends on a specific scenario, and it is always important to assess risks related to each method.