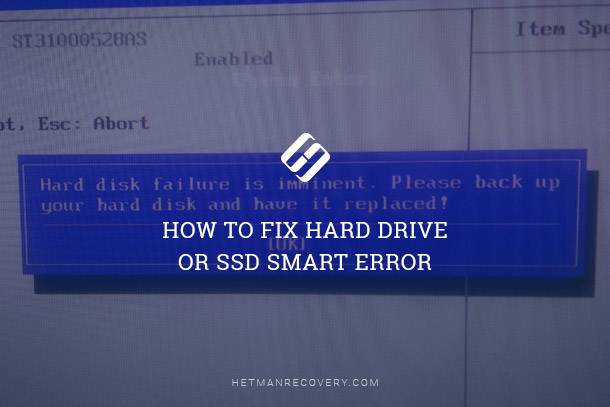
Hard Drive or SSD SMART Error: Troubleshooting
Learn how to troubleshoot and fix SMART errors on your HDD or SSD with this comprehensive guide. Whether you’re encountering warnings about imminent drive failure or facing performance issues, this tutorial covers everything you need to know. Dive deep into step-by-step instructions and essential tips for resolving SMART errors and ensuring the reliability of your storage devices.
Acceptable values of the SMART attribute may differ depending on the hard disk manufacturer – WD (Western Digital), Samsung, Seagate, HGST (Hitachi) or Toshiba.
- What should you do with error?
- How Can You Reset SMART Error?
- Is It Worth Repairing an HDD?
- SMART Error In an SSD
- Questions and answers
- Comments
Actual for Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012, Windows 8, Windows Home Server 2011, Windows 7 (Seven), Windows Small Business Server, Windows Server 2008, Windows Home Server, Windows Vista, Windows XP, Windows 2000, Windows NT.
| Error Code | Error Name | Error Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | “Reallocated Sectors Count” Error | This error is related to sector reassignment when a disk sector becomes defective and data is moved to a spare sector. It may indicate the beginning of a hard disk failure. |
| 5 | “Reallocated Event Count” Error | Indicates the number of reassigned sectors that were replaced. If the value increases, it may suggest problems with the disk surface. |
| 7 | “Seek Error Rate” Error | Indicates errors when seeking data on the disk. Problems with this error can lead to failed read and write attempts, which may suggest issues with the mechanical parts of the device. |
| 9 | “Power-On Hours” Error | Indicates the number of hours the device has been running since it was powered on. This can help assess the device’s lifespan. |
| 10 | “Spin Retry Count” Error | Occurs when the disk cannot start spinning or has problems with retrying the start. It may indicate issues with the motor or other mechanical parts. |
| 11 | “Temperature” Error | Indicates the temperature of the hard disk. High temperatures can lead to rapid wear of the device. |
| 12 | “Power Cycle Count” Error | Indicates the number of power cycles the device has gone through. This value is important for understanding the device’s usage intensity. |
| 187 | “Reported Uncorrectable Errors” Error | Indicates the number of uncorrectable errors that occurred when reading data. If this error repeats frequently, the disk may be failing. |
| 188 | “Command Timeout” Error | Relates to the timeout of a command, which may indicate performance issues or firmware corruption in the disk. |
| 194 | “Temperature” Error | Reports the device’s temperature. High temperatures can lead to overheating and failure. |
What should you do with error?

How to Check Your Hard Disk for Errors and Fix Them in Windows 10 🔎🛠️🗄️
Step 1. Stop Using The Faulty HDD
If you receive a system message about an error diagnosed, it doesn’t mean the disk is out of order already. However, in case of a S.M.A.R.T. error, you should realize the disk is on the way to its breakdown. It can fail completely anytime – both within several minutes or in a month or even in a year. Anyway, it does mean you cannot trust to keep your data there.
You should take some care about the safety of your data, make a backup copy or transfer files to another media. Along with these actions meant to save your data, you should also replace your hard disk. The disk where S.M.A.R.T. errors were found cannot be used – even if it doesn’t break down completely, it can still damage your data partially.
Of course, a hard disk can fail even without showing any S.M.A.R.T. messages, but this technology gives you a certain advantage of warning you about the coming breakdown problem.
Step 2. Restore The Deleted Data From The Disk

How to Recover Data from an Unallocated Area in a Hard Disk, USB Pen Drive or Memory Card 👨🔧🛠️🖥️
If there is a SMART error, restoring data from the disk is not always necessary. In case of an error, it is recommended to create a backup copy of important information immediately, because now the disk can fail completely at any time. However, there are errors that make data copying impossible. In this case, you can use special hard disk data recovery software – Hetman Partition Recovery.
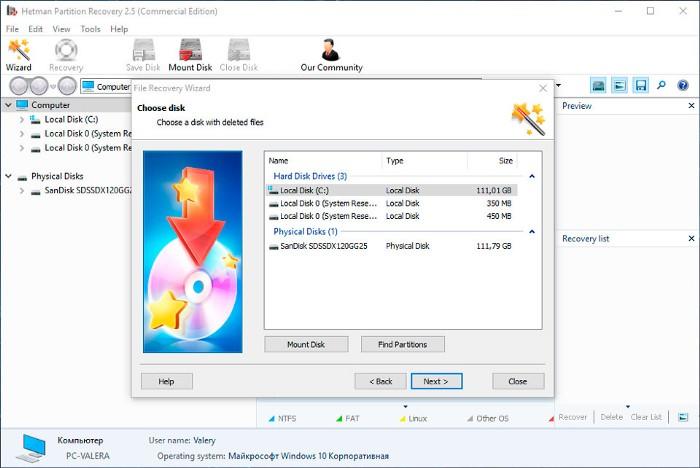
To do it:
- Download the program, install and launch it.
- By default, you will be suggested to use File Recovery Wizard. After clicking Next the program will suggest you to choose a disk to recover files from.
- Double-click on the faulty disk and choose the type of analysis. Select Full analysis and wait for the scanning process to finish.
- After the scanning process is over you will be shown files for recovery. Select the necessary files and click Recover.
- Select one of the suggested ways to save files. Do not save the recovered files to the disk having an error.
Step 3. Scan The Disk For Bad Sectors

How to Repair Bad Sectors on Hard Drive in 2020 with HDD Regenerator ⚕️💻👨💻
Start scanning all partitions of the disk and try correcting any mistakes that are found.
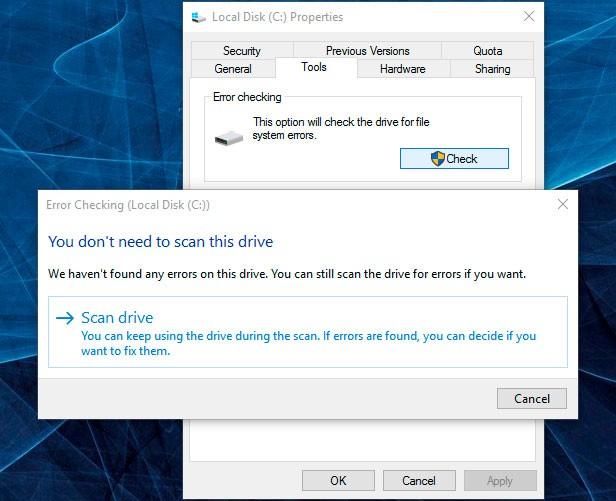
To do it, open This PC and right-click on the disk with a SMART error. Select Properties / Tools / Check in the tab Error checking.
Errors found on the disk as a result of scanning can be corrected.
Step 4. Reduce The Disk Temperature

How to Check the Processor (CPU), Video Card (GPU) or Hard Disk (HDD) Temperature 🌡️ 💻 💊
Sometimes a SMART error can be caused by exceeding the maximum temperature of the disk. This problem can be eliminated by improving the case ventilation. First of all, make sure that your computer has sufficient ventilation and that all coolers are in proper working order.
If you found and eliminated the ventilation problem, which helped to bring the disk temperature back to normal, this SMART error can never appear again.
Step 5. Run Hard Disk Defragmentation

How to Defragment Your PC's Hard Drive on Windows 10 🛠️🗄️⏲️
Open This PC and right-click on the disk having an error. Select Properties / Tools / Optimize in the tab Optimize and defragment drive.
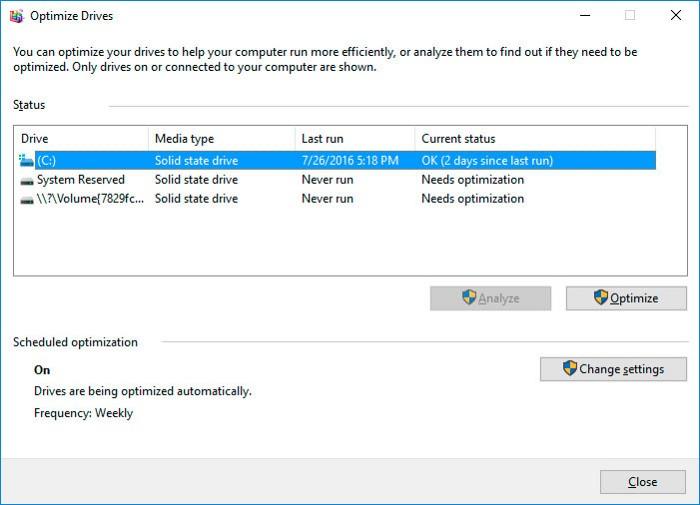
Select the disk you need to optimize and click Optimize.
Note. In Windows 10 disk defragmentation and optimization can be adjusted to take place automatically.
Step 6. Buy a New Hard Disk
If you encounter a hard disk SMART error, then buying a new HDD is only a matter of time. The disk type you need depends on how you work on the computer and the purposes you use your computer for.
Here are some points to consider when buying a new hard disk:
- Disk type: HDD, SSD или SSHD. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages which may be unimportant for one user and crucial for another. These are read and write speed, capacity and tolerance to multiple overwriting.
- Size. There are two main form factors for hard disks, 3.5 inch and 2.5 inch. The size of disks is determined in accordance to the slot in a particular computer or laptop.
- Interface. The main interfaces of hard disks are as follows:
- SATA;
- IDE, ATAPI, ATA;
- SCSI;
- External Disk (USB, FireWire etc).
- Technical characteristics and performance:
- Capacity;
- Read and write speed;
- Memory cache size;
- Response time;
- Fail safety.
- S.M.A.R.T. Availability of this technology in the disk will help determining possible mistakes in its work and prevent loss of data before it is too late.
- Package. This item can include interface or power cables as well as warranty and service options.
How Can You Reset SMART Error?
SMART errors can be easily reset in BIOS (or UEFI) but all OS developers strongly discourage users from this step. Yet if the data on the hard disk is of little importance for you, displaying SMART errors can be disabled.
Here is the procedure to follow:
- Restart the computer, and use combinations of keys shown on the loading screen (they depend on a specific manufacturer, usually F2 or Del) to go to BIOS (or UEFI).
- Go to Аdvanced > SMART settings > SMART self test. Set the value as Disabled.
Note: The place where you disable the function is given approximately, because its specific location depends on the version of BIOS or UEFI and can differ slightly.
Is It Worth Repairing an HDD?
It is important to realize that any of the ways to eliminate a SMART error is self-deception. It is impossible to completely remove the cause of the error, as it often involves physical wear of the hard disk mechanism.
To replace the hard disk components which operate incorrectly you can go to a service center or a special laboratory dealing with hard disks.
However, the cost of work will be higher than the price of a new device, so it is justified only when you need to restore data from a disk which is no longer operable.
SMART Error In an SSD
Even if you have no problems with an SSD performance, its operability is reducing slowly because SSD memory cells have a limited number of overwrite cycles. The wear resistance function minimizes this effect but never takes it away completely.
SSD disks have their specific SMART attributes which send signals about the state of disk memory cells. For example, “209 Remaining Drive Life,” “231 SSD life left” etc. Such errors may occur when memory cell operability is reduced, and it means the information kept there can be damaged or lost.
In case of failure, SSD cells cannot be recovered or replaced.
Is the error fixed now? Leave your feedback and ask questions in your comments.