Choosing the Right Memory Card: A Comprehensive Review of SD Card Formats and Classes
This article provides a comprehensive review of SD card formats and classes to help you make an informed decision. From SDHC to microSDXC, we’ll explore the differences between various formats and their compatibility with different devices. Dive deep into understanding SD card classes and their impact on read and write speeds, essential for capturing high-quality photos and videos. Whether you’re a photographer, videographer, or simply looking to expand your device’s storage capacity, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to select the perfect memory card for your needs.

In this article we would like to have a look at the most frequently asked questions regarding SD cards and choice of cards for various gadgets – a tablet, a camera, a video camera or a phone. We believe this information will be useful for the wide range of our readers.
- Step 1. Memory card dimensions
- Step 2. Speed or class of SD cards
- Step 3. Memory card generations
- Step 4. How to check the real capacity and class of a memory card
- Step 5. Choosing a memory card for a tablet PC
- Step 6. Choosing a memory card for a camera/video camera
- Questions and answers
- Comments

How to Recover Files from the Memory Card of Your Camera, Phone, Video or Dashboard Camera 📁🔥⚕️
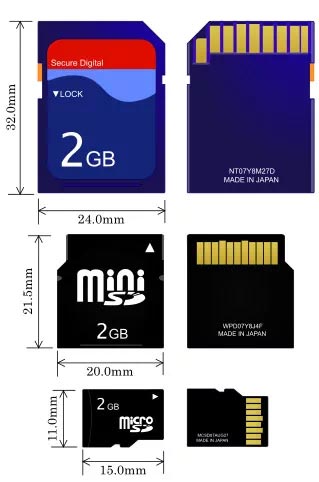
Step 1. Memory card dimensions
Memory cards are produced in three types of dimensions:
- MicroSD: a very popular card type used in smart phones, tablets and other portable devices. The dimensions are 11x15mm;
- MiniSD: a less popular card type often met in mp3 players. The dimensions are 21,5x20mm;
- SD: probably the most popular one used in cameras, video cameras, recording units and other devices. Almost all modern laptops and computers are equipped with card readers that work with this card type. The dimensions are 32x24mm.
| Feature | microSD | miniSD | SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size | 11mm x 15mm x 1mm | 20mm x 21.5mm x 1.4mm | 24mm x 32mm x 2.1mm |
| Storage Capacity | Up to 1TB+ | Up to 16GB | Up to 2TB+ |
| Use Cases | Smartphones, tablets, drones, cameras | Older mobile devices, cameras | Digital cameras, camcorders, laptops |
| Adapter Required | Yes (for SD/miniSD slots) | Yes (for SD slots) | No (direct SD slot compatibility) |
| Durability | Compact and robust | Moderate | High |
| Backward Compatibility | Compatible with SD via adapter | Compatible with SD via adapter | Native to SD slots |
| Cost | Generally affordable, varies by size | Less common, limited production | Widely available, varies by size |
Important notice! In spite of having an adapter supplied together with, for example, a MicroSD card, it is not recommended to use this set of two devices instead of a regular SD card. The matter is that MicroSD cards are usually slower than SD cards which means that a MicroSD card connected to a video camera through an adapter cannot be used to record video in Full HD. That is why the card type should be selected in accordance with requirements of your device manufacturer.

Step 2. Speed or class of SD cards
This is a very important parameter for any memory card. It is because speed influences not only the price but also the range of devices where such card can be used.
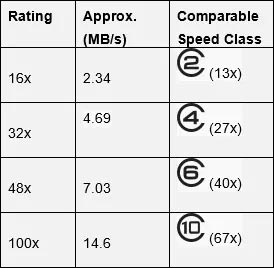
The speed characteristics of a memory card are usually marked by a rating and/or a digit that shows you memory card class. Ratings correspond with the Read mode speed. The Write mode speed is usually two or more times lower and it is determined by the card class.
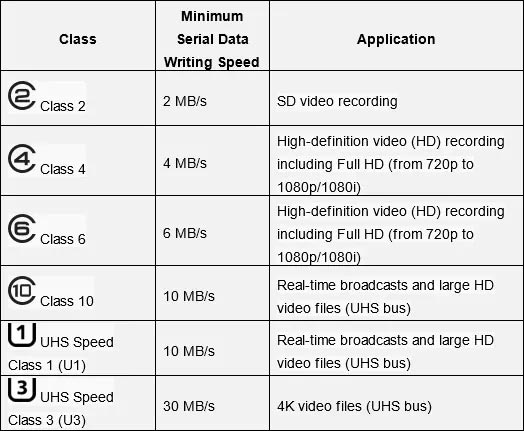
By the way, rating and card class are interrelated.
Manufacturers may use different ways to mark their cards. For example, the picture below shows a Class 4 memory card – according to the table above, its speed is 4 MB/s.

Some manufacturers also specify the speed in addition to the class.
I would like to point to one more detail again. When buying a memory card make sure you know what class your device requires for normal operation.
Step 3. Memory card generations
There are four generation of memory cards:
They differ in capacity, speed and are backward-compatible with each other.
| Feature | SD 1.0 | SD 1.1 | SDHC | SDXC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Release Year | 1999 | 2001 | 2006 | 2009 |
| Capacity | Up to 2 GB | Up to 2 GB | 4 GB to 32 GB | 32 GB to 2 TB |
| File System | FAT16 | FAT16 | FAT32 | exFAT |
| Max Read/Write Speed | 12.5 MB/s (Standard) | 12.5 MB/s (Standard) | 25 MB/s (Class 2, 4, 6, 10) | 50 MB/s to 300 MB/s (UHS-I, UHS-II, UHS-III) |
| Voltage | 3.3V | 3.3V | 3.3V or 1.8V | 3.3V or 1.8V |
| Form Factor | Standard SD Card | Standard SD Card | Standard SD Card (Same as SD 1.0/1.1) | Standard SD Card (Same as SD 1.0/1.1) |
| SD Bus Interface | Default SD Mode (1-bit) | Default SD Mode (1-bit) | UHS-I (High-speed mode 1-bit or 4-bit) | UHS-I/II/III (High-speed, 1-bit/4-bit) |
| Backward Compatibility | N/A | Compatible with SD 1.0 | Compatible with SD 1.0/1.1 (not all) | Not directly compatible with SD 1.0/1.1/SDHC |
| Common Uses | Basic storage in early devices | Basic storage in early devices | Cameras, smartphones, and other portable devices | High-capacity storage in cameras, video recorders, gaming, etc. |
| Physical Size | 32mm x 24mm x 2.1mm | 32mm x 24mm x 2.1mm | 32mm x 24mm x 2.1mm | 32mm x 24mm x 2.1mm |
There is an important aspect, though: A device that can read SDHC cards, will read SD 1.1 and SD 1.0 cards as well, but will not “see” a SDXC card.
Step 4. How to check the real capacity and class of a memory card
Sometimes there are no symbols or letters on a memory card, so you don’t know its real capacity or class without testing. Luckily, there are a lot of special utilities to test memory cards.

How to Unlock a Write Protected USB Drive, a SD or Micro SD Memory Card or a Hard Drive 👨💻🛠️🖥️
Step 5. Choosing a memory card for a tablet PC
In the present-day market, most tablets feature built-in memory and support memory cards. Yes, there are still tablets supporting SDHC cards (up to 32 GB), but they are not too numerous, and most tablets work with SDXC cards.
If you’re not going to record HD video (or you have a low definition camera) then your tablet will work correctly even with a Class 4 card. However, if you have plans for videos, I recommend choosing a Class 6 or Class 10 memory card. As a rule, the real difference between Class 6 and 10 performances is not so big to pay more.
Step 6. Choosing a memory card for a camera/video camera
In this case, you should be more careful. The matter is that if you use a memory card of a class lower than required by the device it may work with some problems, and you can forget about recording good quality videos.
Finally, some advice for you: go to your camera manufacturer’s official website and find the user manual there. In the manual, there must be a page entitled Recommended memory cards (i.е. SD cards that the manufacturer has tested!).
When choosing a memory card pay attention to the manufacturer. We are not going to choose the best from the best now but we recommend buying cards by well-known brands only.
Using memory cards with characteristics recommended by device manufacturers and produced by well-known brands that take care of their reputations and the quality of their products will secure you from many possible issues. These can include instable work of your device and the subsequent risk of losing important data from the memory card.
If you need to recover data from memory cards, we recommend using Hetman Partition Recovery.

How to Recover Cr2, RAW, NEF, CRW Photos after Deleting or Formatting 📷⚕️👨💻








