How to Recover Data in Linux After Formatting a Hard Disk, USB Stick or Memory Card?
Read this article to find out how to recover data lost after formatting a hard disk, USB stick or memory card in Linux.
- How to format a disk in Linux
- Erase/overwrite feature in Linux
- Recovering Linux data after formatting
- Conclusions
- Questions and answers
- Comments
When any storage device is formatted, a part of the information about the location of data on the disk is erased. However, in most cases data recovery after formatting is still possible. Your chances for success depend on the file system type, type of data, and the number of files. Another factor is what information and how much of it was written to the disk after it was formatted.
WARNING!!! You shouldn’t write anything or do other things to your freshly formatted disk since it will greatly reduce your chances for recovery!
In this article, we will explore data recovery methods with the example of Mint, but everything is relevant for other versions of Linux as well (Ubuntu, CentOS, Fedora, Debian, and so on.)

How to Recover Files After Emptying Linux Trash or Using Shift + Del
How to format a disk in Linux
Suppose we have a disk containing some data.
Go to the Disks tool to see that the disk is healthy and has the file system – ext4, xfs, or btrfs.
In fact, it doesn’t matter, what file system is used for your disk. The sequence of actions described in this article will work for all Linux file systems, and soon you will understand why.
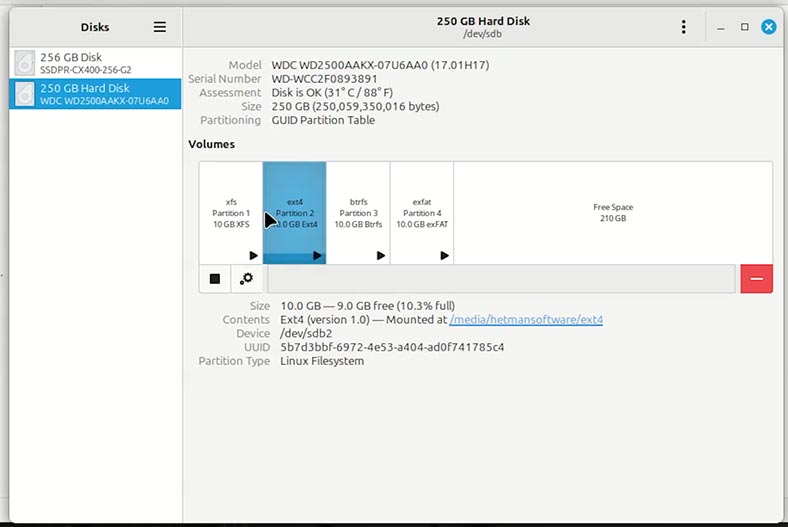
Let’s format the disk in any way you find convenient:
Method 1. With the Terminal.
Type the following command to display the list of all disks and partitions. You can identify the required disk by its size or name, or by its file system.
lsblk –fs
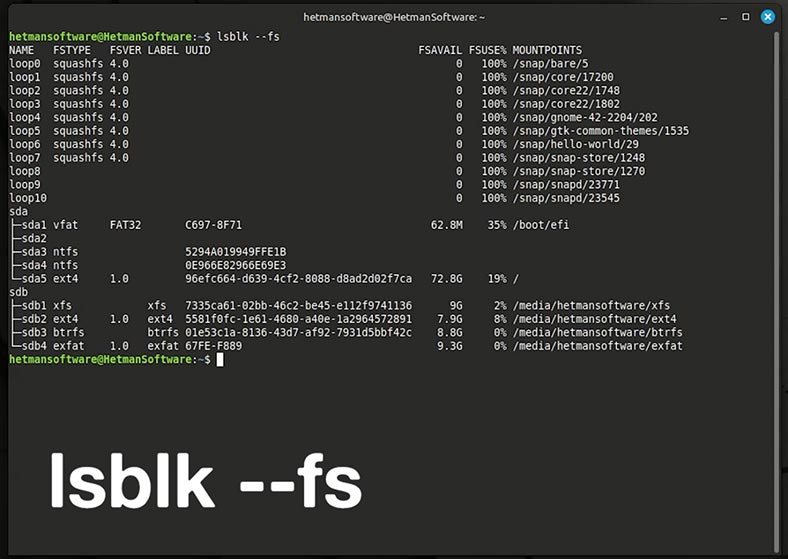
Now you need to unmount the disk if it’s active. Use this command to help you do it:
sudo umount /dev/sdb2
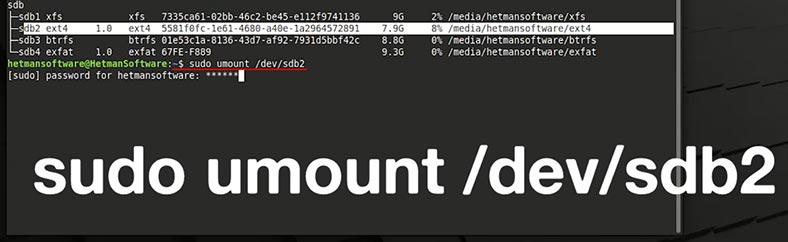
Now format the data storage device in the required file system:
sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb2
where,
- ext4 - the file system;
- /dev/sdX – the disk to be formatted.
| Command /Utility | Purpose | Example of usage | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| mkfs | A general command to create file systems | mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdX1 | used with various file system types |
| mkfs.ext4 | Create EXT4 file system | mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdX1 | The most popular file system on Linux |
| mkfs.ntfs | Format into NTFS | mkfs.ntfs /dev/sdX1 | You need to install the package ntfs-3g |
| mkfs.vfat | Format into FAT32 | mkfs.vfat /dev/sdX1 | Compatible with Windows and most devices |
| mkfs.xfs | Create XFS file system | mkfs.xfs /dev/sdX1 | Suitable for large volumes |
| mkfs.btrfs | Format into Btrfs | mkfs.btrfs /dev/sdX1 | Modern file system with snapshot support |
| parted | Disk formatting and partitioning | parted /dev/sdX mklabel gpt | Supports both GPT and MBR |
| fdisk | Text-mode partitioning (MBR) | fdisk /dev/sdX | Used to create and delete partitions |
| gparted | Graphical disk management utility | — | Needs to be installed separately (apt install gparted) |
| disks (GNOME Disks) | Graphical and convenient utility | — | Suitable for novice users |
Method 2. With specialized software tools.
For example, Gparted or KDE Partition Manager.
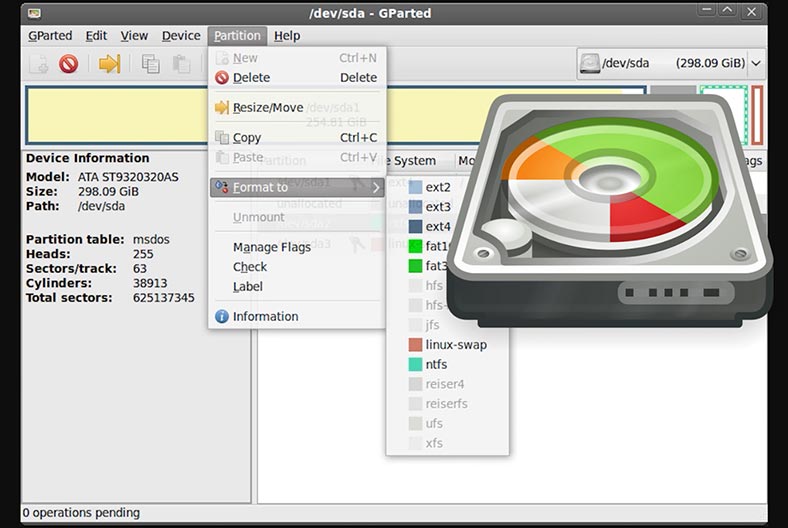
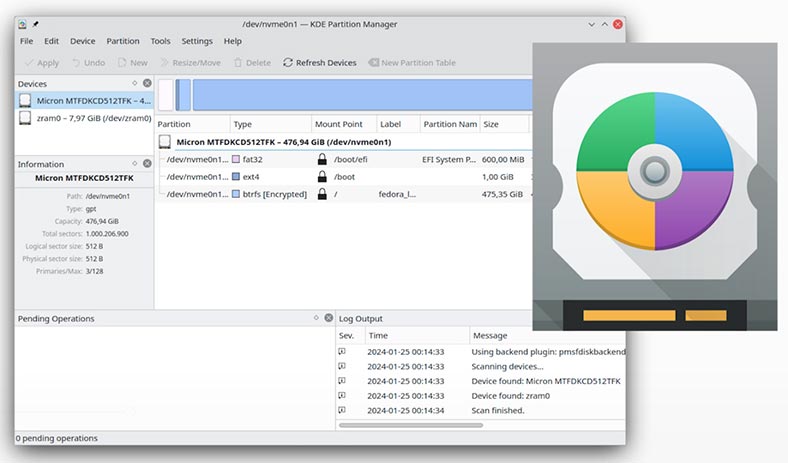
Method 3. With the graphic interface of your system, or with the Disks tool.
If you don’t erase the disk, USB stick or memory card, then your data can be recovered with the same effectiveness regardless of which method you decided to use.
Click on the disk settings menu and choose Format.
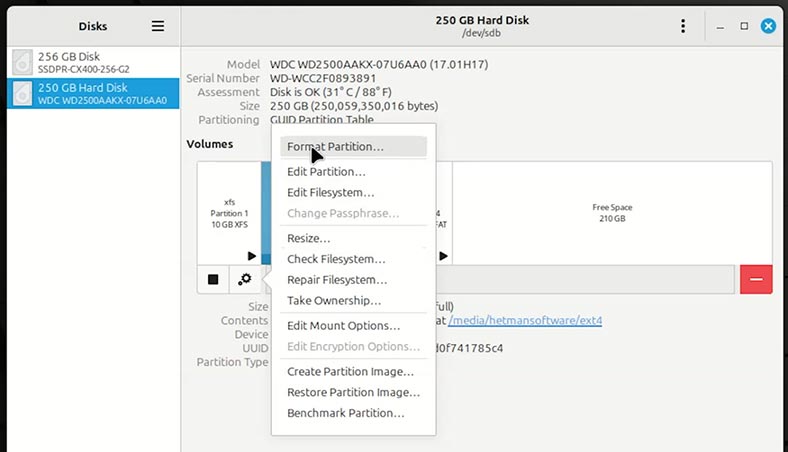
Erase/overwrite feature in Linux
Pay attention to the erase/overwrite feature when formatting your disk.
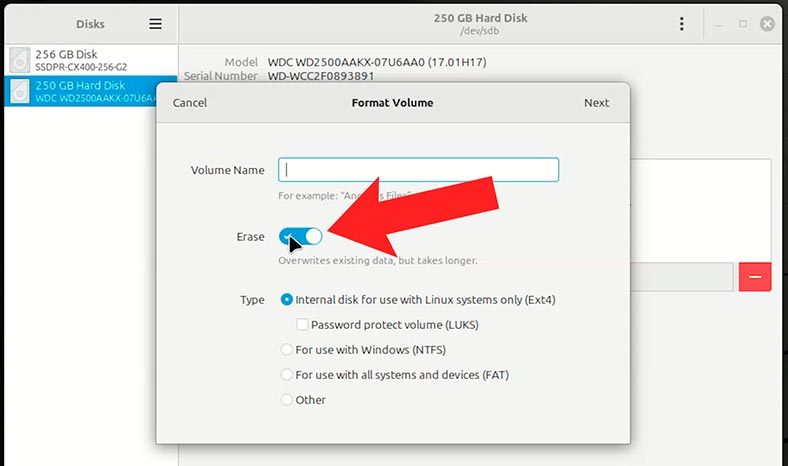
If you don’t enable this option, only the file allocation table will be overwritten. The files themselves will be intact. The operating system will just label them as deleted. After such method, recovering information from the disk won’t be difficult.
But if you enable the Erase feature, it will overwrite all disk data while formatting the storage device. In this case, there’s no guarantee that data recovery can be successful.
Recovering Linux data after formatting
Choose the format type and file system.
As you can see, the disk has been formatted, while its files and folders are removed. What shall we do now?
Run Hetman Partition Recovery:
-
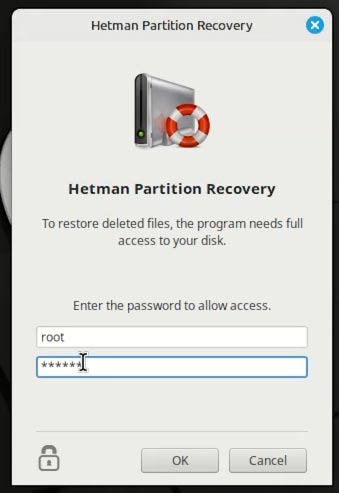
The app will ask you for the root user password. Enter it.
-
Choose your disk.
You can identify the required disk by its size or name, or by its file system.
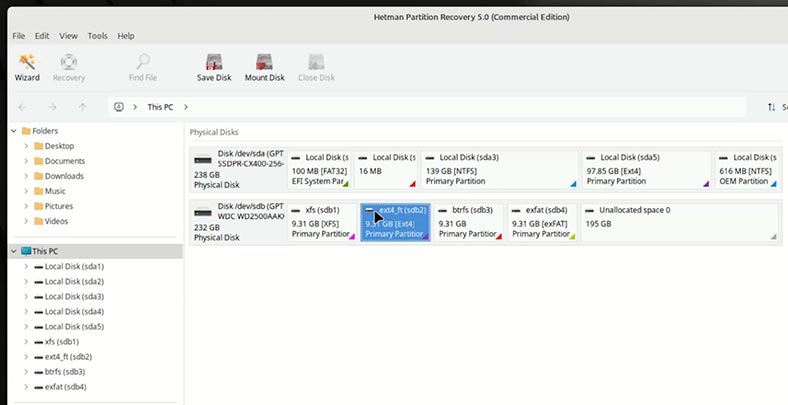
-
Select Full analysis and specify the file system.
Fast scan is not suitable to recover data after formatting a hard disk, USB stick, or memory card.
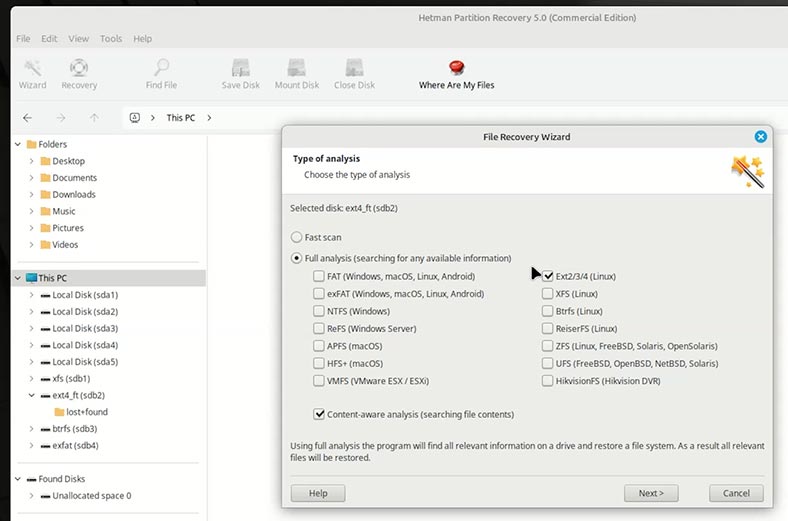
-
As you can see, the recovery tool can deal with almost any file system. That is why we mentioned before that the file system of the formatted disk does not matter. Data in different file systems is actually recovered in the same way.
-
You can see the file system of your disk in the tool itself, or in the Disks utility. However, the recovery tool tends to properly identify the file system of the disks it works with.
-
When the scan is over, click Finish.
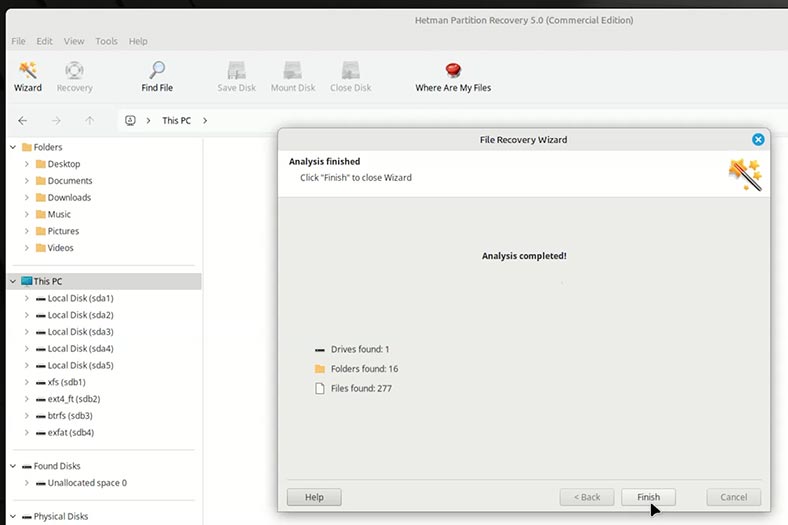
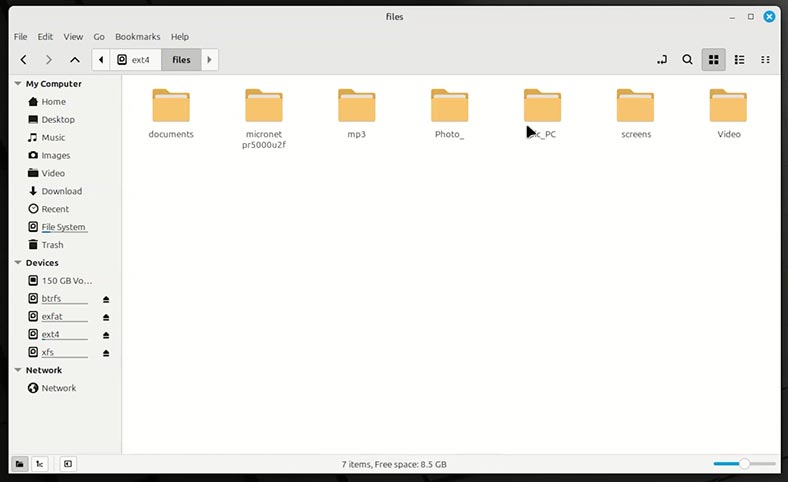
Now you can see the recovery tool has created two folders.
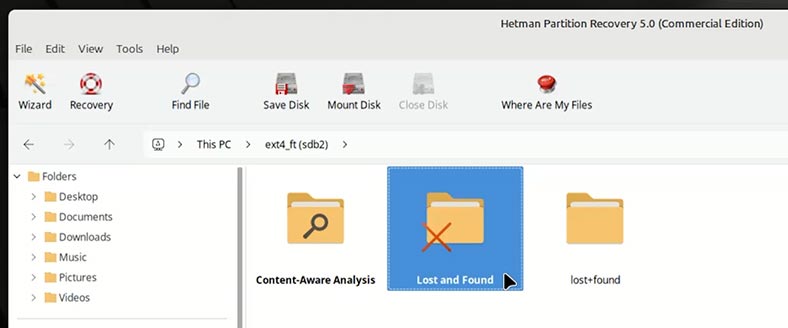
In one of them, you can find the same number of folders that have been lost as a result of formatting.
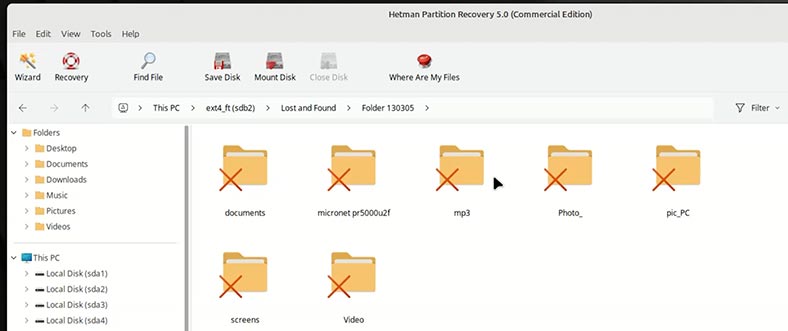
Inside the folders, there are your files.
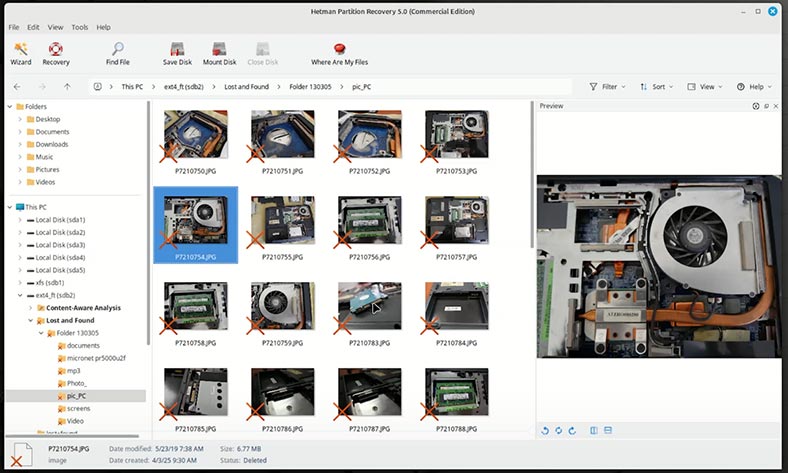
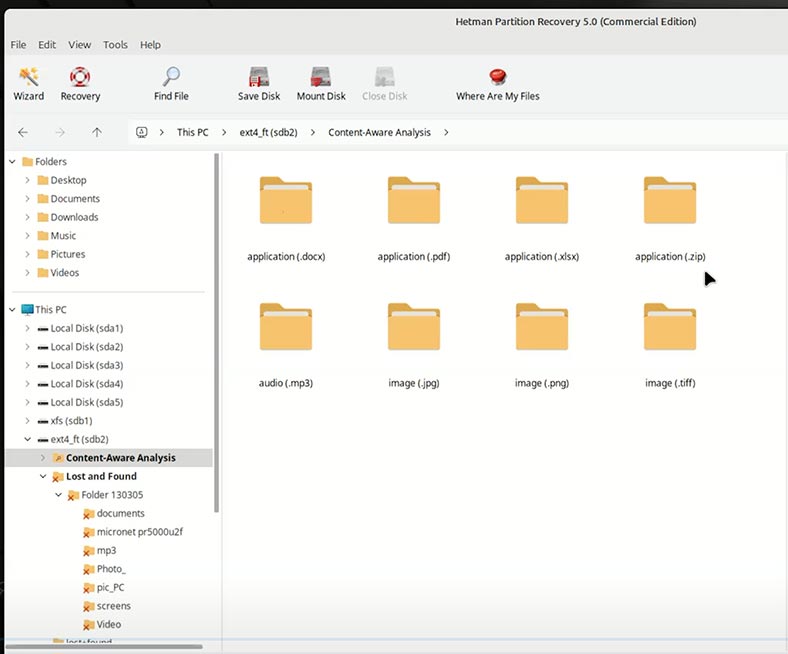
In the other folder (Content-Aware Analysis), there are files that have been found by analyzing the contents of files. They are sorted by type.
In both folders, you can preview the files.
If you’re looking for a specific file of a specific format, then it’s more convenient to find it in Content-Aware Analysis folder. If you need to recover contents of a certain folder, then go to the folder named Lost and Found.
If a partition is formatted in a different file system, or even deleted, the recovery tool will also display the partition with the previously existing file system. In this case, select a particular disk with the file system from which data should be recovered.
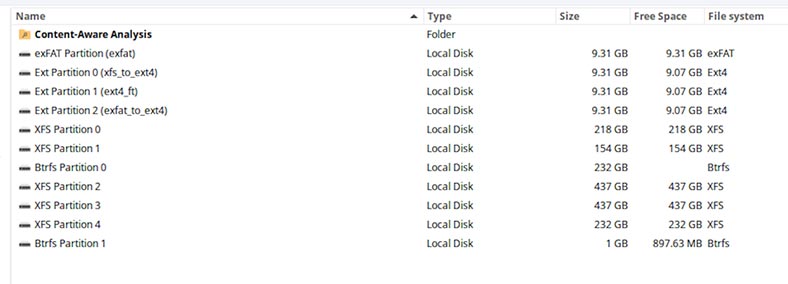
To recover necessary files or folders:
-
To have the files back, select them and hit the Recovery button.
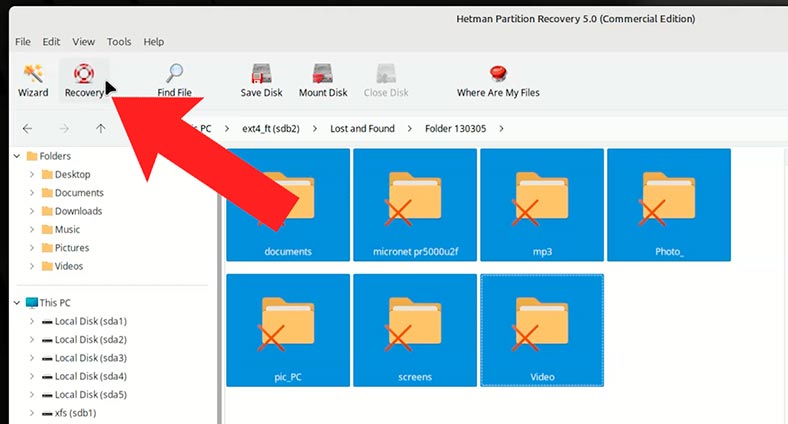
-
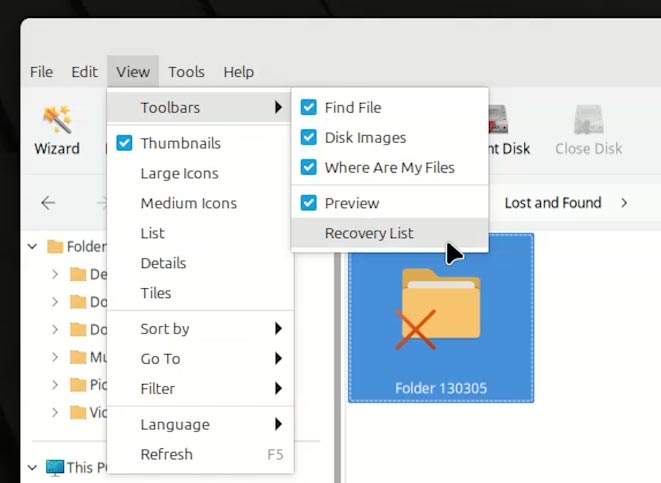
Otherwise, drag them to the Recovery List. If you can’t see one, go to View - Toolbars - Recovery List to open it;
-
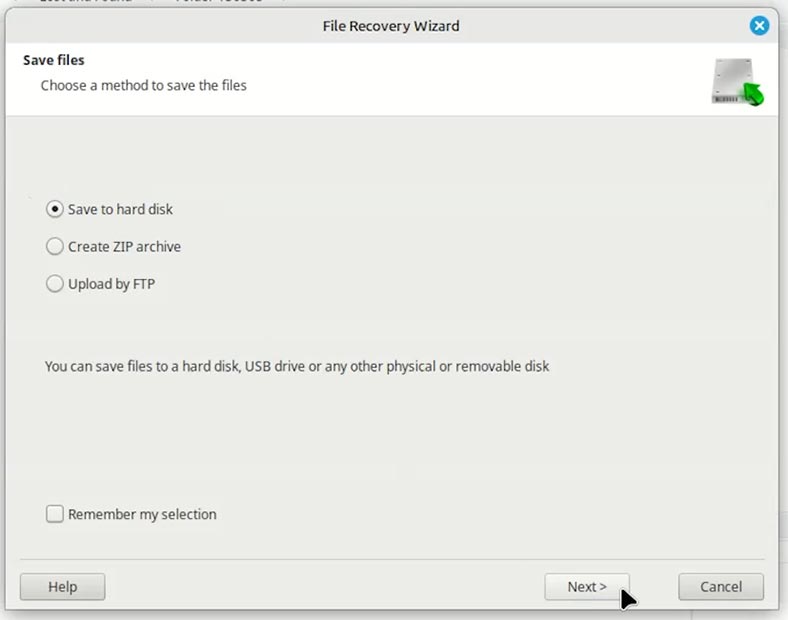
Choose the method to save them;
-
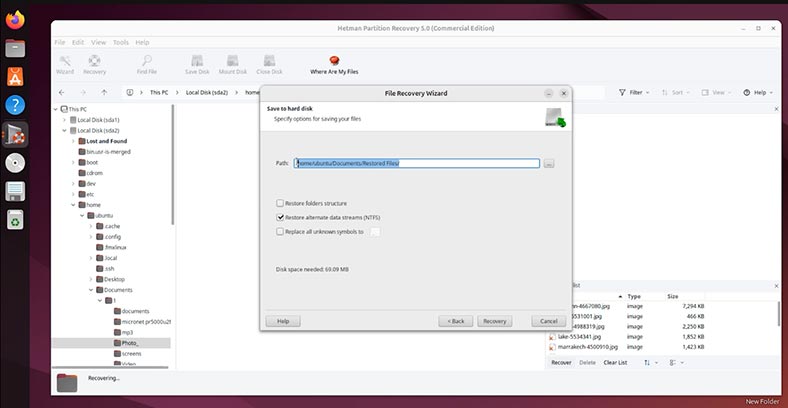
Choose a folder and click Recovery.
-
As you can see, the files are recovered now.
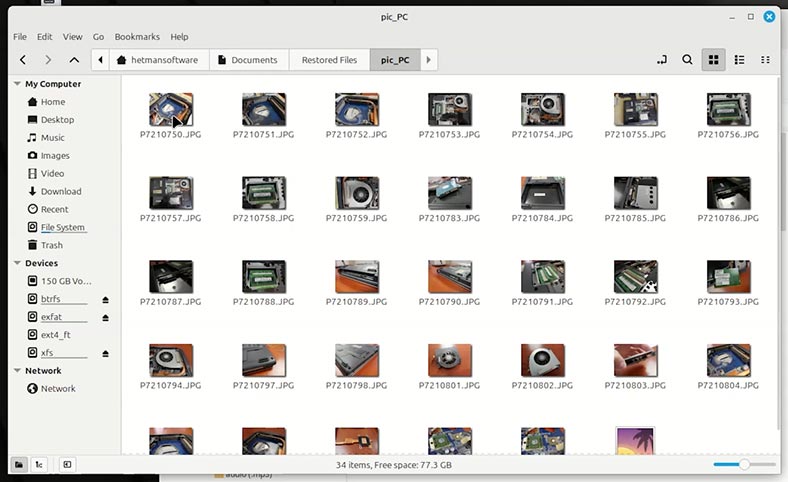
Conclusions
I have shown this example with a hard disk on my computer. However, using this method you can recover data after formatting a USB stick or memory card, an external hard disk or another storage device regardless of the interface used to connect them to a computer, Be it a card reader, USB port, or Type-C port.
Talking of data recovery from SSDs, this process has its own peculiarities, but it’s a topic for another article.